
Concept explainers
Find the area under the standard
a. Between 0 and 1.50
b. Between 0 and −1.25
c. Between 1.56 and 1.96
d. Between −1.20 and −2.25
e. Between −0.06 and 0.73
f. Between 1.10 and −1.80
g. To the right of z = 1.75
h. To the right of z = −1.28
i. To the left of z = −2.12
j. To the left of z = 1.36
(a)
To find: The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
Answer to Problem 18CQ
The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software procedure:
Use Minitab; find the area under the normal curve between 0 and 1.50 with the help of following instructions:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter the Mean as 0.0 and Standard deviation as 1.0.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Click the picture for Middle.
- Type in the smaller value 0 for X value1 and then the larger value 1.50 for the X value2.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
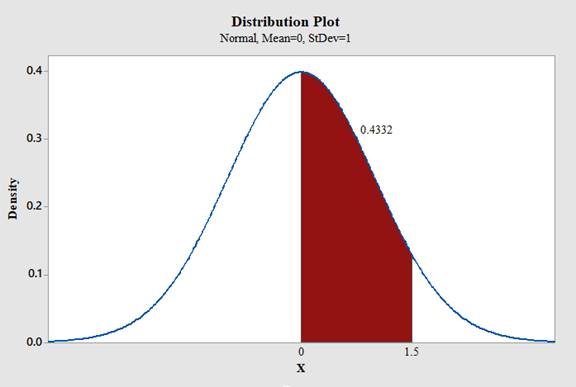
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
(b)
To find: The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
–1.25. That is,
Answer to Problem 18CQ
The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software procedure:
Use Minitab; find the area under the normal curve between 0 and -1.25 with the help of following instructions:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter the Mean as 0.0 and Standard deviation as 1.0.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Click the picture for Middle.
- Type in the smaller value -1.25 for X value1 and then the larger value 0 for the X value2.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
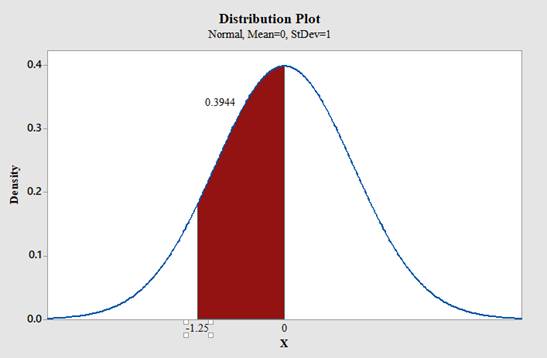
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
(c)
To find: The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
Answer to Problem 18CQ
The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software procedure:
Use Minitab; find the area under the normal curve between 1.56 and 1.96 with the help of following instructions:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter the Mean as 0.0 and Standard deviation as 1.0.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Click the picture for Middle.
- Type in the smaller value 1.56 for X value1 and then the larger value 1.96 for the X value2.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
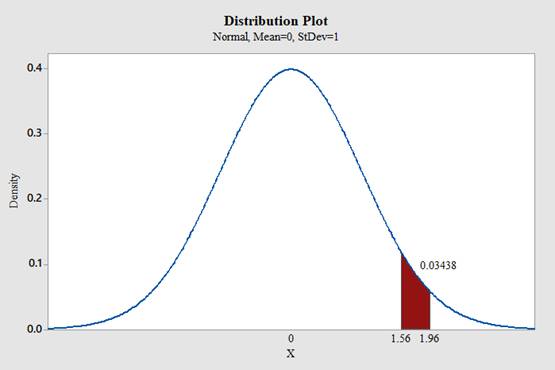 .
.
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
(d)
To find: The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
Answer to Problem 18CQ
The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software procedure:
Use Minitab; find the area under the normal curve between -1.20 and -2.25 with the help of following instructions:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter the Mean as 0.0 and Standard deviation as 1.0.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Click the picture for Middle.
- Type in the smaller value -2.25 for X value1 and then the larger value -1.20 for the X value2.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
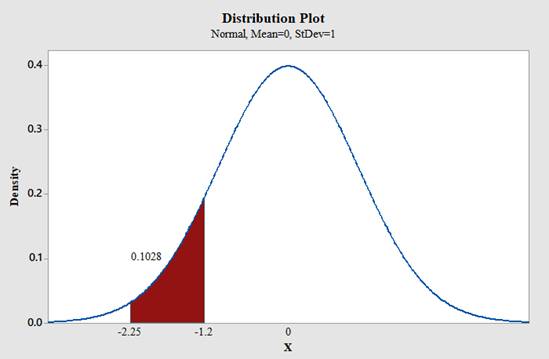
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
(e)
To find: The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
Answer to Problem 18CQ
The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software procedure:
Use Minitab; find the area under the normal curve between -0.06 and 0.73 with the help of following instructions:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter the Mean as 0.0 and Standard deviation as 1.0.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Click the picture for Middle.
- Type in the smaller value -0.06 for X value1 and then the larger value 0.73 for the X value2.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
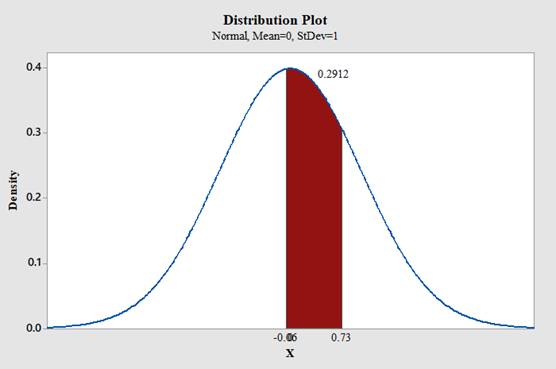 .
.
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
(f)
To find: The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
Answer to Problem 18CQ
The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software procedure:
Use Minitab; find the area under the normal curve between 1.10 and -1.80 with the help of following instructions:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter the Mean as 0.0 and Standard deviation as 1.0.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Click the picture for Middle.
- Type in the smaller value -1.80 for X value1 and then the larger value 1.10 for the X value2.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
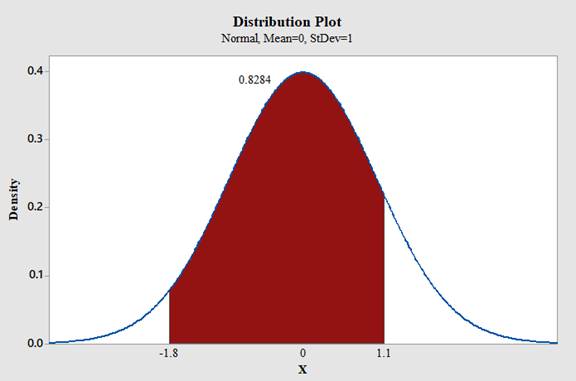
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The area under the standard normal distribution curve for
(g)
To find: The area under the standard normal curve to the right of
Answer to Problem 18CQ
The area under the standard normal curve to the right of
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software procedure:
Use Minitab; find the area under the normal curve to the right of 1.75 with the help of following instructions:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter the Mean as 0.0 and Standard deviation as 1.0.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Click the picture for Right Trail.
- Type in the Z value of 1.75 and click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
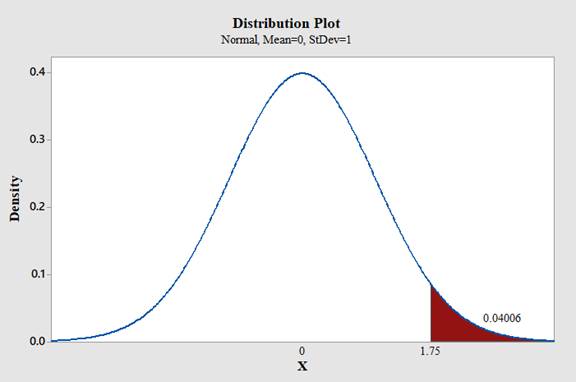
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The area under the standard normal curve to the right of
(h)
To find: The area under the standard normal curve to the right of
Answer to Problem 18CQ
The area under the standard normal curve to the right of
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software procedure:
Use Minitab; find the area under the normal curve to the right of -1.28 with the help of following instructions:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter the Mean as 0.0 and Standard deviation as 1.0.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Click the picture for Right Trail.
- Type in the Z value of -1.28 and click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
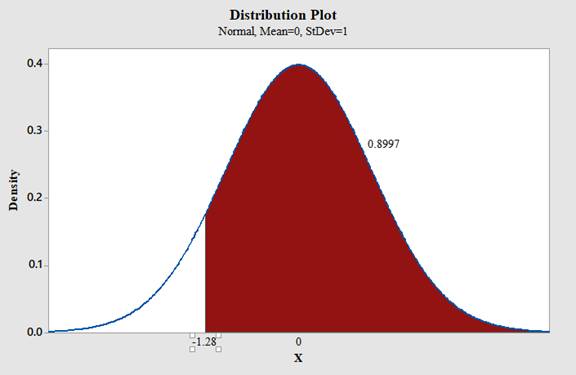
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The area under the standard normal curve to the right of
(i)
To find: The area under the standard normal curve to the left of
Answer to Problem 18CQ
The area under the standard normal curve to the left of
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software procedure:
Use Minitab; find the area under the normal curve to the left of -2.12 with the help of following instructions:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter the Mean as 0.0 and Standard deviation as 1.0.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Click the picture for Left Trail.
- Type in the Z value of -2.12 and click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
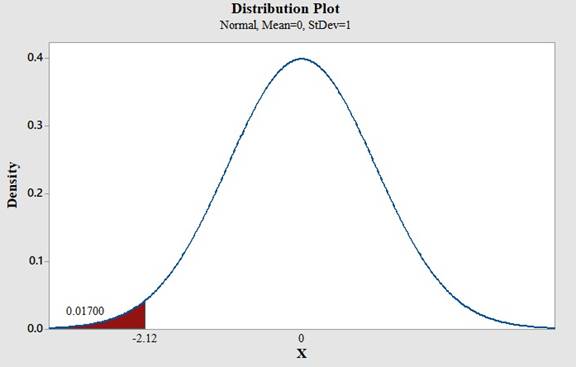
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The area under the standard normal curve to the left of
(j)
To find: The area under the standard normal curve to the left of
Answer to Problem 18CQ
The area under the standard normal curve to the left of
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software procedure:
Use Minitab; find the area under the normal curve to the left of 1.36 with the help of following instructions:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter the Mean as 0.0 and Standard deviation as 1.0.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Click the picture for Left Trail.
- Type in the Z value of 1.36 and click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
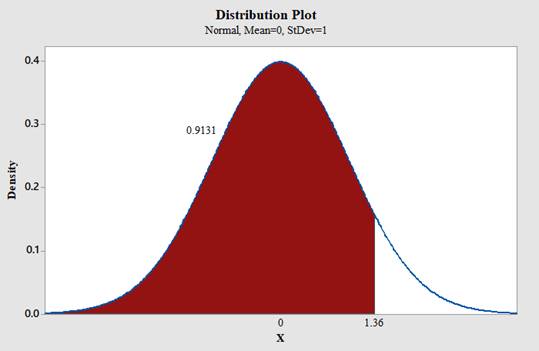
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The area under the standard normal curve to the left of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Elementary Statistics: A Step By Step Approach
- step by step on Microssoft on how to put this in excel and the answers please Find binomial probability if: x = 8, n = 10, p = 0.7 x= 3, n=5, p = 0.3 x = 4, n=7, p = 0.6 Quality Control: A factory produces light bulbs with a 2% defect rate. If a random sample of 20 bulbs is tested, what is the probability that exactly 2 bulbs are defective? (hint: p=2% or 0.02; x =2, n=20; use the same logic for the following problems) Marketing Campaign: A marketing company sends out 1,000 promotional emails. The probability of any email being opened is 0.15. What is the probability that exactly 150 emails will be opened? (hint: total emails or n=1000, x =150) Customer Satisfaction: A survey shows that 70% of customers are satisfied with a new product. Out of 10 randomly selected customers, what is the probability that at least 8 are satisfied? (hint: One of the keyword in this question is “at least 8”, it is not “exactly 8”, the correct formula for this should be = 1- (binom.dist(7, 10, 0.7,…arrow_forwardKate, Luke, Mary and Nancy are sharing a cake. The cake had previously been divided into four slices (s1, s2, s3 and s4). What is an example of fair division of the cake S1 S2 S3 S4 Kate $4.00 $6.00 $6.00 $4.00 Luke $5.30 $5.00 $5.25 $5.45 Mary $4.25 $4.50 $3.50 $3.75 Nancy $6.00 $4.00 $4.00 $6.00arrow_forwardFaye cuts the sandwich in two fair shares to her. What is the first half s1arrow_forward
- Question 2. An American option on a stock has payoff given by F = f(St) when it is exercised at time t. We know that the function f is convex. A person claims that because of convexity, it is optimal to exercise at expiration T. Do you agree with them?arrow_forwardQuestion 4. We consider a CRR model with So == 5 and up and down factors u = 1.03 and d = 0.96. We consider the interest rate r = 4% (over one period). Is this a suitable CRR model? (Explain your answer.)arrow_forwardQuestion 3. We want to price a put option with strike price K and expiration T. Two financial advisors estimate the parameters with two different statistical methods: they obtain the same return rate μ, the same volatility σ, but the first advisor has interest r₁ and the second advisor has interest rate r2 (r1>r2). They both use a CRR model with the same number of periods to price the option. Which advisor will get the larger price? (Explain your answer.)arrow_forward
- Question 5. We consider a put option with strike price K and expiration T. This option is priced using a 1-period CRR model. We consider r > 0, and σ > 0 very large. What is the approximate price of the option? In other words, what is the limit of the price of the option as σ∞. (Briefly justify your answer.)arrow_forwardQuestion 6. You collect daily data for the stock of a company Z over the past 4 months (i.e. 80 days) and calculate the log-returns (yk)/(-1. You want to build a CRR model for the evolution of the stock. The expected value and standard deviation of the log-returns are y = 0.06 and Sy 0.1. The money market interest rate is r = 0.04. Determine the risk-neutral probability of the model.arrow_forwardSeveral markets (Japan, Switzerland) introduced negative interest rates on their money market. In this problem, we will consider an annual interest rate r < 0. We consider a stock modeled by an N-period CRR model where each period is 1 year (At = 1) and the up and down factors are u and d. (a) We consider an American put option with strike price K and expiration T. Prove that if <0, the optimal strategy is to wait until expiration T to exercise.arrow_forward
- We consider an N-period CRR model where each period is 1 year (At = 1), the up factor is u = 0.1, the down factor is d = e−0.3 and r = 0. We remind you that in the CRR model, the stock price at time tn is modeled (under P) by Sta = So exp (μtn + σ√AtZn), where (Zn) is a simple symmetric random walk. (a) Find the parameters μ and σ for the CRR model described above. (b) Find P Ste So 55/50 € > 1). StN (c) Find lim P 804-N (d) Determine q. (You can use e- 1 x.) Ste (e) Find Q So (f) Find lim Q 004-N StN Soarrow_forwardIn this problem, we consider a 3-period stock market model with evolution given in Fig. 1 below. Each period corresponds to one year. The interest rate is r = 0%. 16 22 28 12 16 12 8 4 2 time Figure 1: Stock evolution for Problem 1. (a) A colleague notices that in the model above, a movement up-down leads to the same value as a movement down-up. He concludes that the model is a CRR model. Is your colleague correct? (Explain your answer.) (b) We consider a European put with strike price K = 10 and expiration T = 3 years. Find the price of this option at time 0. Provide the replicating portfolio for the first period. (c) In addition to the call above, we also consider a European call with strike price K = 10 and expiration T = 3 years. Which one has the highest price? (It is not necessary to provide the price of the call.) (d) We now assume a yearly interest rate r = 25%. We consider a Bermudan put option with strike price K = 10. It works like a standard put, but you can exercise it…arrow_forwardIn this problem, we consider a 2-period stock market model with evolution given in Fig. 1 below. Each period corresponds to one year (At = 1). The yearly interest rate is r = 1/3 = 33%. This model is a CRR model. 25 15 9 10 6 4 time Figure 1: Stock evolution for Problem 1. (a) Find the values of up and down factors u and d, and the risk-neutral probability q. (b) We consider a European put with strike price K the price of this option at time 0. == 16 and expiration T = 2 years. Find (c) Provide the number of shares of stock that the replicating portfolio contains at each pos- sible position. (d) You find this option available on the market for $2. What do you do? (Short answer.) (e) We consider an American put with strike price K = 16 and expiration T = 2 years. Find the price of this option at time 0 and describe the optimal exercising strategy. (f) We consider an American call with strike price K ○ = 16 and expiration T = 2 years. Find the price of this option at time 0 and describe…arrow_forward
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
