
Determine the roots of the simultaneous nonlinear equations
Use a graphical approach to obtain your initial guesses. Determine refined estimates with the two-equation Newton-Raphson method described in Sec. 6.6.2.
To calculate: The root of the non-linear simultaneous equations,
By the two-equation Newton-Raphson method and find the initial guess by the graphical method.
Answer to Problem 23P
Solution:
The root of the simultaneous non-linear equations
For the initial root
For the initial root
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The non-linear simultaneous equation,
Formula used:
The Newton-Raphson formula for two non-linear equation is,
Calculation:
Use MATLAB to draw the graph of the equations,
Code:
%x-coordinates spacing is defined.
%first function is defined.
%second function is defined.
%Plot command is used to draw the two function.
Output:
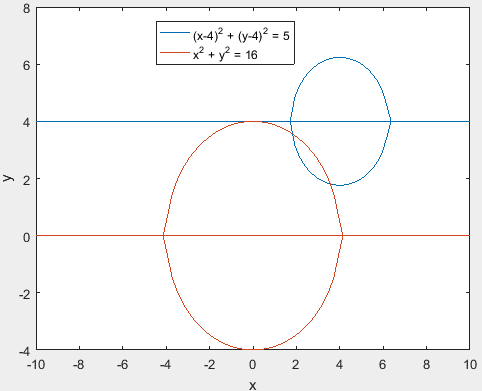
From the above graph, it is observed that there are two roots at
Consider theequations,
Rewrite the equation as below,
Partial differentiate the above functions with respect to x,
And,
Now, partial differentiate the above functions with respect to y,
And,
Use initial guesses
And,
Now, use
And,
Now, use
And,
Thus, all the iteration can be summarized as below,
| 0 | 1.8 | 3.6 |
| 1 | 1.8056 | 3.5694 |
| 2 | 1.80583 | 3.56917 |
| 3 | 1.80583 | 3.56917 |
Hence, the root of the simultaneous non-linear equations
Use initial guesses
And,
Now, use
And,
Now, use
And,
Thus, all the iteration can be summarized as below,
| 0 | 3.6 | 1.8 |
| 1 | 3.56944 | 1.80556 |
| 2 | 3.56917 | 1.80583 |
| 3 | 3.56917 | 1.80583 |
Hence, the root of the simultaneous non-linear equations
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Numerical Methods for Engineers
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Graphical Approach To College Algebra
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- Golden Ratio search Method f(x) = 2x^3 - 3x^2 - 12x + 1 Golden ratio search rules 1.If f(x) < f(x2): 1. Eliminate all x values less than x2 2. X2 becomes the new a 3. x, becomes the new x2 4. no change in b If f(x) > f(x2): 1. Eliminate all x values greater than x 2. x, becomes the new b 3. x2 becomes the new x 4. no change in aquesion=Narrow the interval in which the minimizer of the function f is located using the golden search method, starting with the initial interval (0,6], until its width is less than 2. Then, accept the midpoint of this interval as an approximate value of the minimizer of the function fand determine it. (ф=0.62)According to the question above, fill in the table below using the algorithm until the appropriate place.please write every step by step in a verry comprehensive wayarrow_forwardIn preparing for the upcoming holiday season, Fresh Toy Company (FTC) designed a new doll called The Dougie that teaches children how to dance. The fixed cost to produce the doll is $100,000. The variable cost, which includes material, labor, and shipping costs, is $31 per doll. During the holiday selling season, FTC will sell the dolls for $39 each. If FTC overproduces the dolls, the excess dolls will be sold in January through a distributor who has agreed to pay FTC $10 per doll. Demand for new toys during the holiday selling season is extremely uncertain. Forecasts are for expected sales of 60,000 dolls with a standard deviation of 15,000. The normal probability distribution is assumed to be a good description of the demand. FTC has tentatively decided to produce 60,000 units (the same as average demand), but it wants to conduct an analysis regarding this production quantity before finalizing the decision. (a) Determine the equation for computing FTC's profit for given values of the…arrow_forwardFor all integers a and b, (a + b)^4 ≡ a^4 + b^4 (mod 4).arrow_forward
- Let Χ be a real-valued character (mod k). Let k S = Σnx(n). n=1 If (a, k) = 1, ax(a)S = S (mod k). (iii) Write k = 2ºq where q is odd. Show that there is an integer a with (a, k) = 1 such that a = 3 (mod 2ª) and a = 2 (mod q). Deduce that 12S = 0 (mod k).arrow_forwardProve that (1) Σσς (α) μ(η/α) = n d/n (ii) Σσς(d) = η Σσο(α)/d d❘n d❘n (iii) σ (d) σ (n/d) = Σ d³oo(d) σo(n/d). d|n dnarrow_forwardhow to do part b,carrow_forward
- If p = 5 (mod 8), where p is prime, show that p|2 (P-1)/2 + 1. State and prove the corresponding result when p = 7 (mod 8). Deduce that 250 + 1 and 251 1 are composite. -arrow_forwardWhy the character no change for my remark?arrow_forwardIn preparing for the upcoming holiday season, Fresh Toy Company (FTC) designed a new doll called The Dougie that teaches children how to dance. The fixed cost to produce the doll is $100,000. The variable cost, which includes material, labor, and shipping costs, is $31 per doll. During the holiday selling season, FTC will sell the dolls for $39 each. If FTC overproduces the dolls, the excess dolls will be sold in January through a distributor who has agreed to pay FTC $10 per doll. Demand for new toys during the holiday selling season is extremely uncertain. Forecasts are for expected sales of 60,000 dolls with a standard deviation of 15,000. The normal probability distribution is assumed to be a good description of the demand. FTC has tentatively decided to produce 60,000 units (the same as average demand), but it wants to conduct an analysis regarding this production quantity before finalizing the decision. (a) Determine the equation for computing FTC's profit for given values of the…arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage


