
Concept explainers
Calculate inventory amounts when costs are rising (LO6–3)
During the year, TRC Corporation has the following inventory transactions.
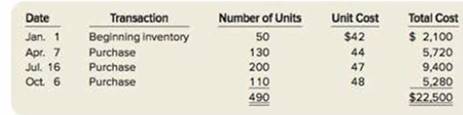
For the entire year, the company sells 440 units of inventory for $60 each.
Required:
1. Using FIFO, calculate (a) ending inventory, (b) cost of goods sold, (c) sales revenue, and (d) gross profit.
2. Using LIFO, calculate (a) ending inventory, (b) cost of goods sold, (c) sales revenue, and (d) gross profit.
3. Using weighted-average cost, calculate (a) ending inventory, (b) cost of goods sold, (c) sales revenue, and (d) gross profit.
4. Determine which method will result in higher profitability when inventors' costs are rising.
1. (a)
To calculate: The cost of ending inventory.
Explanation of Solution
Perpetual Inventory System:
Perpetual Inventory System refers to the inventory system that maintains the detailed records of every inventory transactions related to purchases, and sales on a continuous basis. It shows the exact on-hand-inventory at any point of time.
First-in-First-Out:
In First-in-First-Out method, the costs of the initially purchased items are considered as cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the ending inventory consists of the recent purchased items.
Ending Inventory: It represents the quantity and price of the goods unsold and laying at the store at the end of a particular period.
- Calculate the cost of ending inventory:
| Calculation of Cost of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| October 6 | 50 | 48 | 2,400 |
| Ending Inventory | 50 | 2,400 | |
Table 1
Note:
- The ending inventory is 50 units.
- In FIFO method the ending inventory comprises of the inventory purchased last, because the inventory purchased first were sold first.
- Therefore, the ending inventory of 50 units from October 6th purchases.
Working notes:
- Calculate the total Cost and units of Goods Available for Sales:
| Particulars | Number of units | Rate per unit ($) | Total cost ($) |
| Beginning balance | 50 | 42 | 2,100 |
| Add: Purchases | |||
| April 7 | 130 | 44 | 5,720 |
| July 16 | 200 | 47 | 9,400 |
| October 6 | 110 | 48 | 5,280 |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 490 | 22,500 |
Table 2
- Calculate the units of ending inventory:
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the FIFO is $2,400.
1. (b)
To calculate: The cost of goods sold.
Explanation of Solution
Cost of goods sold:
Cost of goods sold is the accumulate total of all direct cost incurred in manufacturing the goods or the products which has been sold during a period. Cost of goods sold involves direct material, direct labor, and manufacturing overheads.
Determine the cost of goods sold:
| Particulars | Number of units | Rate per unit ($) | Total cost ($) |
| Beginning balance | 50 | 42 | 2,100 |
| Add: Purchases | |||
| April 7 | 130 | 44 | 5,720 |
| July 16 | 200 | 47 | 9,400 |
| October6 [440 - (50+130+200)] |
60 |
48 |
2,880 |
| Cost of goods sold | 440 | 20,100 |
Table 3
Note:
- units are sold.
- As it is FIFO method the earlier purchased items will sell first.
- Hence, the cost of goods sold will be the earlier purchased items.
Therefore, the cost of goods sold in the FIFO Method is $20,100.
1. (c)
To calculate: the Sales Revenue.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the amount of sales revenue:
Therefore, the sales revenue in FIFO method is $26,400.
1. (d)
To calculate: The gross profit.
Explanation of Solution
Gross profit is the difference between the sales and the cost of goods sold.
Calculate the gross profit:
| Calculation of Gross Margin | |
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 26,400 (1) |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold (Refer to table 4) | ($20,100) |
| Gross Margin | 6,300 |
Table 4
Therefore, the amount of Gross margin in FIFO method is $6,300.
2. (a)
To calculate: The cost of ending inventory.
Explanation of Solution
Perpetual Inventory System:
Perpetual Inventory System refers to the inventory system that maintains the detailed records of every inventory transactions related to purchases, and sales on a continuous basis. It shows the exact on-hand-inventory at any point of time.
Last-in-Last-Out:
In Last-in-First-Out method, the costs of last purchased items are considered as the cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the closing stock consists of the initial purchased items.
- Calculate the cost of ending inventory.
| Calculation of Cost of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning Inventory | 50 | 42 | 2,100 |
| Ending Inventory | 50 | 42 | 2,100 |
Table 5
Note:
- The ending inventory is 50 units (Refer to Table 2).
- In LIFO method the ending inventory comprises of the inventory purchased first, because the inventory purchased last were sold first.
- Therefore, the ending inventory of 50 units is from the beginning inventory.
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the LIFO method is $2,100.
2. (b)
To calculate: The cost of goods sold.
Explanation of Solution
Cost of goods sold:
Cost of goods sold is the accumulate total of all direct cost incurred in manufacturing the goods or the products which has been sold during a period. Cost of goods sold involves direct material, direct labor, and manufacturing overheads.
Determine the cost of goods sold:
| Particulars | Number of units | Rate per unit ($) | Total cost ($) |
| October 6 | 110 | 48 | 5,280 |
| July 16 | 200 | 47 | 9,400 |
| April 7 | 130 | 44 | 5,720 |
| Cost of goods sold | 440 | 20,400 |
Table 6
Note:
- units are sold.
- As it is LIFO method the recent purchased items will sell first.
- Hence, the cost of goods sold will be the recent purchased items.
Therefore, the Cost of Goods Sold in the LIFO Method is $20,400
2. (c)
To calculate: the Sales Revenue.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the amount of sales revenue:
Therefore, the sales revenue in LIFO method is $26,400.
2. (d)
To calculate: The gross profit.
Explanation of Solution
Gross profit is the difference between the sales and the cost of goods sold.
Calculate the gross profit:
| Calculation of Gross Margin | |
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 26,400 (2) |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold (Refer to table 8) | ($20,400) |
| Gross Margin | 6,000 |
Table 7
Therefore, the amount of Gross margin in LIFO method is $6,000.
3. (a)
To calculate: The cost of ending inventory.
Explanation of Solution
Perpetual Inventory System:
Perpetual Inventory System refers to the inventory system that maintains the detailed records of every inventory transactions related to purchases, and sales on a continuous basis. It shows the exact on-hand-inventory at any point of time.
Weighted-average cost method:
Under Weighted average cost method, the company calculates a new average cost after every purchase is made. It is determined by dividing the cost of goods available for sale by the units on hand.
- Calculate the cost of ending inventory:
Working note:
- Calculate the Weighted-average cost:
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the Weighted-average-cost Method is $45.91837.
3. (b)
To calculate: The cost of goods sold.
Explanation of Solution
Cost of goods sold:
Cost of goods sold is the accumulate total of all direct cost incurred in manufacturing the goods or the products which has been sold during a period. Cost of goods sold involves direct material, direct labor, and manufacturing overheads.
Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold.
Therefore, the Cost of goods sold in the Weighted-average-cost Method is $20,204.08
3. (c)
To calculate: the Sales Revenue.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the amount of sales revenue:
Therefore, the sales revenue in Weighted-average-cost Method is $26,400.
3. (d)
To calculate: The gross profit.
Explanation of Solution
Gross profit is the difference between the sales and the cost of goods sold.
Calculate the gross profit:
| Calculation of Gross Margin | |
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 26,400 (7) |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold | (20,204.08) (5) |
| Gross Margin | 6,195.92 |
Table 8
Therefore, the amount of Gross margin in Weighted-average-cost Method is $6,19592.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Compare the profitability in the three methods:
| Methods | FIFO | LIFO | WA |
| Gross Margin | $6,300 | $6,000 | 6,195.92 |
Table 9
The gross margin computed by using the LIFO method results higher profitability when inventory costs are rising in comparison to the other two methods.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTINGLL W/CONNECT >IC<
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forwardI am searching for the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid calculations.arrow_forward
- Please provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid calculations.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem using the correct accounting principles.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forward
 Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENTPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENTPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning





