
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTINGLL W/CONNECT >IC<
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781259934773
Author: SPICELAND
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.5BE
Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold using FIFO (LO6–3)
During the year, Wright Company sells 470 remote-control airplanes for $110 each. The company has the following inventory purchase transactions for the year.
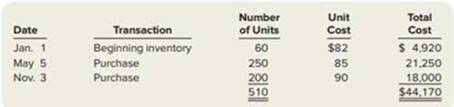
Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold for the year, assuming the company uses FIFO.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
subject = general accounting
Benevolent Professor Martin Company has an overhead cost pool for inspecting. The expected overhead cost is $420,000, and the estimated number of inspections is 15,000. The activity-based overhead rate (ABOR) used to assign the costs of the inspecting cost pool to products is __.
Can you explain this general accounting question using accurate calculation methods?
Chapter 6 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTINGLL W/CONNECT >IC<
Ch. 6 - 1.What is inventory? Where in the financial...Ch. 6 - Prob. 2RQCh. 6 - What is the difference among raw materials...Ch. 6 - Prob. 4RQCh. 6 - Prob. 5RQCh. 6 - What is a multiple-step income statement? What...Ch. 6 - Cheryl believes that companies report cost of...Ch. 6 - What are the three primary cost flow assumptions?...Ch. 6 - 9.Which cost flow assumption generally results in...Ch. 6 - Prob. 10RQ
Ch. 6 - Prob. 11RQCh. 6 - 12.Explain how LIFO generally results in lower...Ch. 6 - Prob. 13RQCh. 6 - Explain how freight charges, purchase returns, and...Ch. 6 - Explain the method of reporting inventory at lower...Ch. 6 - 16.How is cost of inventory determined? How is net...Ch. 6 - 17.Describe the entry to adjust from cost to net...Ch. 6 - Prob. 18RQCh. 6 - Prob. 19RQCh. 6 - How is gross profit calculated? What is the gross...Ch. 6 - 21.Explain how the sale of inventory on account is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 22RQCh. 6 - Prob. 23RQCh. 6 - Prob. 24RQCh. 6 - Understand terms related to types of companies...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.2BECh. 6 - Calculate cost of goods sold (LO62) At the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.4BECh. 6 - Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold...Ch. 6 - Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold...Ch. 6 - Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.8BECh. 6 - Identify financial statement effects of FIFO and...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10BECh. 6 - Record freight charges for inventory using a...Ch. 6 - Record purchase returns of inventory using a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.13BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.14BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.15BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.16BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.17BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.18BECh. 6 - Record purchase returns of inventory using a...Ch. 6 - Refer to the information in BE613, but now assume...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.21BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.22BECh. 6 - Calculate cost of goods sold (LO62) Russell Retail...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.2ECh. 6 - Prob. 6.3ECh. 6 - Calculate inventory amounts when costs are rising...Ch. 6 - Calculate inventory amounts when costs are...Ch. 6 - Record Inventory transactions using o perpetual...Ch. 6 - Record inventory purchase and purchase return...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.8ECh. 6 - Prob. 6.9ECh. 6 - Prob. 6.10ECh. 6 - Record transactions using a perpetual system...Ch. 6 - Record transactions using a perpetual system...Ch. 6 - Calculate inventory using lower of cost and net...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.14ECh. 6 - Calculate cost of goods sold, the inventory...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.16ECh. 6 - Prob. 6.17ECh. 6 - Prob. 6.18ECh. 6 - Record inventory purchases and sales using a...Ch. 6 - Mulligan Corporation purchases inventory on...Ch. 6 - Complete the accounting cycle using Inventory...Ch. 6 - Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.2APCh. 6 - Prob. 6.3APCh. 6 - Prob. 6.4APCh. 6 - Calculate ending inventory end cost of goods sold...Ch. 6 - Record transactions using a perpetual system,...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.7APCh. 6 - Prob. 6.8APCh. 6 - Record transactions and prepare a partial income...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10APCh. 6 - Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.2BPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.3BPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.4BPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.5BPCh. 6 - Record transactions using a perpetual system,...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.7BPCh. 6 - Use the inventory turnover retio end gross profit...Ch. 6 - Record transactions and prepare a partial income...Ch. 6 - Determine the effects of inventory errors using...Ch. 6 - Great Adventures (This is a continuation of the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.2APFACh. 6 - Prob. 6.3APFACh. 6 - Comparative Analysis American Eagle Outfitters,...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.5APECh. 6 - Prob. 6.6APIRCh. 6 - Written Communication You have just been hired as...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.8APEM
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you explain this general accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardI am looking for a reliable way to solve this financial accounting problem using accurate principles.arrow_forwardKendra had a gross weekly paycheck of $915 last week. Kendra worked 6 hours for 4 of the days and 8 hours on 1 day. What is Kendra’s hourly rate of pay?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning  Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172685
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Individual Income Taxes
Accounting
ISBN:9780357109731
Author:Hoffman
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:9781337794756
Author:HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Chapter 6 Merchandise Inventory; Author: Vicki Stewart;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DnrcQLD2yKU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Accounting for Merchandising Operations Recording Purchases of Merchandise; Author: Socrat Ghadban;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iQp5UoYpG20;License: Standard Youtube License