
Concept explainers
a1.
Whether Division MS should accept the special order by ignoring the qualitative considerations.
a1.
Explanation of Solution
Variable cost: It is also called as production costs that change in extent to the measure of goods that are manufactured. In other words, for each product that is manufactured, variable costs increment by a similar amount.
Opportunity cost: Opportunity cost is the forfeit of certain benefits such as cost savings, incomes, which is surrendered by not picking an option. Opportunity costs are applicable in decisions where the acknowledgment of one option disqualifies the likelihood of selecting different alternatives.
Determine the unit-level incremental costs
Therefore the unit-level incremental cost is $592.
From the result obtained above, the fixed costs are irrelevant since they will continue the similar irrespective of whether the special order is accepted. The total unit-level incremental costs that will be incurred if the special order is accepted will be $592. Because the incremental cost per unit of $592 is less than the incremental income of $800 per unit, hence the special order should be accepted.
Therefore the special order should be accepted.
a2.
Whether Division MS should outsource producing the software by ignoring the qualitative considerations.
a2.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the total avoidable costs
Therefore the total avoidable cost is $5,568,000.
Determine the total avoidable cost per unit
Therefore the avoidable cost per unit is $464.
From the result obtained above, the total avoidable expense per unit is $464. Since the avoidable cost is less than the value required to buy of $600, Division MS would be in an ideal situation to keep on producing the software.
Therefore Division MS should produce the software.
a3.
Whether Company Z should eliminate Division MS.
a3.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the total avoidable costs at 12,000 units
If the division is eliminated, all expenses with the exception of the assigned companywide facility level expense and the

Table (1)
(Refer excel for workings)
Therefore the total avoidable cost at 12,000 units is -$458,000.
From the result obtained above, the avoidable costs surpass the incremental revenue, the division must be eliminated.
Therefore Division MS should be eliminated.
Whether the answer changes if the sales increase by 1,000 units.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the total avoidable costs at 13,000 units
The additional selling units of 1,000 units would build add up to the total sales of 13,000 units.
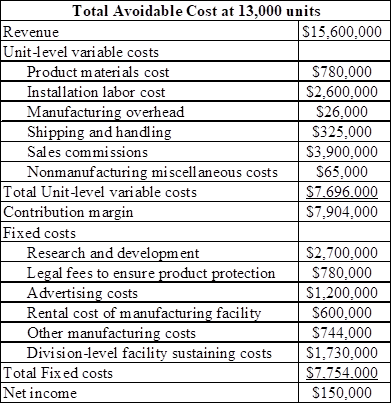
Table (2)
(Refer excel for workings)
Therefore the total avoidable cost at 13,000 units is $150,000.
From the result obtained above, At a sales volume level of 13,000 units, the division must not be eliminated.
Therefore Division MS should not be eliminated.
b1.
Whether the conclusion is valid.
b1.
Explanation of Solution
The reason on whether the conclusion is valid is as follows:
All the variable costs are not constantly relevant. For instance, assume that the special order customer move towards the organization openly, in this way eliminating the requirement to pay sales commissions. Under these conditions the sales commissions would not be relevant to a choice with respect to whether the special order should be accepted. The variable costs can be either relevant or irrelevant contingent upon the specific conditions related with the special decision.
b2.
The criteria for determining whether a cost is relevant or not relevant.
b2.
Explanation of Solution
The criteria for determining whether a cost is relevant or not relevant are as follows:
The research and development expenditures are applicable on the grounds that they are not incurred if the item is outsourced. The advertising costs are not relevant since they are important to advance the item irrespective of whether it is produced or outsourced. In other words, the costs must vary between the choices and be future arranged.
b3.
The reason on the segment elimination decision changes when the volume of production and sales increased.
b3.
Explanation of Solution
The reason on the segment elimination decision changes when the volume of production and sales increased are as follows:
Increases in volume influence the total contribution margin to increment. In like manner, additional margin is accessible to take care of fixed costs or to add to the productivity.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamental Managerial Accounting Concepts

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





