
EBK CORPORATE FINANCE
4th Edition
ISBN: 8220103164535
Author: DeMarzo
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 25P
Suppose you are given the following information about the default-free, coupon-paying yield curve:
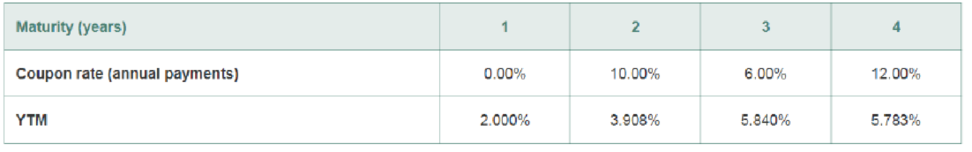
- a. Use arbitrage to determine the yield to maturity of a two-year. zero-coupon bond.
- b. What is the zero-coupon yield curve for years 1 through 4?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Explain in detail the principle of Compounding of interest and why is it so important
in Finance.
What is the bond quote for a $1,000 face value bond with an 8 percent coupon rate (paid semiannually) and a required return of 7.5 percent if the bond is 6.48574, 8.47148, 10.519, and 14.87875 years from maturity?
Gentherm Incorporated has a convertible bond issue outstanding. Each bond, with a face value of $1,000, can be converted into common shares at a rate of 42.25 shares of stock per $1,000 face value bond (the conversion rate), or $19.85 per share. Gentherm’s common stock is trading (on the NYSE) at $19.85 per share and the bonds are trading at $1,025.
Calculate the conversion value of each bond.
Note: Round your answer to 4 decimal places
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK CORPORATE FINANCE
Ch. 6.1 - What is the relationship between a bonds price and...Ch. 6.1 - The risk-free interest rate for a maturity of...Ch. 6.2 - If a bonds yield to maturity does not change, how...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 2CCCh. 6.2 - How does a bonds coupon rate affect its...Ch. 6.3 - How do you calculate the price of a coupon bond...Ch. 6.3 - How do you calculate the price of a coupon bond...Ch. 6.3 - Explain why two coupon bonds with the same...Ch. 6.4 - There are two reasons the yield of a defaultable...Ch. 6.4 - What is a bond rating?
Ch. 6.5 - Why do sovereign debt yields differ across...Ch. 6.5 - What options does a country have if it decides it...Ch. 6 - A 30-year bond with a face value of 1000 has a...Ch. 6 - Assume that a bond will make payments every six...Ch. 6 - The following table summarizes prices of various...Ch. 6 - Suppose the current zero-coupon yield curve for...Ch. 6 - Prob. 5PCh. 6 - Prob. 6PCh. 6 - Suppose a five-year, 1000 bond with annual coupons...Ch. 6 - Prob. 8PCh. 6 - Explain why the yield of a bond that trades at a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 10PCh. 6 - Prob. 11PCh. 6 - Consider the following bonds: Bond Coupon Rate...Ch. 6 - Prob. 14PCh. 6 - Prob. 17PCh. 6 - Prob. 18PCh. 6 - Prob. 19PCh. 6 - Prob. 20PCh. 6 - Prob. 22PCh. 6 - Prob. 23PCh. 6 - Suppose you are given the following information...Ch. 6 - Prob. 26PCh. 6 - Grumman Corporation has issued zero-coupon...Ch. 6 - The following table summarizes the yields to...Ch. 6 - Prob. 30PCh. 6 - Prob. 31PCh. 6 - A BBB-rated corporate bond has a yield to maturity...Ch. 6 - Prob. 33PCh. 6 - Prob. 34PCh. 6 - Prob. 35P
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Graphically portray the Keynesian transmission mechanism under the following conditions: a. A decrease in the m...
Macroeconomics
•• 4.6 The monthly sales for Yazici Batteries, Inc., were as follows:
MONTH SALES
January 20
February 21
March ...
Operations Management
To what does the lifetime value of the customer refer, and how is it calculated?
MARKETING:REAL PEOPLE,REAL CHOICES
Determine the price elasticity of demand if, in response to an increase in price of 10 percent, quantity demand...
Microeconomics
10-10 What challenges do managers face in managing global teams? How should those challenges be handled?
Fundamentals of Management (10th Edition)
1-1. Define marketing and outline the steps in the marketing process. (AASCB: Communication)
Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are looking to lease a 2019 Subaru Forester. You have found a 36 - month closed end lease on a Forester with an MSRP of $25, 270 and a lease end purchase option of $15,667 (residual value). To get the lease you have to pay a fee of $1,765 due at signing, and the monthly payment was calculated to be $ 265. A) What is the nominal rate of return the dealership is earning on the lease? (Hint: think of the cash flows from the dealerships prospective) B) What would the lease payment be if the dealership wanted a nominal 6% compounded monthly on the lease?arrow_forwardWhat should business people learn about the problem started with Sears and organizational consequences?How the traditional retail businesses face significant challenges in remaining competitive in the digital age? What is the broad exploration of retail industry challenges without assuming specific causes or outcomes, making them suitable for research and why?arrow_forwardWhat are Biblical principles researchers can follow to mitigate Unintended errors in research?How a Christian conduct during a research proposal and study can be a witnessof the Gospel to others.arrow_forward
- What is Sears business problem? What cause Sears to collapse and closeout the company? Would you please help to explain, what is the problem statement, and general problem? Could you help to provide four research questions that align with the problem statement, ensuring they are exploratory, not assumptive, and not specific to an organization.arrow_forwardHilton Hotels Corporation has a convertible bond issue outstanding. Each bond, with a face value of $1,000, can be converted into common shares at a rate of 61.2983 shares of stock per $1,000 face value bond (the conversion rate), or $16.316 per share. Hilton’s common stock is trading (on the NYSE) at $15.90 per share and the bonds are trading at $975. a. Calculate the conversion value of each bond. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places. (e.g., 32.16)). (974.50 was wrong)arrow_forwardConsider an investor who, on January 1, 2022, purchases a TIPS bond with an original principal of $100,000, an 8 percent annual (or 4 percent semiannual) coupon rate, and 10 years to maturity. If the semiannual inflation rate during the first six months is 0.3 percent, calculate the principal amount used to determine the first coupon payment and the first coupon payment (paid on June 30, 2022). From your answer to part a, calculate the inflation-adjusted principal at the beginning of the second six months. Suppose that the semiannual inflation rate for the second six-month period is 1 percent. Calculate the inflation-adjusted principal at the end of the second six months (on December 31, 2022) and the coupon payment to the investor for the second six-month period.arrow_forward
- A municipal bond you are considering as an investment currently pays a yield of 6.75 percent. Calculate the tax-equivalent yield if your marginal tax rate is 28 percent. Calculate the tax-equivalent yield if your marginal tax rate is 21 percent.arrow_forwardWhat would your assessment of the plight of the working poor? Explain.arrow_forwardWhat is considered to be "living on the edge"? Explain.arrow_forward
- How close to the edge are the working poor living? Explain.arrow_forwardSuppose three countries’ per capita Gross Domestic Products (GDPs) are £1000, £2000, and £3000. What is the average of each pair of countries’ GDPs per capita? (b) What is the difference between each of the individual observations and the overall average? What is the sum of these differences? (c) Suppose instead of three countries, we had a sample of 100 countries with the same sample average GDP per capita as the overall average for the three observations above, with the standard deviation of these 100 observations being £1000. Form the 95% confidence interval for the population mean. (d) What might explain differences in GDP across countries? Consider the following regression equation, where Earnings is measured in £/hour, and Experience is measured in years in a particular job, with standard errors in parentheses: Earnings \ = −0.25 (−0.5) + 0.2 (0.1) Experience, One of these numbers has been reported incorrectly - it shouldn’t be negative. Which one and why? (b)…arrow_forwardI need answer typing clear urjent no chatgpt used pls i will give 5 Upvotes.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
The U.S. Treasury Markets Explained | Office Hours with Gary Gensler; Author: U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uKXZSzY2ZbA;License: Standard Youtube License