
Concept explainers
A small feeder airline knows that the
(a)
Find the probability of all passengers with reservation will show up.
Answer to Problem 77CE
The probability of all passengers with reservation will show up is 0.3487.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given information is that the airline knows that the probability of a reservation holder will not show up its regular 7:15 a.m. flight into a hub airport is 0.10. The number of passengers carries in the flight is 10.
Binomial Distribution:
The random variable X is the number of success in n trails. The random variable X follows binomial distribution with parameters n and
The PDF of the distribution is,
Here, the random variable X is the number of no shows, n is 10 and the probability of no shows is 0.10.
The probability of all passengers with reservations will show up is
Probability = BINOM.DIST (numbers, trails, probability, cumulative).
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the probability by using EXCEL software:
- Open new EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula as “=BINOM.DIST (0,10,0.10,0)”.
Output using EXCEL software is given as follows:
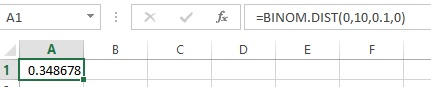
From the output, the value of
Thus, the probability of all passengers with reservation will show up is 0.3487.
(b)
Find the probability of no one passengers will have to be bumped if selling of 11 seats.
Answer to Problem 77CE
The probability of no one passengers will have to be bumped if selling of 11 seats is 0.6862.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The airline overbooks by the selling of 11 seats, that is n is 11.
The probability of no one will be bumped means more than one passenger is not show up is,
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the probability by using EXCEL software:
- Open new EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula as “=BINOM.DIST (0,11,0.10,0)”.
Output using EXCEL software is given as follows:
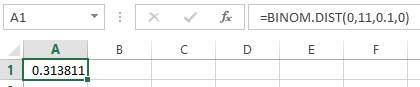
From the output, the value of
Thus, the probability of no one passengers will have to be bumped if selling of 11 seats is 0.6862.
(c)
Find the probability of more than one passenger has to be bumped if selling of 11 seats.
Answer to Problem 77CE
The probability of more than one passenger has to be bumped if selling of 11 seats is 0.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The airline overbooks by the selling of 11 seats, that is n is 11.
The probability of more than one passenger has to be bumped is,
In practical situation, the number of passenger is 10 if the airline overbooks by selling 11 seats. The one person may has to be bumped but it is not possible to bumped more than one person. That is the probability of more than one passenger has to be bumped is 0.
Thus, the probability of more than one passengers will have to be bumped if selling of 11 seats is 0.
(d)
Find the number of seats would be sell to ensure that the flight will be filled by 95%.
Answer to Problem 77CE
The number of seats would be sell to ensure that the flight will be filled by 95% is 13.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Assume the random variable X represents the number of passengers show up and the probability for the event is 0.90.
Calculate the number of seats need to be sell to get the 95% of the flight to be filled,
The value of
Probability = BINOM.DIST (9, n, 0.90, 1).
For
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the probability by using EXCEL software:
- Open new EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula as “=BINOM.DIST (9,11,0.90,1)”.
Output using EXCEL software is given as follows:
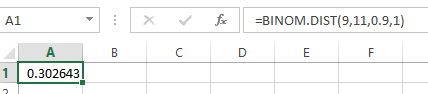
From the output, the value of
For
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the probability by using EXCEL software:
- Open new EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula as “=BINOM.DIST (9,12,0.90,1)”.
Output using EXCEL software is given as follows:
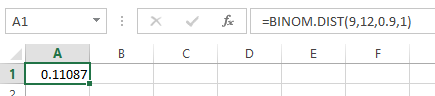
From the output, the value of
For
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the probability by using EXCEL software:
- Open new EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula as “=BINOM.DIST (9,13,0.90,1)”.
Output using EXCEL software is given as follows:
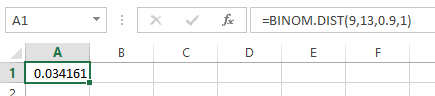
From the output, the value of
Thus, the number of seats would be sell to ensure that the flight will be filled by 95% is 13.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
APPLIED STAT.IN BUS.+ECONOMICS
- Business Discussarrow_forwardThe following data represent total ventilation measured in liters of air per minute per square meter of body area for two independent (and randomly chosen) samples. Analyze these data using the appropriate non-parametric hypothesis testarrow_forwardeach column represents before & after measurements on the same individual. Analyze with the appropriate non-parametric hypothesis test for a paired design.arrow_forward
- Should you be confident in applying your regression equation to estimate the heart rate of a python at 35°C? Why or why not?arrow_forwardGiven your fitted regression line, what would be the residual for snake #5 (10 C)?arrow_forwardCalculate the 95% confidence interval around your estimate of r using Fisher’s z-transformation. In your final answer, make sure to back-transform to the original units.arrow_forward

 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL

