
College Physics (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780321902788
Author: Hugh D. Young, Philip W. Adams, Raymond Joseph Chastain
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 1P
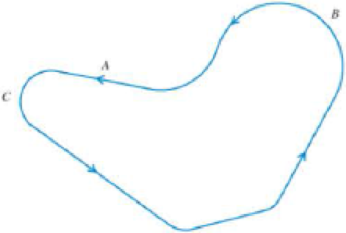
A racing car drives at constant speed around the horizontal track shown in Figure 6.27. At points A, B, and C, draw a vector showing the magnitude and direction of the net force on this car. Make sure that the lengths of your arrows represent the relative magnitudes of the three forces.
Figure 6.27 Problem 1.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please answer this. I will surely upvote!!!
The following information pertains to questions 1, 2, and 3. A workman pulls a sled
across an asphalt road using a rope at angle 0 above the horizontal direction. The
workman pulls with 1,000[N] of force. The coefficients of friction of the sled with
the road are u=1.00 and µ=0.70. The sled has mass m. The sled is initially at rest.
T710Q0[N].
1) Which expression gives the magnitude of fmax for the situation illustrated above?
A) mg
B)
mg – 1000cos(0)
C)
-
mg + 1000cos(0)
D) mg-1000sin(0)
E) mg+ 1000sin(0)
F) None of the above
A force P = 873 kN whose line of action passes
through points A(1, 1, 4) and B(5, 8, 10). Determine
the z-component of force P in kN. Write the numerical
value only and in 2 decimal places.
Chapter 6 Solutions
College Physics (10th Edition)
Ch. 6 - If there is a net force on a particle in uniform...Ch. 6 - As a car rounds a banked circular curve at...Ch. 6 - A student wrote, The reason an apple falls...Ch. 6 - Non-physicists often ask questions such as What...Ch. 6 - During an actual interview for a college teaching...Ch. 6 - If two planets have the same mass, will they...Ch. 6 - True or false? Astronauts in satellites orbiting...Ch. 6 - True or false? If a rock is acted upon by a...Ch. 6 - On an icy road, you approach a curve that has the...Ch. 6 - You are riding on a roller coaster with a hill...
Ch. 6 - The moon is accelerating toward the earth. Does...Ch. 6 - A passenger in a car rounding a sharp curve feels...Ch. 6 - If the earth had twice its present mass, its...Ch. 6 - An astronaut is floating happily outside her...Ch. 6 - A frictional force f provides the centripetal...Ch. 6 - Two masses m and 2m are each forced to go around a...Ch. 6 - A stone of weight W is attached to a strong string...Ch. 6 - If a planet had twice the earths radius, but only...Ch. 6 - When a mass goes in a horizontal circle with speed...Ch. 6 - In the previous problem, if both the speed and the...Ch. 6 - Two 1.0 Kg point masses a distance D apart each...Ch. 6 - Two massless bags contain identical bricks, each...Ch. 6 - When two point masses are a distance D apart, each...Ch. 6 - If human beings ever travel to a planet whose mass...Ch. 6 - A racing car drives at constant speed around the...Ch. 6 - A stone with a mass of 0.80 kg is attached to one...Ch. 6 - Force on a skaters wrist. A 52 kg ice skater spins...Ch. 6 - A flat (unbanked) curve on a highway has a radius...Ch. 6 - The Giant Swing at a county fair consists of a...Ch. 6 - A small button placed on a horizontal rotating...Ch. 6 - Using only astronomical data from Appendix E,...Ch. 6 - A highway curve with radius 900.0 ft is to be...Ch. 6 - The Indy 500. The Indianapolis Speedway (home of...Ch. 6 - A bowling ball weighing 71.2 N is attached to the...Ch. 6 - A lead fishing weight of mass 0.2 kg is tied to a...Ch. 6 - A 50.0 kg stunt pilot who has been diving her...Ch. 6 - Effect on blood of walking. While a person is...Ch. 6 - Stay dry! You tie a cord to a pail of water, and...Ch. 6 - Stunt pilots and fighter pilots who fly at high...Ch. 6 - If two tiny identical spheres attract each other...Ch. 6 - What is the ratio of the suns gravitational pull...Ch. 6 - Rendezvous in space! A couple of astronauts agree...Ch. 6 - What is the ratio of the gravitational pull of the...Ch. 6 - A 2150 kg satellite used in a cellular telephone...Ch. 6 - At a distance N RE from the earths surface, where...Ch. 6 - Find the magnitude and direction of the net...Ch. 6 - How far from a very small 100 kg ball would a...Ch. 6 - Each mass in Figure 6.30 is 3.00 kg. Find the...Ch. 6 - An 8.00 kg point mass and a 15.0 kg point mass are...Ch. 6 - How many kilometers would you have to go above the...Ch. 6 - Your spaceship lands on an unknown planet. To...Ch. 6 - If an objects weight is W on the earth, what would...Ch. 6 - Huygens probe on Titan. In January 2005 the...Ch. 6 - The mass of the moon is about 1/81 the mass of the...Ch. 6 - Neutron stars, such as the one at the center of...Ch. 6 - The asteroid 243 Ida has a mass of about 4.0 1016...Ch. 6 - Prob. 33PCh. 6 - What is the period of revolution of a satellite...Ch. 6 - Prob. 35PCh. 6 - Planets beyond the solar system. On October 15,...Ch. 6 - Communications satellites. Communications...Ch. 6 - Prob. 38PCh. 6 - Apparent weightlessness in a satellite. You have...Ch. 6 - Baseball on Deimos! Deimos, a moon of Mars, is...Ch. 6 - International Space Station. The International...Ch. 6 - Artificial gravity. One way to create artificial...Ch. 6 - Shortest possible day. Consider the fact that an...Ch. 6 - Volcanoes on lo. Jupiters moon lo has active...Ch. 6 - You tie one end of 0.3-m-long spring to a 0.5 kg...Ch. 6 - An astronaut carefully measures the gravitational...Ch. 6 - Prob. 47GPCh. 6 - A 1125 kg car and a 2250 kg pickup truck approach...Ch. 6 - Exploring Europa. Europa, a satellite of Jupiter,...Ch. 6 - The star Rho1 Cancri is 57 light-years from the...Ch. 6 - A 4.00 kg block is attached to a vertical rod by...Ch. 6 - As your bus rounds a flat curve at constant speed...Ch. 6 - Artificial gravity in space stations. One problem...Ch. 6 - Based on these data, what is the most likely...Ch. 6 - How many times the acceleration due to gravity g...Ch. 6 - Exoplanets. As planets with a wide variety of...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Consider the two experiments described above. When the momentum of an object or system of objects did not chang...
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
7.71 ••• CP A small block with mass 0.0500 kg slides in a vertical circle of radius R = 0.800 m on the inside o...
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
25. The 100 kg block in FIGURE EX7.25 takes 6.0 s to reach the floor after being released from rest. What is th...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
If acceleration is proportional to the net force or is equal to net force.
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
Which can store more energy: a 1.0-F capacitor rated or a 470-pF capacitor rated at 3 kV?
