
1.
Calculate cost per bag of chemicals transferred to finished goods using the FIFO method.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate cost per bag of chemicals transferred out to finished goods.
Therefore, cost per bag of chemical transferred out to finished goods is $341.65.
Working notes:
Calculate physical flow schedule for baking department.
| Particulars | Units | Workings |
| Units to account for: | ||
| Beginning work in process | 10,000 | (5,000 × 2) |
| Units started | 100,000 | (50,000 ×2) |
| Total units to account for | 110,000 | |
| Units accounted for: | ||
| Units transferred out | 100,000 | (110,000 - 10,000) |
| Add: Normal spoilage | 5,000 | |
| Abnormal spoilage | 5,000 | |
| Total units accounted for | 110,000 |
Table (1)
Prepare equivalent units of production for baking department
| Particulars | Conversion costs | Transferred In |
| Units started and completed | 90,000 | 90,000 |
| Equivalent units in beginning work in process | 7,500 | 0 |
| Normal spoilage | 2,500 | 5,000 |
| Abnormal spoilage | 2,500 | 5,000 |
| Total equivalent units | 102,500 | 100,000 |
Table (2)
Prepare equivalent cost per unit for baking department.
| Particulars | Conversion | Transferred In |
| Cost (A) | $205,000 | $250,000 |
| Equivalent units of production (B) | 102,500 | 100,000 |
| Cost per unit (A ÷ B) | $2 | $2.50 |
Table (3)
Calculate cost of goods transferred out.
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Started and completed (90,000 × ($2 + $2.50) | $405,000 | |
| Units from beginning work in process: | ||
| Prior period costs | $35,000 | |
| Cost to finished (7,500 × $2) | $15,000 | $50,000 |
| Normal spoilage (2,500 × $2)+ (2,500 × $2.50) | $17,500 | |
| Total | $472,500 |
Table (4)
Calculate abnormal spoilage loss for banking department.
Calculate physical flow schedule for grinding department.
| Particulars | Units | Workings |
| Units to account for: | ||
| Beginning work in process | 500 | (25,000 ÷50) |
| Units started | 2,000 | (100,000 ÷50) |
| Total units to account for | 2,500 | |
| Units accounted for: | ||
| Started and completed | 2,000 | (110,000 - 10,000) |
| Add: Beginning work in process | 500 | |
| Total units accounted for | 2,500 |
Table (5)
Prepare equivalent units of production for grinding
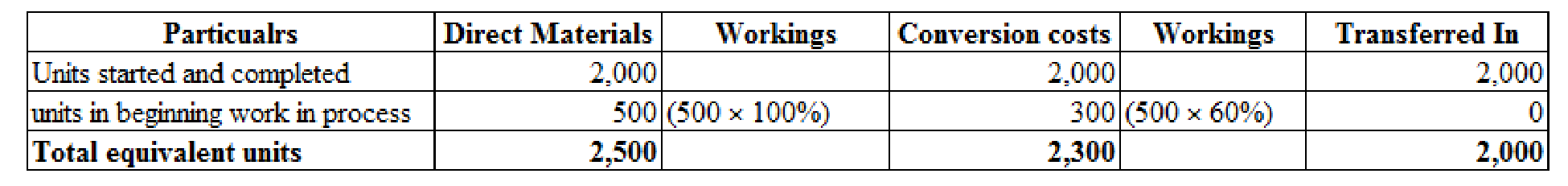
Figure (1)
Prepare equivalent cost per unit for grinding department.
| Particulars | Direct Materials | Conversion | Transferred In |
| Cost in beginning work in process | $0 | $15,000 | $132,500 |
| Add: Cost added (A) | $4,125 | $172,500 | $472,500 |
| Total costs | $4,125 | $187,500 | $605,000 |
| Equivalent units of production (B) | 2,500 | 2,300 | 2,000 |
| Cost per unit (A ÷ B) | $1.65 | $75 | $236.25 |
Table (6)
Calculate cost added for direct materials.
Calculate total prior costs for grinding department.
Calculate ending work in process inventory for direct materials.
Calculate ending work in process inventory for conversion cost.
2.
Prepare
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record to remove spoilage from the baking and grinding departments
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| Loss Due to spoilage | $17,500 | ||
| Work in process - Baking department | $17,500 | ||
| (To record remove spoilage for baking department) |
Table (7)
- Loss due to spoilage is a component of
stockholders’ equity , and it is decreased. Therefore, debit loss due to spoilage account for $17,500. - Work in process inventory- Baking department is a current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit work in process inventory – Baking department account for $17,500.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning

