
Concept explainers
(a) Draw two typical curves y = f(x) and y = g(x), where f(x) ≥ g(x) for a ≤ x ≤ b. Show how to approximate the area between these curves by a Riemann sum and sketch the corresponding approximating rectangles. Then write an expression for the exact area.
(b) Explain how the situation changes if the curves have equations x = f(y) and x = g(y), where f(y) ≥ g(y) for c ≤ y ≤ d.
(a)
To Draw: the two typical curves
To define: A Riemann sum that approximates the area between the two typical curves with drawing of the corresponding approximating rectangles and exact area between the two typical curves and the expression for the exact area.
Explanation of Solution
Consider the two curves
Here, the top curve function is
Assume f and g are continuous function and
Here, the lower limit is a and the upper limit is b.
Show the approximate ith strip rectangle with base
Sketch the two typical curves
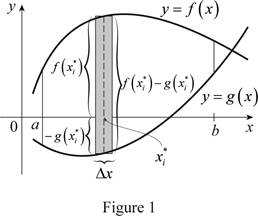
Refer to figure 1.
The two typical curves
The expression for the exact area is
Divide the area between the two typical curves into n strips of equal width and take the entire sample points to be right endpoints, in which
Sketch thecorresponding approximating rectangles as shown in Figure 2.
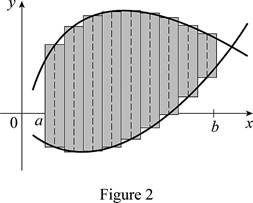
The better and better approximation occurs in
Thus, the Riemann sum with the sketch of corresponding approximating rectangles and the exact area between the two typical curves shown.
Therefore, the approximation of the area between the two typical curves using Riemann sum with the sketch of the corresponding approximating rectangles and the sum of the areas corresponding approximating rectangles is the exact area.
(b)
To Draw: The two typical curves with the changing the situation as
To define: The situation if the curves changes from
The expression for the exact area is
Explanation of Solution
Consider the two curves
Here, the right curve function is
Assume f and g are continuous function and
Here, the bottom limit is c and the top limit is d.
Sketch the two typical curves
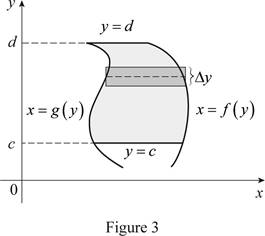
Thus, the two typical curves
Normally the height calculated from the top function minus bottom one and integrating from left to right. Instead of normal calculation, use “right minus left” and integrating from bottom to top. Therefore the exact area, A written as
Therefore, the changes of the situation if the curves have equations
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Single Variable Calculus: Concepts and Contexts, Enhanced Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Precalculus: A Unit Circle Approach (3rd Edition)
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Precalculus
Beginning and Intermediate Algebra
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
- For each graph in Figure 16, determine whether f (1) is larger or smaller than the slope of the secant line between x = 1 and x = 1 + h for h > 0. Explain your reasoningarrow_forwardPoints z1 and z2 are shown on the graph.z1 is at (4 real,6 imaginary), z2 is at (-5 real, 2 imaginary)Part A: Identify the points in standard form and find the distance between them.Part B: Give the complex conjugate of z2 and explain how to find it geometrically.Part C: Find z2 − z1 geometrically and explain your steps.arrow_forwardA polar curve is represented by the equation r1 = 7 + 4cos θ.Part A: What type of limaçon is this curve? Justify your answer using the constants in the equation.Part B: Is the curve symmetrical to the polar axis or the line θ = pi/2 Justify your answer algebraically.Part C: What are the two main differences between the graphs of r1 = 7 + 4cos θ and r2 = 4 + 4cos θ?arrow_forward
- A curve, described by x2 + y2 + 8x = 0, has a point A at (−4, 4) on the curve.Part A: What are the polar coordinates of A? Give an exact answer.Part B: What is the polar form of the equation? What type of polar curve is this?Part C: What is the directed distance when Ø = 5pi/6 Give an exact answer.arrow_forwardNew folder 10. Find the area enclosed by the loop of the curve (1- t², t-t³)arrow_forward1. Graph and find the corresponding Cartesian equation for: t X== y = t +1 2 te(-∞, ∞) 42,369 I APR 27 F5 3 MacBook Air stv A Aa T 4 DIIarrow_forward
- Middle School GP... Echo home (1) Addition and su... Google Docs Netflix Netflix New folder 9. Find the area enclosed by x = sin²t, y = cost and the y-axis.arrow_forward2. Graph and find the corresponding Cartesian equation for: (4 cos 0,9 sin 0) θ ε [0, 2π) 42,369 I APR 27 3 MacBook Air 2 tv A Aaarrow_forward30 Page< 3. Find the equation of the tangent line for x = 1+12, y = 1-3 at t = 2 42,369 APR A 27 M . tv NA 1 TAGN 2 Aa 7 MacBook Air #8arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





