
EBK HUMAN BIOLOGY
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780100545939
Author: MCMILLAN
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 6, Problem 2RQ
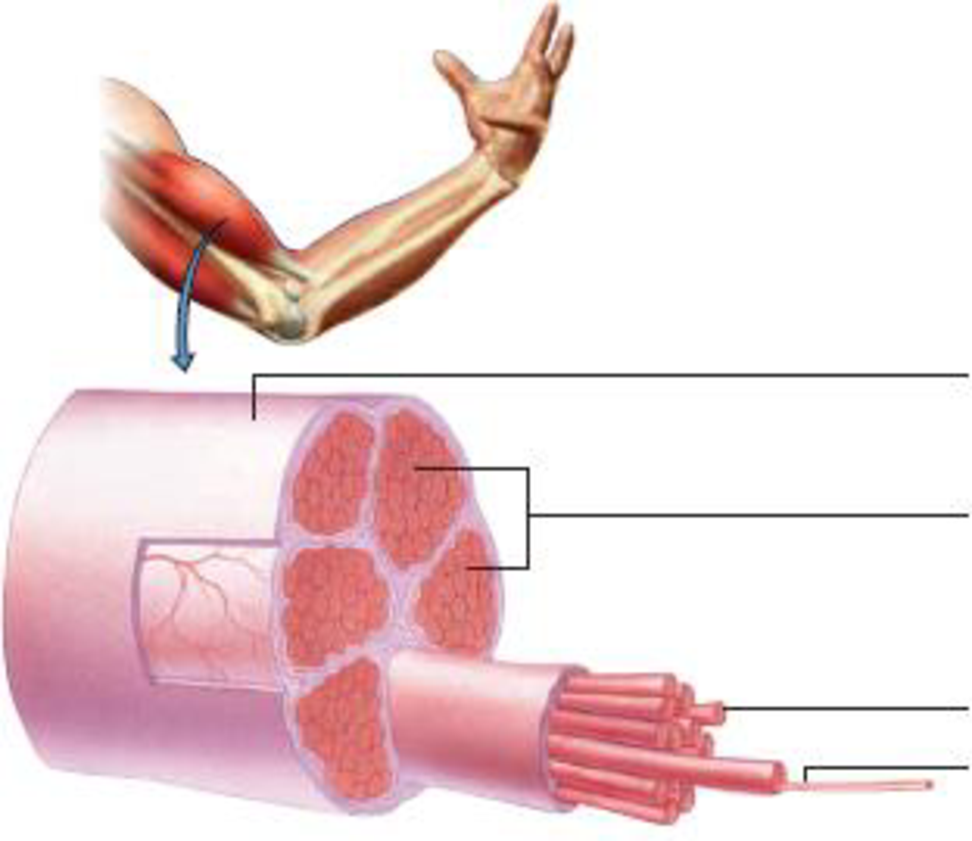
In the diagram below, label the fine structure of a muscle, down to one of its myofibrils. Identify the basic unit of contraction in a myofibril.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Build a model of a prokaryotic cell using any material of
your choice. In your model be sure to include all the
structures appropriate to your cell. You may model a
bacterial cell or an archaea. You will model at least 4
structures in any model.
Next, build a model of a virus using the same type of
materials. You may choose any type of virus but be sure
you can illustrate the key features of a virus (head shape
for example).
Once complete, take multiple photographs of your models
from all angles. Include these images in a document that
also contains the following completed table format. You
may need to add rows to your table depending on the
type of prokaryote you model.
Structure
Model
Key
Found in
Different in
Function
Virus
Virus
Once your model is complete, write a brief description of
your cell and your virus. Emphasize features that are
absent in viruses that classify them as non-living. You can
refer to specific structures in your table in this
explanation.
Some suggestions for…
(This is a 2-part work, Part 1 is done, only Part 2 is to be worked on at the bottom)Part 1 (Done): Describe the levels of structural hierarchy for the human body, starting with the organismal level and ending with the chemical level. In addition, you should make sure you link each level to the previous level, emphasizing the structural relationships.
The human body is organized into a structural hierarchy that progresses from the macroscopic organismal level down to the microscopic chemical level. Each level builds upon the previous one, creating increasingly complex structures. Below is the hierarchy, from largest to smallest, with explanations linking each level to its predecessor:
1. Organismal Level
The entire living human body.Relationship: All lower levels work together to sustain life at this highest level.
2. Organ System Level
Groups of organs working together to perform major functions.Examples: circulatory, nervous, digestive systems.Relationship: The organismal…
Describe the levels of structural hierarchy for the human body, starting with the organismal level and ending with the chemical level. In addition, you should make sure you link each level to the previous level, emphasizing the structural relationships.
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK HUMAN BIOLOGY
Ch. 6 - In a general sense, how do skeletal muscles...Ch. 6 - In the diagram below, label the fine structure of...Ch. 6 - How do actin and myosin interact in a sarcomere to...Ch. 6 - How does a muscle fiber incur an oxygen debt?Ch. 6 - What is the function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum...Ch. 6 - Explain why (a) calcium ions and (b) ACh are vital...Ch. 6 - What is a motor unit? Why does a rapid series of...Ch. 6 - What are the structural and functional differences...Ch. 6 - Prob. 1SQCh. 6 - Prob. 2SQ
Ch. 6 - Prob. 3SQCh. 6 - The _____ is the basic unit of muscle contraction....Ch. 6 - Skeletal muscle contraction requires _________. a....Ch. 6 - Nerve impulses first stimulate a skeletal muscle...Ch. 6 - Prob. 7SQCh. 6 - Prob. 8SQCh. 6 - Prob. 9SQCh. 6 - Prob. 10SQCh. 6 - You are training athletes for the 100-meter dash....Ch. 6 - Prob. 2CTCh. 6 - Prob. 3CTCh. 6 - At the gym Sean gets on a stair-climbing machine...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 9 S es Read the section "Investigating Life: In (Extremely) Cold Blood." Then, drag and drop the terms on the left to complete the concept map. Red blood cells Genes Icefishes -have mutated have colorless Oxygen have few lack encode Blood Cellular respiration consists of- contain carries is a Platelets White blood cells carries low amounts of Hemoglobin is necessary for Plasma Protein Reset.arrow_forwardPlating 50 microliters of a sample diluted by a factor of 10-6 produced 91 colonies. What was the originalcell density (CFU/ml) in the sample?arrow_forwardEvery tutor here has got this wrong, don't copy off them.arrow_forward
- Suppose that the population from question #1 (data is in table below) is experiencing inbreeding depression (F=.25) (and no longer experiencing natural selection). Calculate the new expected genotype frequencies (f) in this population after one round of inbreeding. Please round to 3 decimal places. Genotype Adh Adh Number of Flies 595 Adh Adh 310 Adhs Adhs 95 Total 1000 fladh Adh- flAdn Adh fAdhs Adharrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes why it is difficult to develop antiviral drugs? Explain why. A. antiviral drugs are very difficult to develop andhave no side effects B. viruses are difficult to target because they usethe host cell’s enzymes and ribosomes tometabolize and replicate C. viruses are too small to be targeted by drugs D. viral infections usually clear up on their ownwith no problemsarrow_forwardThis question has 3 parts (A, B, & C), and is under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forward
- They got this question wrong the 2 previous times I uploaded it here, please make sure it's correvct this time.arrow_forwardThis question has multiple parts (A, B & C), and under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forwardCalculate the CFU/ml of a urine sample if 138 E. coli colonies were counted on a Nutrient Agar Plate when0.5 mls were plated on the NA plate from a 10-9 dilution tube. You must highlight and express your answerin scientific notatioarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax- Lifetime Physical Fitness & WellnessHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337677509Author:HOEGERPublisher:Cengage
 Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Lifetime Physical Fitness & Wellness
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337677509
Author:HOEGER
Publisher:Cengage

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College

GCSE PE - ANTAGONISTIC MUSCLE ACTION - Anatomy and Physiology (Skeletal and Muscular System - 1.5); Author: igpe_complete;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6hm_9jQRoO4;License: Standard Youtube License