
Concept explainers
Assign the peaks in the
NMR spectrum of eugenol (Fig. 6.23) to specific protons in the molecule. The OH peak is at 5.1 ppm.
Interpretation:
The peak in
Concept introduction:
NMR is an analytical method that is utilized to identify the structure of a compound. It determines the framework of carbon-hydrogen bonds present in the compound.
Number of signals in the
The protons that are present in the different chemical environment are known as non-equivalent protons while the protons that are present in same chemical environment are known as equivalent protons.
Answer to Problem 1Q
Eugenol has 12 different hydrogen atoms. The three hydrogen atom present on the aromatic ring show peak around
Explanation of Solution
The structure of eugenol is as follows:
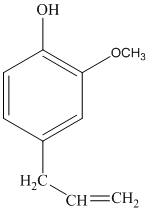
Eugenol has 12 different hydrogen atoms. The integration of peaks from right to left is 3:2:2:3:2.
There are two peaks for the three hydrogens around
There are two peaks for four hydrogen atoms around
There are two peaks for six around
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Owlv2 With Labskills, 4 Terms (24 Months) Printed Access Card For Williamson/masters' Macroscale And Microscale Organic Experiments, 7th
- This thermodynamic cycle describes the formation of an ionic compound MX2 from a metal element M and nonmetal element X in their standard states. What is the lattice enthalpy of MX2 ? What is the enthalpy formation of MX2 ? Suppose both the heat of sublimation of M and the ionization enthalpy of M were smaller. Would MX2 be more stable? Or less? or impossible to tell without more information?arrow_forward7. Draw the mechanism to describe the following transformation: Note: This is a base catalyzed reaction. So, the last steps must make [OH]- OH [OH]¯ OH Heat Oarrow_forwardShow work with explanation...don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Br. , H+ .OH Mg ether solvent H+, H₂O 17. Which one of the compounds below is the final product of the reaction sequence shown above? HO A HO HO OH D B OH HO OH C OH HO OH Earrow_forward8:57 PM Sun Jan 26 Content ← Explanation Page X Content X ALEKS Jade Nicol - Le A https://www-av C www-awa.aleks.com O States of Matter Understanding consequences of important physical properties of liquids ? QUESTION Liquid A is known to have a lower viscosity and lower surface tension than Liquid B. Use these facts to predict the result of each experiment in the table below, if you can. experiment Liquid A and Liquid B are each pumped through tubes with an inside diameter of 27.0 mm, and the pressures PA and PB needed to produce a steady flow of 2.4 mL/s are measured. 25.0 mL of Liquid A are poured into a beaker, and 25.0 mL of Liquid B are poured into an identical beaker. Stirrers in each beaker are connected to motors, and the forces FA and FB needed to stir each liquid at a constant rate are measured. predicted outcome OPA will be greater than PB OPA will be less than PB OPA will be equal to PB It's impossible to predict whether PA or PB will be greater without more information.…arrow_forwardShow work. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- 5. Please draw in the blanks the missing transition states and the correlated products. Explicitly display relevant absolute stereochemical configuration. MeOH I OMe H Endo transition state, dienophile approaching from the bottom of diene + H ཎྞཾ ཌཱརཱ༔,_o OMe H H OMe Endo transition state, dienophile approaching from the top of diene or from the bottom but horizontally flipped (draw one) + Exo transition state, dienophile approaching from the top of diene or from the bottom but horizontally flipped (draw one) Exo transition state, dienophile approaching from the top of diene or from the bottom but horizontally flipped (draw one) MeO H H MeO H MeO H MeO H Harrow_forwardH H (1) H C. C C .H (2) (3) Cl H The ideal value for bond angle (1) is (Choose one) and the ideal value for bond angle (3) is (Choose one) degrees, the value for bond angle (2) is (Choose one) degrees, degrees.arrow_forwardShow work.....don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning





