
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure is also known as Lewis dot diagrams or electron dot structures. The bond between atoms and lone pairs of electrons that is present in the molecule. Lewis structure represents each atom and their position in structure using the chemical symbol. Excess electrons forms the lone pair are given by pair of dots, and are located next to the atom.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Oxygen is in Group 6A and Chlorine is in Group 7A and the valence electrons present in the
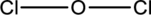
The two chlorine atoms connect with one Oxygen atom through single bonds.
Chlorine atoms attain octet by adding six electrons as dots in pairs.
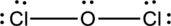
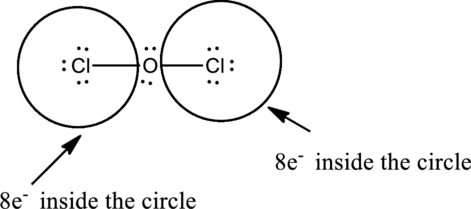
Complete the octet of the two chlorine atom uses
Put the last six electrons on Oxygen atom.
The correct Lewis structure of the
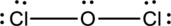
Oxygen has eight electrons four in the bonds and four as dots, hence the structure is complete.
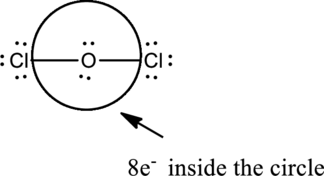
Hence, the total number of electrons can be counted as
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Hydrogen atom is from Group one A and Oxygen atom is from group 6A, hence the valence electrons are
Complete the octet of the two chlorine atom uses
The incomplete Lewis structure of
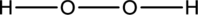
The correct Lewis structure of the

Hence, the total number of electrons can be counted as
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The four Hydrogen atoms connect to boron with single bonds uses eight electrons. Boron atom is the central atom with the hydrogen atoms around it. So, the valence electron present in the
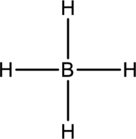
Boron atom must be the central atom with the four Hydrogen atoms bonded to it. Boron has eight electrons so, the structure is complete. Boron has eight electrons, and each Hydrogen atom has just two electrons, the structure clockwise, the total number of electrons can be counted
The correct Lewis structure of the
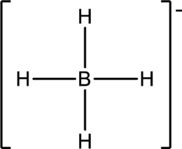
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The four Hydrogen atoms connect to Phosphorous with single bonds uses eight electrons. Phosphorous atom is the central atom with the hydrogen atoms around it. So, the valence electrons present in the
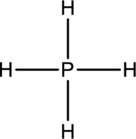
Phosphorous atom must be the central atom with the four Hydrogen atoms bonded to it. Phosphorous has eight electrons so, the structure is complete. It has eight electrons, and each Hydrogen atom has just two electrons, the structure clockwise, the total number of electrons can be counted
The structure is a
The correct Lewis structure of the
(e)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The five chlorine atoms connect to Phosphorous with single bonds uses ten electrons. Phosphorous atom is the central atom with the Chlorine atoms around it.
The number of valence electrons present in
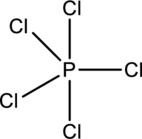
Chlorine atoms prefer making only one bond, and Phosphorous prefers to make three and five bonds. So use Phosphorous atom as central atom with the five Chlorine atoms around it.
Each Chlorine atom has three lone pair and one bond pair so it attains octet.
The correct Lewis structure of the
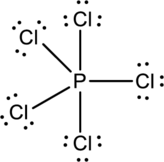
The total number of electrons can be counted as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
OWLV2 FOR MOORE/STANITSKI'S CHEMISTRY:
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
- What would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forwardFor benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forward
- The reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
