
Concept explainers
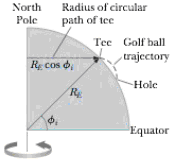
A golfer tees off from a location precisely at ϕi = 35.0° north latitude. He hits the ball due south, with range 285 m. The ball’s initial velocity is at 48.0° above the horizontal. Suppose air resistance is negligible for the golf ball. (a) For how long is the ball in flight? The cup is due south of the golfer’s location, and the golfer would have a hole-in-one if the Earth were not rotating. The Earth’s rotation makes the tee move in a circle of radius RE cos ϕi = (6.37 × 106 m) cos 35.0° as shown in Figure P6.47. The tee completes one revolution each day. (b) Find the eastward speed of the tee relative to the stars. The hole is also moving cast, but it is 285 m farther south and thus at a slightly lower latitude ϕf. Because the hole moves in a slightly larger circle, its speed must he greater than that of the tee. (c) By how much does the hole’s speed exceed that of the tee? During the time interval the ball is in flight, it moves upward and downward as well as southward with the projectile motion you studied in Chapter 4, but it also moves eastward with the speed you found in part (b). The hole moves to the east at a faster speed, however, pulling ahead of the ball with the relative speed you found in part (c). (d) How far to the west of the hole does the ball land?
Figure P6.47
(a)
The time of flight of the ball.
Answer to Problem 6.67CP
The time for which the ball be in flight is
Explanation of Solution
The range of the motion after hitting the ball is
The range of the parabolic motion
Here,
Write the expression for the equation for parabolic motion
As initial and final distance is equal,
Rearrange the above expression for
Substitute
Rearrange the above expression for
Substitute
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the time for which the ball be in flight is
(b)
The relative eastward speed of the tee with respect to the stars.
Answer to Problem 6.67CP
The relative eastward speed of the tee with respect to the stars is
Explanation of Solution
Write the formula to calculate the eastward speed of the tee relative to the stars
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the relative eastward speed of the tee with respect to the stars is
(c)
The value by which the hole's speed exceed that of the tee.
Answer to Problem 6.67CP
The value by which the hole's speed exceed that of the tee is
Explanation of Solution
Write the formula to calculate the length of the arc
Rearrange the above expression for
Substitute
Write the formula to calculate the speed of the hole
Here,
Substitute
Calculate the difference between the speed of tee and the speed of hole.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the value by which the hole's speed exceed that of the tee is
(d)
The distance to the west of the hole from the position where the ball lands.
Answer to Problem 6.67CP
The distance to the west of the hole from the position where the ball land is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the distance to west of the hole
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the distance to the west of the hole from the position where the ball land is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Question 01 A solid circular cylinder and a solid spherical ball of the same mass and radius are rolling together down the same inclined. Calculate the ratio of their kinetic energy. Assume pure rolling motion Question 02 A sphere and cylinder of the same mass and radius start from ret at the same point and more down the same plane inclined at 30° to the horizontal Which body gets the bottom first and what is its acceleration b) What angle of inclination of the plane is needed to give the slower body the same acceleration Question 03 i) Define the angular velocity of a rotating body and give its SI unit A car wheel has its angular velocity changing from 2rads to 30 rads seconds. If the radius of the wheel is 400mm. calculate ii) The angular acceleration iii) The tangential linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the wheel Question 04 in 20arrow_forwardQuestion B3 Consider the following FLRW spacetime: t2 ds² = -dt² + (dx² + dy²+ dz²), t2 where t is a constant. a) State whether this universe is spatially open, closed or flat. [2 marks] b) Determine the Hubble factor H(t), and represent it in a (roughly drawn) plot as a function of time t, starting at t = 0. [3 marks] c) Taking galaxy A to be located at (x, y, z) = (0,0,0), determine the proper distance to galaxy B located at (x, y, z) = (L, 0, 0). Determine the recessional velocity of galaxy B with respect to galaxy A. d) The Friedmann equations are 2 k 8πG а 4πG + a² (p+3p). 3 a 3 [5 marks] Use these equations to determine the energy density p(t) and the pressure p(t) for the FLRW spacetime specified at the top of the page. [5 marks] e) Given the result of question B3.d, state whether the FLRW universe in question is (i) radiation-dominated, (ii) matter-dominated, (iii) cosmological-constant-dominated, or (iv) none of the previous. Justify your answer. f) [5 marks] A conformally…arrow_forwardSECTION B Answer ONLY TWO questions in Section B [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-B sub question.] Question B1 Consider the line element where w is a constant. ds²=-dt²+e2wt dx², a) Determine the components of the metric and of the inverse metric. [2 marks] b) Determine the Christoffel symbols. [See the Appendix of this document.] [10 marks] c) Write down the geodesic equations. [5 marks] d) Show that e2wt it is a constant of geodesic motion. [4 marks] e) Solve the geodesic equations for null geodesics. [4 marks]arrow_forward
- Page 2 SECTION A Answer ALL questions in Section A [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-A sub question.] Question A1 SPA6308 (2024) Consider Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates th = (t, x, y, z), such that ds² = dt² + dx² + dy² + dz². (a) Consider the vector with components V" = (1,-1,0,0). Determine V and V. V. (b) Consider now the coordinate system x' (u, v, y, z) such that u =t-x, v=t+x. [2 marks] Write down the line element, the metric, the Christoffel symbols and the Riemann curvature tensor in the new coordinates. [See the Appendix of this document.] [5 marks] (c) Determine V", that is, write the object in question A1.a in the coordinate system x'. Verify explicitly that V. V is invariant under the coordinate transformation. Question A2 [5 marks] Suppose that A, is a covector field, and consider the object Fv=AAμ. (a) Show explicitly that F is a tensor, that is, show that it transforms appropriately under a coordinate transformation. [5 marks] (b)…arrow_forwardHow does boiling point of water decreases as the altitude increases?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 14 Z In figure, a closed surface with q=b= 0.4m/ C = 0.6m if the left edge of the closed surface at position X=a, if E is non-uniform and is given by € = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the (3+2x²) net electric flux leaving the closed surface.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardsuggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?arrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





