
In this chapter, we have learned about the
suppose it is hypothesized that it requires more energy to remove an electron from a metal that has atoms with one or more half-filled shells than from those that do not.
- Design a series of experiments involving the photoelectric effect that would test the hypothesis.
- What experimental apparatus would be needed to test the hypothesis? Its not necessary that you name actual equipment but rather that you imagine how the apparatus would work-think in terms of the types of measurements that would be needed, and what capability you would need in your apparatus.
- Describe the type of data you would collect and how you would analyze the data to see whether the hypothesis were correct.
- Could your experiments be extended to test the hypothesis for other parts of the periodic table, such as the lanthanide or actinide elements?
Interpretation: The experiments, apparatus and the type of data to test the given hypothesis is to be determined.
(a) A series of experiment involving the photoelectric effect that would test the hypothesis needs to be designed.
(b) The experimental apparatus required to test the given hypothesis should be determined.
(c)The type of data required to conclude whether the given hypothesis is correct or not should be determined.
(d) If the given hypothesis can be tested on lanthanides or actinides or not should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The light falls on the surface of the metal and results in the ejection of electron form its surface. This process is known as the photoelectric effect.
Answer to Problem 1DE
Solution: (a) When the light incident on the metal plate having one or more half-filled orbital; one does not observe the collection of electrons on the collector plate. But as the energy increases the electrons started collecting on the collector plate. This proves the given hypothesis.
(b) The experimental apparatus to study the photoelectric effect consists of the metal plate, collector plate, battery and voltmeter.
(c) The plot of stopping potential as a function of frequency is used to conclude that the given hypothesis is correct.
(d) The given hypothesis is not applicable on lanthanides and actinides because of the presence of d and f orbitals.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The hypothesis says that that it requires more energy to remove an electron from the metal that has one or more half filled shells.
The ejection of electrons from the metal surface is tested by using the photoelectric effect by considering the apparatus consists of the metal plate on which the light is incident and the collector plate on which the electrons get collected. These two plates are connected to the electric circuit consists of battery, photodiode with amplifier and the voltmeter with reverse voltage.
When the light incident on the metal plate having one or more half filled orbital; one does not observed the collection of electrons on the collector plate. But as the energy increases the electrons starting collecting on the collector plate. This proves the given hypothesis.
(b)
Explanation:
The apparatus to study the photoelectric effect has the following parts,
- A photodiode with an amplifier.
- A digital voltmeter with reverse voltage.
- Batteries to operate amplifier and to provide reverse voltage.
- A monochromatic light source.
- The incident light beam intensity must adjust using a neutral filter.
The apparatus for testing the given hypothesis is shown below:
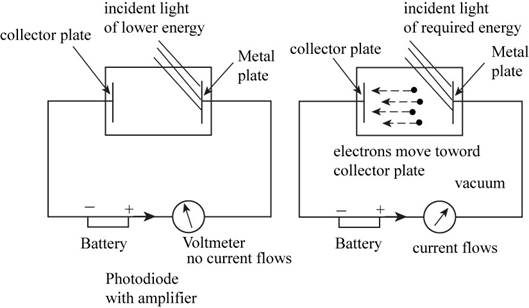
Figure 1
(c)
Explanation:
The data of frequency and wave length of different light source is collected and it is used in the apparatus of photoelectric effect. The different percentage transmission values as the function of intensity will be observed. The plot of stopping potential as a function of frequency will be observed from this data which conclude whether the hypothesis is correct or not.
(d)
Explanation:
The given hypothesis says that more energy is required to eject the electron form a metal having half filled orbitals as compared to those who have not. But the orbital of lanthanides and actinides are diffused in nature and they are larger in size. Therefore, they can easily accept and eject electrons by using lower energy radiation. Therefore, the given hypothesis cannot be tested on the lanthanides and actinides.
- The ejection of electrons is tested by using the apparatus consists of metal plate and collector plate.
- The experimental apparatus to study the photoelectric effect consists of the metal plate, collector plate, battery and voltmeter.
- The plot of stopping potential as a function of frequency is used to conclude that the given hypothesis is correct.
- The given hypothesis is not applicable on lanthanides and actinides because of the presence of d and f orbitals.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
CHEMISTRY: THE CENTRAL SCIENCE
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- The table shows the tensile stress-strain values obtained for various hypothetical metals. Based on this, indicate which is the most brittle and which is the most tough (or most resistant). Breaking strength Elastic modulus Material Yield strength Tensile strength Breaking strain A (MPa) 415 (MPa) (MPa) (GPa) 550 0.15 500 310 B 700 850 0.15 720 300 C Non-effluence fracture 650 350arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardMaterials. The following terms are synonyms: tension, effort and stress.arrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardThe table shows the tensile stress-strain values obtained for various hypothetical metals. Based on this, indicate which material will be the most ductile and which the most brittle. Material Yield strength Tensile strength Breaking strain Breaking strength Elastic modulus (MPa) (MPa) (MPa) (GPa) A 310 340 0.23 265 210 B 100 120 0.40 105 150 с 415 550 0.15 500 310 D 700 850 0.14 720 210 E - Non-effluence fracture 650 350arrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardConsider the following Figure 2 and two atoms that are initially an infinite distance apart, x =00, at which point the potential energy of the system is U = 0. If they are brought together to x = x, the potential energy is related to the total force P by dU dx = P Given this, qualitatively sketch the variation of U with x. What happens at x=x? What is the significance of x = x, in terms of the potential energy? 0 P, Force 19 Attraction Total Repulsion x, Distance Figure 2. Variation with distance of the attractive, repulsive, and total forces between atoms. The slope dP/dx at the equilibrium spacing xe is proportional to the elastic modulus E; the stress σb, corresponding to the peak in total force, is the theoretical cohesive strength.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





