
Term Bond Debt Service Fund Transactions. (LO6-5) On July 1, 2019, the first day of its 2020 fiscal year, the Town of Bear Creek issued at par $2,000,000 of 6 percent term bonds to renovate a historic wing of its main administrative building. The bonds mature in five years on July 1, 2024. Interest is payable semiannually on January 1 and July 1.
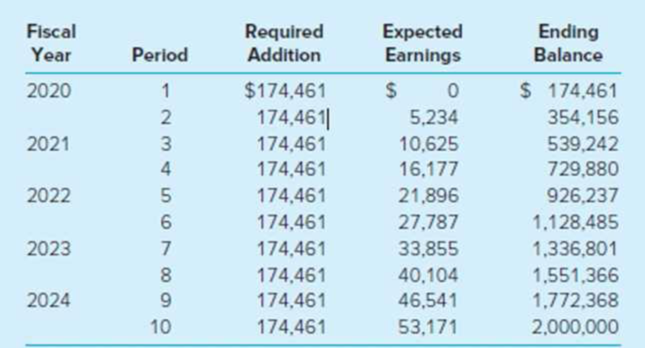
As illustrated in the table below, a sinking fund is to be established with equal semiannual additions made on June 30 and December 31. Cash for the sinking fund additions and the semiannual interest payments will be transferred from the General Fund shortly before the due dates. Investment earnings are added to the investment principal.
Required
Create a term bond debt service fund for the town and prepare
- a. On July 1, 2019, record the budget for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2020. Include all interfund transfers to be received from the General Fund during the year. An appropriation should be provided only for the interest payment due on January 1, 2020.
- b. On December 28, 2019, the General Fund transferred $234,461 to the debt service fund. The addition to the sinking fund was immediately invested in 6 percent certificates of deposit.
- c. On December 28, 2019, the city issued checks to bondholders for the interest payment due on January 1, 2020.
- d. On June 27, 2020, the General Fund transferred $234,461 to the debt service fund. The addition for the sinking fund was invested immediately in 6 percent certificates of deposit.
- e. Actual interest earned on sinking fund investments at year-end (June 30, 2020) was the same as the amount budgeted in the table. This interest adds to the sinking fund balance.
- f. All appropriate closing entries were made at June 30, 2020, for the debt service fund.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
ACCOUNTING F/GOV.+..(LL)-W/CODE>CUSTOM<
- Need solutionarrow_forwardThe weighted average contribution margin is?arrow_forwardUse the information provided by iLembe Enterprises to answer the following questions independently. The expanded contribution margin model must be used to answer questions 3.3 to 3.5. 3.1 Use the contribution margin ratio to calculate the break-even value. 3.2 Determine the selling price per unit (expressed to the nearest cent) that will enable iLembe Enterprises to break even. 3.3 Calculate the sales volume required to achieve an operating profit of R2 001 000. 3.4 Calculate the total Contribution Margin and Operating Profit/Loss if the sales price drops by 10%. 3.5 The management of iLembe Enterprises is considering an increase of R100 000 in the advertising expenditure with the expectation that the sales volume will increase by 1 000 units. Will the profitability improve? Motivate your answer with the relevant calculationsarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





