
Concept explainers
Draw all of the resonance structures for the following species and show formal charges: (a) HCO, (b) CH2NO. The relative positions of the atoms are as follows:
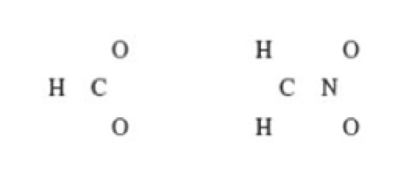
(a)
Interpretation: The resonance structure of
Concept Introduction: Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance.
In some molecules, there is possibility of more than one Lewis structure where all the structures are equally acceptable. One of the acceptable Lewis structures of these molecules is called resonance structure.
All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real.
Any of the possible structure does not exist as such like a stable real molecule. So it is not possible to isolate one resonance structure.
These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Structure with greater number of covalent bonds are more stable comparing to that with lower number of covalent bonds.
Structure which does not involve charge separation is more stable when comparing with structure having positive and negative charge separation.
While drawing resonance structure of a molecule some rules should be followed where the position, over whole charge and chemical framework remains intact. Also only π and nonbonding electron has been moved in all the three resonance structures
Formal charge:
A formal charge (FC) is the charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, irrespective of relative electronegativity by thinking that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally among atoms.
This method is used to identify the most probable Lewis structures if more than one possibility exists for a compound.
The Lewis structure with formal charge on each of the atoms close to zero is taken as the most plausible structure.
Formal charge of an atom can be determined by the given formula.
Answer to Problem 6.35QP
Resonance structure:
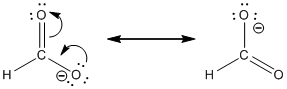
Formal charges:
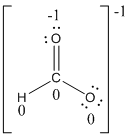
Explanation of Solution
Determine the resonance structure for

In the case of chlorate ion, the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. The chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons forming 2 possible resonance structures. Both the resonance structures are similar. In all the 2 resonance structures the position, over whole charge and chemical framework remains intact.
Structure of the chlorate ion chlorate ion is given below.
The formal charge of the given compound is calculated,
- Hydrogen atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Carbon atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- First oxygen atom having double bond with carbon
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Oxygen atom which having single bond with carbon
Substituting these values to the equation,
(b)
Interpretation: The resonance structure of
Concept Introduction: Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance.
In some molecules, there is possibility of more than one Lewis structure where all the structures are equally acceptable. One of the acceptable Lewis structures of these molecules is called resonance structure.
All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real.
Any of the possible structure does not exist as such like a stable real molecule. So it is not possible to isolate one resonance structure.
These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Structure with greater number of covalent bonds are more stable comparing to that with lower number of covalent bonds.
Structure which does not involve charge separation is more stable when comparing with structure having positive and negative charge separation.
While drawing resonance structure of a molecule some rules should be followed where the position, over whole charge and chemical framework remains intact. Also only π and nonbonding electron has been moved in all the three resonance structures
Formal charge:
A formal charge (FC) is the charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, irrespective of relative electronegativity by thinking that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally among atoms.
This method is used to identify the most probable Lewis structures if more than one possibility exists for a compound.
The Lewis structure with formal charge on each of the atoms close to zero is taken as the most plausible structure.
Formal charge of an atom can be determined by the given formula.
Answer to Problem 6.35QP
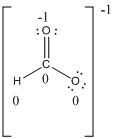
Resonance structure:
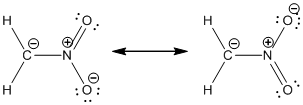
Formal charges:
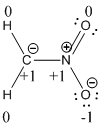
Explanation of Solution
Resonance structure of

In the case of chlorate ion, the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. The chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons forming 2 possible resonance structures. Both the resonance structures are similar. In all the 2 resonance structures the position, over whole charge and chemical framework remains intact.
Structure of the chlorate ion chlorate ion is given below.

The formal charge of the given compound is calculated,
- First hydrogen atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Second hydrogen atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Carbon atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Nitrogen atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- First oxygen atom having double bond with nitrogen
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Oxygen atom which having single bond with nitrogen
Substituting these values to the equation,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
CHEMISTRY: ATOMS FIRST VOL 1 W/CONNECT
- Please help me answer this homework questionarrow_forwardCalculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3+ H2(g)+2OH¯ (aq) + 2Fe³+ (aq) → 2H₂O (1)+2Fe²+ (aq) 0 kJ x10 Х ? olo 18 Ararrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 184.2 mL of a 0.7800M solution of dimethylamine ((CH3) NH with a 0.3000M solution of HClO4. The pK₁ of dimethylamine is 3.27. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 424.1 mL of the HClO solution to it. 2 4 Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HClO 4 solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = ☐ ☑ ? 000 18 Ar 1 Barrow_forward
- Using the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: MnO2 (s)+4H* (aq)+2Cr²+ (aq) → Mn²+ (aq)+2H₂O (1)+2Cr³+ (aq) + 2+ 2+ 3+ Suppose the cell is prepared with 7.44 M H* and 0.485 M Cr²+ in one half-cell and 7.92 M Mn² and 3.73 M Cr³+ in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. ☐ x10 μ Х 5 ? 000 日。arrow_forwardCalculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. NO (g) +H₂O (1) + Cu²+ (aq) → HNO₂ (aq) +H* (aq)+Cu* (aq) kJ - ☐ x10 x10 olo 18 Ararrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid b An analytical chemist is titrating 116.9 mL of a 0.7700M solution of aniline (C6H5NH2) with a 0.5300M solution of HNO3. The pK of aniline is 9.37. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 184.2 mL of the HNO 3 solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO3 solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = ☐ ☑ 5arrow_forward
- QUESTION: Find the standard deviation for the 4 different groups 5.298 3.977 223.4 148.7 5.38 4.24 353.7 278.2 5.033 4.044 334.6 268.7 4.706 3.621 305.6 234.4 4.816 3.728 340.0 262.7 4.828 4.496 304.3 283.2 4.993 3.865 244.7 143.6 STDEV = STDEV = STDEV = STDEV =arrow_forwardQUESTION: Fill in the answers in the empty green boxes regarding 'Question 5: Calculating standard error of regression' *The images of the data showing 'coefficients for the standard curve' have been providedarrow_forwardUsing the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage Try Again Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations. A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 2+ 2+ Sn²+ Ba(s) (aq) + Ba (s) Sn (s) + Ba²+ (aq) →>> Suppose the cell is prepared with 6.10 M Sn 2+ 2+ in one half-cell and 6.62 M Ba in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 1.71 V ☐ x10 ☑ 5 0/5 ? 00. 18 Ararrow_forward
- Question: Find both the b (gradient) and a (y-intercept) value from the list of data below: (x1 -x̄) 370.5 (y1 - ȳ) 5.240 (x2 - x̄) 142.5 (y2 - ȳ) 2.004 (x3 - x̄) 28.5 (y3 - ȳ) 0.390 (x4 - x̄) -85.5 (y4 - ȳ) -1.231 (x5 - x̄) -199.5 (y5 - ȳ) -2.829 (x6 - x̄) -256.5 (y6 - ȳ) -3.575arrow_forwardCalculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3Cu+ (aq) + Cro²¯ (aq) +4H₂O (1) → 3Cu²+ (aq) +Cr(OH)3 (s)+5OH˜¯ (aq) 0 kJ ☐ x10 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 241.7 mL of a 0.4900M solution of methylamine (CH3NH2) with a 0.7800M solution of HNO3. The pK of methylamine is 3.36. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 17.7 mL of the HNO3 solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO3 solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = ☑ ? 18 Ararrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





