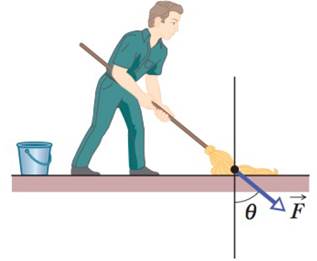
Problem 1Q: In Fig. 6-12, if the box is stationary and the angle between the horizontal and force F is... Problem 2Q Problem 3Q: In Fig. 6-13, horizontal force F1 of magnitude 10 N is applied to a box on a floor, but the box does... Problem 4Q: In three experiments, three different horizontal forces are applied to the same block lying on the... Problem 5Q: If you press an apple crate against a wall so hard that the crate cannot slide down the wall, what... Problem 6Q: In Fig. 6-14, a block of mass m is held stationary on a ramp by the frictional force on it from the... Problem 7Q: Reconsider Question 6 but with the force F now directed down the ramp. As the magnitude of F is... Problem 8Q: In Fig. 6-15, a horizontal force of 100 N is to be applied to a 10 kg slab that is initially... Problem 9Q Problem 10Q Problem 11Q: A person riding a Ferris wheel moves through positions at 1 the top, 2 the bottom, and 3 midheight.... Problem 12Q: During a routine flight in 1956, test pilot Tom Attridge put his jet fighter into a 20 dive for a... Problem 13Q: A box is on a ramp that is at angle to the horizontal. As is increased from zero, and before the... Problem 1P: The floor of a railroad flatcar is loaded with loose crates having a coefficient of static friction... Problem 2P: In a pickup game of dorm shuffleboard, students crazed by final exams use a broom to propel a... Problem 3P: SSM WWW A bedroom bureau with a mass of 45 kg, including drawers and clothing, rests on the floor. a... Problem 4P: A slide-loving pig slides down a certain 35 slide in twice the time it would take to slide down a... Problem 5P: GO A 2.5 kg block is initially at rest on a horizontal surface. A horizontal force F of magnitude... Problem 6P: A baseball player with mass m 79 kg, sliding into second base, is retarded by a frictional force of... Problem 7P: SSM ILW A person pushes horizontally with a force of 220 N on a 55 kg crate to move it across a... Problem 8P: The mysterious sliding stones. Along the remote Racetrack Playa in Death Valley, California, stones... Problem 9P: GO A 3.5 kg block is pushed along a horizontal floor by a force F of magnitude 15 N at an angle =... Problem 10P: Figure 6-20 shows an initially stationary block of mass m on a floor. A force of magnitude 0.500mg... Problem 11P: SSM A 68 kg crate is dragged across a floor by pulling on a rope attached to the crate and inclined... Problem 12P: In about 1915, Henry Sincosky of Philadelphia suspended himself from a rafter by gripping the rafter... Problem 13P: A worker pushes horizontally on a 35 kg crate with a force of magnitude 110 N. The coefficient of... Problem 14P: Figure 6-22 shows the cross section of a road cut into the side of a mountain. The solid line AA... Problem 15P: The coefficient of static friction between Teflon and scrambled eggs is about 0.04. What is the... Problem 16P: A loaded penguin sled weighing 80 N rests on a plane inclined at angle = 20 to the horizontal Fig.... Problem 17P: In Fig. 6-24, a force P acts on a block weighing 45 N. The block is initially at rest on a plane... Problem 18P: GO You testify as an expert witness in a case involving an accident in which car A slid into the... Problem 19P: A 12 N horizontal force F pushes a block weighing 5.0 N against a vertical wall Fig. 6-26. The... Problem 20P: GO In Fig. 6-27, a box of Cheerios mass mC = 1.0 kg and a box of Wheaties mass mW = 3.0 kg are... Problem 21P: An initially stationary box of sand is to be pulled across a floor by means of a cable in which the... Problem 22P: GO In Fig. 6-23, a sled is held on an inclined plane by a cord pulling directly up the plane. The... Problem 23P: When the three blocks in Fig. 6-29 are released from rest, they accelerate with a magnitude of 0.500... Problem 24P: A 4.10 kg block is pushed along a floor by a constant applied force that is horizontal and has a... Problem 25P: SSM WWW Block B in Fig. 6-31 weighs 711 N. The coefficient of static friction between block and... Problem 26P: GO Figure 6-32 shows three crates being pushed over a concrete floor by a horizontal force F of... Problem 27P: GO Body A in Fig. 6-33 weighs 102 N, and body B weighs 32 N. The coefficients of friction between A... Problem 28P: In Fig. 6-33, two blocks are connected over a pulley. The mass of block A is 10 kg, and the... Problem 29P: GO In Fig. 6-34, blocks A and B have weights of 44 N and 22 N, respectively. a Determine the minimum... Problem 30P: A toy chest and its contents have a combined weight of 180 N. The coefficient of static friction... Problem 31P: SSM Two blocks, of weights 3.6 N and 7.2 N, are connected by a massless string and slide down a 30... Problem 32P: GO A block is pushed across a floor by a constant force that is applied at downward angle Fig.... Problem 33P: SSM A 1000 kg boat is traveling at 90 km/h when its engine is shut off. The magnitude of the... Problem 34P: GO In Fig. 6-37, a slab of mass m1= 40 kg rests on a frictionless floor, and a block of mass m2= 10... Problem 35P: ILW The two blocks m = 16 kg and M = 88 kg in Fig. 6-38 are not attached to each other. The... Problem 36P: The terminal speed of a sky diver is 160 km/h in the spread-eagle position and 310 km/h in the... Problem 37P: Continuation of Problem 8. Now assume that Eq. 6-14 gives the magnitude of the air drag force on the... Problem 38P: Assume Eq. 6-14 gives the drag force on a pilot plus ejection seat just after they are ejected from... Problem 39P: Calculate the ratio of the drag force on a jet flying at 1000 km/h at an altitude of 10 km to the... Problem 40P: In downhill speed skiing a skier is retarded by both the air drag force on the body and the kinetic... Problem 41P: A cat dozes on a stationary merry-go-round in an amusement park, at a radius of 5.4 m from the... Problem 42P: Suppose the coefficient of static friction between the road and the tires on a car is 0.60 and the... Problem 43P: ILW What is the smallest radius of an unbanked flat track around which a bicyclist can travel if her... Problem 44P: During an Olympic bobsled run, the Jamaican team makes a turn of radius 7.6 m at a speed of 96.6... Problem 45P: SSM ILW A student of weight 667 N rides a steadily rotating Ferris wheel the student sits upright.... Problem 46P: A police officer in hot pursuit drives her car through a circular turn of radius 300 m with a... Problem 47P: A circular-motion addict of mass 80 kg rides a Ferris wheel around in a vertical circle of radius 10... Problem 48P: A roller-coaster car at an amusement park has a mass of 1200 kg when fully loaded with passengers.... Problem 49P: GO In Fig. 6-39, a car is driven at constant speed over a circular hill and then into a circular... Problem 50P: An 85.0 kg passenger is made to move along a circular path of radius r = 3.50 m in uniform circular... Problem 51P: SSM WWW An airplane is flying in a horizontal circle at a speed of 480 km/h Fig. 6-41. If its wings... Problem 52P: An amusement park ride consists of a car moving in a ver tical circle on the end of a rigid boom of... Problem 53P: An old streetcar rounds a flat corner of radius 9.1 m, at 16 km/h. What angle with the vertical will... Problem 54P: In designing circular rides for amusement parks, mechanical engineers must consider how small... Problem 55P: A bolt is threaded onto one end of a thin horizontal rod, and the rod is then rotated horizontally... Problem 56P: GO A banked circular highway curve is designed for traffic moving at 60 km/h. The radius of the... Problem 57P: GO A puck of mass m = 1.50 kg slides in a circle of radius r = 20.0 cm on a frictionless table while... Problem 58P: Brake or turn? Figure 6- 44 depicts an overhead view of a cars path as the car travels toward a... Problem 59P: SSM ILW In Fig. 6-45, a 1.34 kg ball is connected by means of two massless strings, each of length L... Problem 60P: GO In Fig. 6-46, a box of ant aunts total mass m1 = 1.65 kg and a box of ant un cles total mass m2 =... Problem 61P: SSM A block of mass mt = 4.0 kg is put on top of a block of mass mb = 5.0 kg. To cause the top block... Problem 62P: A 5.00 kg stone is rubbed across the horizontal ceiling of a cave passageway Fig. 6-48. If the... Problem 63P: In Fig. 6-49, a 49 kg rock climber is climbing a chimney. The coefficient of static friction between... Problem 64P: A high-speed railway car goes around a flat, horizontal circle of radius 470 m at a constant speed.... Problem 65P: Continuation of Problems 8 and 37. Another explanation is that the stones move only when the water... Problem 66P: GO In Fig. 6-50, block 1 of mass m1 = 2.0 kg and block 2 of mass m2 = 3.0 kg are connected by a... Problem 67P: In Fig. 6-51, a crate slides down an inclined right-angled trough. The coefficient of kinetic... Problem 68P: Engineering a highway curve. If a car goes through a curve too fast, the car tends to slide out of... Problem 69P: A student, crazed by final exams, uses a force P of magnitude 80 N and angle = 70 to push a 5.0 kg... Problem 70P: GO Figure 6-53 shows a conical pendulum, in which the bob the small object at the lower end of the... Problem 71P: An 8.00 kg block of steel is at rest on a horizontal table. The coefficient of static friction... Problem 72P: A box of canned goods slides down a ramp from street level into the basement of a grocery store with... Problem 73P: In Fig. 6-54, the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and inclined plane is 0.20, and... Problem 74P: A 110 g hockey puck sent sliding over ice is stopped in 15 m by the frictional force on it from the... Problem 75P: A locomotive accelerates a 25-car train along a level track. Every car has a mass of 5.0 104 kg and... Problem 76P: A house is built on the top of a hill with a nearby slope at angle = 45 Fig. 6-55. An engineering... Problem 77P: What is the terminal speed of a 6.00 kg spherical ball that has a radius of 3.00 cm and a drag... Problem 78P: A student wants to determine the coefficients of static friction and kinetic friction between a box... Problem 79P: SSM Block A in Fig. 6-56 has mass mA = 4.0 kg, and block B has mass mB = 2.0 kg. The coefficient of... Problem 80P: Calculate the magnitude of the drag force on a missile 53 cm in diameter cruising at 250 m/s at low... Problem 81P: SSM A bicyclist travels in a circle of radius 25.0 m at a constant speed of 9.00 m/s. The... Problem 82P: In Fig. 6-57, a stuntman drives a car without negative lift over the top of a hill, the cross... Problem 83P: You must push a crate across a floor to a docking bay. The crate weighs 165 N. The coefficient of... Problem 84P: In Fig. 6-58, force F is applied to a crate of mass m on a floor where the coefficient of static... Problem 85P: In the early afternoon, a car is parked on a street that runs down a steep hill, at an angle of 35.0... Problem 86P: A sling-thrower puts a stone 0.250 kg in the slings pouch 0.010 kg and then begins to make the stone... Problem 87P: SSM A car weighing 10.7 kN and traveling at 13.4 m/s without negative lift attempts to round an... Problem 88P: In Fig. 6-59, block 1 of mass m1 = 2.0 kg and block 2 of mass m2 = 1.0 kg are connected by a string... Problem 89P: SSM A filing cabinet weighing 556 N rests on the floor. The coefficient of static friction between... Problem 90P: In Fig. 6-60, a block weighing 22 N is held at rest against a vertical wall by a horizontal force F... Problem 91P Problem 92P: A circular curve of highway is designed for traffic moving at 60 km/h. Assume the traffic consists... Problem 93P: A 1.5 kg box is initially at rest on a horizontal surface when at t = 0 a horizontal force... Problem 94P: A child weighing 140 N sits at rest at the top of a playground slide that makes an angle of 25 with... Problem 95P: In Fig. 6-61 a fastidious worker pushes directly along the handle of a mop with a force F. The... Problem 96P: A child places a picnic basket on the outer rim of a merry-go-round that has a radius of 4.6 m and... Problem 97P: SSM A warehouse worker exerts a constant horizontal force of magnitude 85 N on a 40 kg box that is... Problem 98P: In Fig. 6-62, a 5.0 kg block is sent sliding up a plane inclined at = 37 while a horizontal force F... Problem 99P: An 11 kg block of steel is at rest on a horizontal table. The coefficient of static friction between... Problem 100P: A ski that is placed on snow will stick to the snow. However, when the ski is moved along the snow,... Problem 101P: Playing near a road construction site, a child falls over a barrier and down onto a dirt slope that... Problem 102P: A 100 N force, directed at an angle above a horizontal floor, is applied to a 25.0 kg chair sitting... Problem 103P: A certain string can withstand a maximum tension of 40 N without breaking. A child ties a 0.37 kg... Problem 104P: A four-person bobsled total mass = 630 kg comes down a straightaway at the start of a bobsled run.... Problem 105P: As a 40 N block slides down a plane that is inclined at 25 to the horizontal, its acceleration is... format_list_bulleted


 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning




