
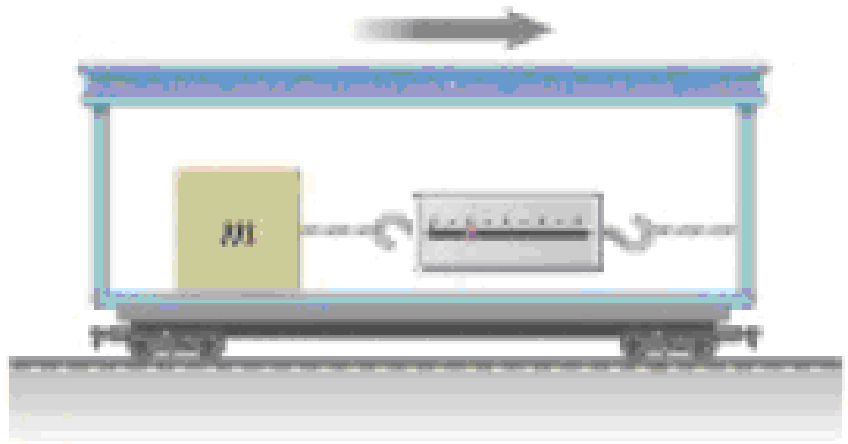
An object of mass m = 5.00 kg, attached to a spring scale, rests on a frictionless, horizontal surface as shown in Figure P6.14. The spring scale, attached to the front end of a boxcar, reads zero when the car is at rest. (a) Determine the acceleration of the car if the spring scale has a constant reading of 18.0 N when the car is in motion. (b) What constant reading will the spring scale show if the car moves with constant velocity? Describe the forces on the object as observed (c) by someone in the car and (d) by someone at rest outside the car.
Figure P6.14
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern, Revised Hybrid (with Enhanced WebAssign Printed Access Card for Physics, Multi-Term Courses)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
- Find the ratio of the diameter of silver to iron wire, if they have the same resistance per unit length (as they might in household wiring). d. Ag dFe = 2.47 ×arrow_forwardFind the ratio of the diameter of silver to iron wire, if they have the same resistance per unit length (as they might in household wiring). d Ag = 2.51 dFe ×arrow_forwardShow that the units 1 v2/Q = 1 W, as implied by the equation P = V²/R. Starting with the equation P = V²/R, we can get an expression for a watt in terms of voltage and resistance. The units for voltage, V, are equivalent to [? v2 v2 A, are equivalent to J/C ✓ X . Therefore, 1 = 1 = 1 A V1 J/s Ω V-A X = 1 W. . The units for resistance, Q, are equivalent to ? The units for current,arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





