
Interpretation:
Each line in the phase diagram, in terms of the derivative it represents, is to be labeled.
Concept introduction:
Phase diagram represents the different physical states of a substance at different values of temperature and pressure. In the water, the molar volume of solid is greater than the molar volume of the liquid.
Answer to Problem 6.66E
The phase transition between solid phase to liquid phase is represented by the derivative,
The phase transition between solid phase to liquid phase is represented by the derivative,
The phase transition between solid phase to liquid phase is represented by the derivative,
The phase transition between solid phases is represented by the derivative,
Explanation of Solution
The phase diagram of water shown in Figure 6.6 is shown below.
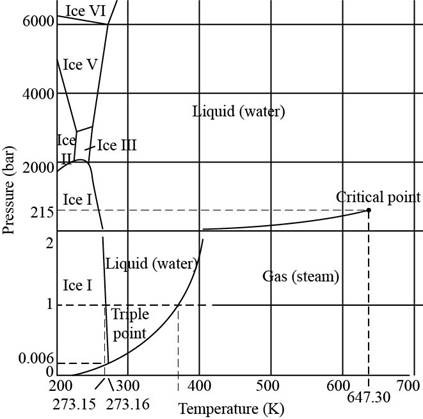
Figure 1
In the given diagram, the total numbers of phase transitions represented are,
1. Gas phase to liquid phase
2. Gas phase to ice phase
3. Liquid phase to ice phase
4. Liquid phase to ice phase
5. Liquid phase to ice phase
6. Liquid phase to ice phase
7. Ice phase
8. Ice phase
9. Ice phase
10. Ice phase
11. Ice phase
12. Ice phase
Thus, the total number of phase transitions are
The phase transition between solid phase to liquid phase, that is, ice phase
Where,
•
•
The phase transition between gas phase to ice phase
Where,
•
•
The volume of gas is much greater than the volume of solid. Therefore, it can be neglected.
The phase transition between solid phase and liquid phase is represented by the derivative,
Where,
•
•
The volume of gas is much greater than the volume of liquid. Therefore, it can be neglected.
The phase transition between solid phases is represented by the derivative,
Where,
•
•
The phase transition between solid phase to liquid phase is represented by the derivative,
The phase transition between solid phase to liquid phase is represented by the derivative,
The phase transition between solid phase to liquid phase is represented by the derivative
The phase transition between solid phases is represented by the derivative,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physical Chemistry
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
- What would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forwardFor benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning  Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning