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Which of these statements is a key ass...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chandelier hangs h = 0.62 m down from two chains of equal length. The chains are separated from one another by a length L = 0.45 m at the ceiling. The chandelier has a mass of m = 21 kg.Randomized Variablesh = 0.62 mL = 0.45 mm = 21 kgWhat is the angle, θ in degrees, between one of the chains and the vertical where it contacts the chandelier? Write an expression for FT,y, the magnitude of the y-component of the tension in one chain, in terms of the given information and variables available in the palette. FT,y = Using your previous results, find the tension, FT in Newtons, in one chain. FT =arrow_forwardPhysics written by hand.arrow_forwardQUESTION 2 Consider the diagram for question 2. A person of mass 70.5 kg is on a roller coaster at the top of the first hill with speed 4.29 m/s. The top of the first hill is at a height of 20.4 Im above the ground. Position B is situated atop a hill that we can approximate using a circle of radius 13.9 m. At B, the person experiences a net force precisely equal to the force of gravity, Fg = mg[down]. Througout the ride, assume perfect conservation of mechanical energy. a) Calculate the total work done on the person from the starting position to position B. Hint: Find the speed at B and use the work-energy theorem. b) Calculate the height of B above the ground. A Barrow_forward
- Problem 16: A 50 kg block and a100 kg block are connected by a string as shown in the figure. The pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the 50 kg block and the incline is 0.250. Find the speed of the 100 kg block after it has fallen 1.5 m, causing the 50 kg block to move from position A to B. 50.0 kg 37.0⁰ A 100 kgarrow_forwardThree forces act on an object, considered to be a particle, which moves with constant velocity v =(3 m/s)î +(−2 m/s)ĵ Two of the forces are shown in the picture below., while the third force, F_3 is not given. 1.) What are the x, y, and z components of F_3?arrow_forwardForce, Force, Baby! Two constant forces of magnitudes F and F, act on a particle of mass 5.00 [kg] which is at rest at the origin. The force F1 points at 14.5° west of north, while the force F, points at 58.3° west of south. Due to the two forces, the particle accelerates and is later located at 32.4 [m], 17.0° north of west with speed 12.2 [m/s]. What is F1? O 0.524 [N] O 9.03 [N] O 9.28 [N] O 10.7 [N]arrow_forward
- Particle A lies on the x-y plane and is acted on by the three forces shown. Find the resultant of the three forces. 4.5m 2.1m A 1400 N 900N 1.8m 1000N 0,6m 18m 1.2m /Carrow_forwardTwo constant forces act on an object of mass m = 4.30 kg object moving in the xy plane as shown in the figure below. Force F, is 26.5 N at 35.0°, and force F, is 48.0 N at 150°. At time t = 0, the object is at the origin and has velocity (3.50î + 2.15j) m/s. 150° 35.0° (a) Express the two forces in unit-vector notation. F, - N (b) Find the total force exerted on the object. N (c) Find the object's acceleration. m/s2 Now, consider the instant t = 3.00 s. (d) Find the object's velocity. m/s (e) Find its position. (f) Find its kinetic energy from V½mv2. kJ (g) Find its kinetic energy from 2mv,2 + EF · AF. kJarrow_forwardA woman pushes a 10.0 kg box across a horizontal floor with a constant force of magnitude 40.0 N directed at an angle of -25° with respect to the positive x-axis. The box moves horizontally to the right. At the origin (x=0) the box has an initial speed of 4.00 m/s and the woman pushes it to a location ofx=3.00 m. what is the force of the woman? what is the force of gravity? what is the normal force of the floor?arrow_forward
- A ball of mass m moves along a track in the shape of vertical circular loop. There are 2 forces acting on the ball -- the normal force exerted by track (Ntrack) and gravity (mg). Ignore friction and air resistance. The vectors v (velocity) and a (total acceleration) have an angle ◊ between them, which changes as the ball moves. Check all the answers which are true statements. There may be more than one correct answer! when the ball is on the way up the loop, 0 > 90°º the magnitude of a is always smaller than g, no matter how fast the ball moves 0 = 90° at the "side" points (halfway up the loop) at the bottom of the loop, Ntrack is stronger than mg the ball falls off the track if Ntrack = 0arrow_forwardQ. Two workers, A and B, are each pulling identical crates of tools a distance of 10 m along a level floor. Worker A pulls the crate with a force of 850 N at an angle of 30° with respect to the floor, and Worker B also pulls the crate with a force of 850 N, but at an angle of 45° with respect to the floor. Assume that in both cases, the crates are moved from (0, 0, 0) to (10, 0, 0), and the z-axis points upward, perpendicular to the floor. Find the amount of work done by each person in moving the crate.arrow_forwardCarol wants to move her 32kg sofa to a different room in the house. She places "sofa disks", slippery disks with mu k =.080 , on the carpet, under the feet of the sofa. She then pushes the sofa at a steady.4 .4 m/s across the floor. How much force does she apply to the sofa?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY