
Financial Accounting (12th Edition) (What's New in Accounting)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780134725987
Author: C. William Thomas, Wendy M. Tietz, Walter T. Harrison Jr.
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.23AE
LO 5
(Learning Objective 5: Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit) Supply the missing income statement amounts for each of the following companies:
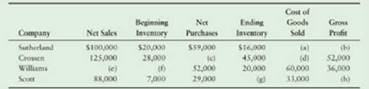
Requirement
1. Prepare the income statement for Sutherland Company for the year ended December 31, 2018. Use the cost-of-goods-sold model to compute cost of goods sold. Sutherland’s operating and other expenses for the year were $36,000. Ignore income tax.
Note: E6-24A builds on E6-23A with a profitability analysis of these companies.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
General Accounting question
Provide correct option general Accounting
Hello tutor please given correct answer general Accounting
Chapter 6 Solutions
Financial Accounting (12th Edition) (What's New in Accounting)
Ch. 6 - Ravenna Candles recently purchased candleholders...Ch. 6 - Which inventory system maintains a running record...Ch. 6 - How is cost of goods sold classified in the...Ch. 6 - Snyders total cost of goods available for sale...Ch. 6 - Snyders cost of goods sold using the average-cost...Ch. 6 - Snyders ending inventory using the FIFO method...Ch. 6 - Snyders cost of goods sold using the LIFO method...Ch. 6 - Which U.S. GAAP principle or rule would apply if...Ch. 6 - Corrigan Corporation had beginning inventory of...Ch. 6 - Corrigans gross profit for the period is a.79,000....
Ch. 6 - What is Corrigans gross profit percentage (rounded...Ch. 6 - Prob. 12QCCh. 6 - A companys beginning inventory is 150,000, its net...Ch. 6 - An understatement of ending inventory by 2 million...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.1ECCh. 6 - LO 1 (Learning Objective 1: Show how to account...Ch. 6 - LO 1 (Learning Objective 1: Show how to account...Ch. 6 - LO 1 (Learning Objective 1: Show how to account...Ch. 6 - (Learning Objective 2: Apply the average-cost,...Ch. 6 - (Learning Objective 2: Compare income tax effects...Ch. 6 - LO 2 (Learning Objective 2: Apply the average-cost...Ch. 6 - (Learning Objective 2: Apply the FIFO method)...Ch. 6 - (Learning Objective 2: Apply the LIFO method)...Ch. 6 - (Learning Objective 2: Compare income, tax, and...Ch. 6 - LO 3 (Learning Objective 3: Apply the...Ch. 6 - (Learning Objective 4: Compute ratio data to...Ch. 6 - (Learning Objective 5: Estimate ending inventory...Ch. 6 - (Learning Objective 6: Analyze the effect of an...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.14SCh. 6 - LO 1,2 (Learning Objectives 1, 2: Show how to...Ch. 6 - LO 1,2 (Learning Objectives 1, 2: Show how to...Ch. 6 - LO 2 (Learning Objective 2: Compare ending...Ch. 6 - (Learning Objective 2: Compare the tax advantage...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.19AECh. 6 - LO 2 (Learning Objective 2: Compare ending...Ch. 6 - LO 2 (Learning Objective 2: Compare gross...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.22AECh. 6 - LO 5 (Learning Objective 5: Compute cost of goods...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.24AECh. 6 - LO 4 (Learning Objective 4: Compute and evaluate...Ch. 6 - LO 5 (Learning Objective 5: Use the COGS model to...Ch. 6 - LO 5 (Learning Objective 5: Use the COGS model to...Ch. 6 - LO 6 (Learning Objective 6: Analyze the effect of...Ch. 6 - LO 1, 2 (Learning Objectives 1, 2: Show how to...Ch. 6 - LO 1, 2 (Learning Objectives 1, 2: Show how to...Ch. 6 - LO1, 2 (Learning Objectives 1, 2: Show how to...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.32BECh. 6 - LO 2 (Learning Objective 2: Apply the average,...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.34BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.35BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.36BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.37BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.38BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.39BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.40BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.41BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.42BECh. 6 - Prob. 6.43QCh. 6 - Prob. 6.44QCh. 6 - Prob. 6.45QCh. 6 - The word market as used in the lower of cost or...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.47QCh. 6 - Prob. 6.48QCh. 6 - Prob. 6.49QCh. 6 - In a period of rising prices, a.cost of goods sold...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.51QCh. 6 - The following data come from the inventory records...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.53QCh. 6 - Prob. 6.54QCh. 6 - Prob. 6.55QCh. 6 - Prob. 6.56QCh. 6 - Prob. 6.57QCh. 6 - Prob. 6.58QCh. 6 - Prob. 6.59QCh. 6 - LO 1, 2 (Learning Objectives 1, 2: Show how to...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.61APCh. 6 - LO 2 (Learning Objective 2: Compare inventory by...Ch. 6 - LO 2 (Learning Objective 2: Compare various...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.64APCh. 6 - (Learning Objective 4: Compute and evaluate gross...Ch. 6 - LO 4, 5 (Learning Objectives 4, 5: Compute gross...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.67APCh. 6 - Prob. 6.68APCh. 6 - Prob. 6.69BPCh. 6 - LO 2 (Learning Objective 2: Apply various...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.71BPCh. 6 - LO 2 (Learning Objective 2: Compare various...Ch. 6 - LO 3 (Learning Objective 3: Explain GAAP and apply...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.74BPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.75BPCh. 6 - LO 5 (Learning Objective 5: Use the COGS model to...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.77BPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.78CEPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.79CEPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.80CEPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.81CEPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.82SCCh. 6 - Prob. 6.83DCCh. 6 - Prob. 6.85EICCh. 6 - Prob. 1FFCh. 6 - Prob. 1FA
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
INVENTORY & COST OF GOODS SOLD; Author: Accounting Stuff;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OB6RDzqvNbk;License: Standard Youtube License