
To determine: The bond’s price at different periods
Introduction:
A bond refers to the debt securities issued by the governments or corporations for raising capital. The borrower does not return the face value until maturity. However, the investor receives the coupons every year until the date of maturity.
Answer to Problem 15QP
The price of the bond at different periods is as follows:
| Time to maturity (Years) | Bond X | Bond Y |
| 13 | $1,167.1529 | $850.2619 |
| 12 | $1,158.8537 | $856.7855 |
| 10 | $1,140.4715 | $871.6468 |
| 5 | $1,082.004 | $922.2068 |
| 1 | $1,018.6915 | $981.6514 |
| 0 | $1,000.0000 | $1,000.0000 |
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Bond X is selling at a premium. The coupon rate of Bond X is 9 percent and its yield to maturity is 7 percent. The bond will mature in 13 years. Bond Y is selling at a discount. The coupon rate of Bond Y is 7 percent and its yield to maturity is 9 percent. The bond will mature in 13 years. Both the bonds make annual coupon payments. Assume that the face value of bonds is $1,000.
The formula to calculate annual coupon payment:
The formula to calculate the bonds’ current price:
Where,
“C” refers to the coupon paid per period
“F” refers to the face value paid at maturity
“r” refers to the yield to maturity
“t” refers to the periods to maturity
Compute the bond price of Bond X at different maturities:
Compute the annual coupon payment of Bond X:
Hence, the annual coupon payment of Bond X is $90.
The bond value or the price of Bond X at present:
The bond pays the coupons annually. The annual coupon payment is $90. However, the bondholder will receive the same in one installment. Hence, annual coupon payment is $90.
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 13 years. As the coupon payment is annual.
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations are annual, the yield to maturity must also be annual.
Hence, the current price of the bond is $1,167.1529.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after one year:
The bond pays the coupons annually. The annual coupon payment is $90. However, the bondholder will receive the same is one installment. Hence, annual coupon payment is $90
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 12 years after one year from now. As the coupon payment is annual, the annual periods to maturity is12 years.
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations is annual, the yield to maturity must also be annual. Hence, the annual yield to maturity is 7 percent.
Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,158.8537 after one year.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after 3 years:
The bond pays the coupons annually. The annual coupon payment is $90. However, the bondholder will receive the same in one installment. Hence, annual coupon payment is $90.
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 10 years after three years from now. As the coupon payment is annual, the annual periods to maturity is 10 years
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations is annual, the yield to maturity is 7 percent.
Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,140.4715 after three years.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after eight years:
The bond pays the coupons annually. The annual coupon payment is $90. However, the bondholder will receive the same is one installment. Hence, annual coupon payment is $90
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 5 years after eight years from now. As the coupon payment is annual, the annual periods to maturity is 5 years.
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations is annual, the yield to maturity is 7 percent
Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,082.004 after eight years.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after twelve years:
The bond pays the coupons annually. The annual coupon payment is $90. However, the bondholder will receive the same is one installment. Hence, annual coupon payment is $90
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 1 years after twelve years from now. As the coupon payment is annual, the annual periods to maturity is 1 years.
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations is annual, the yield to maturity is 7 percent.
Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,018.6915 after twelve years.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after thirteen years:
The thirteenth year is the year of maturity for Bond X. In this year, the bondholder will receive the face value of the bond. Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,000 after thirteen years.
Compute the bond price of Bond Y at different maturities:
Compute the annual coupon payment of Bond Y:
Hence, the annual coupon payment of Bond Y is $70.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y at present:
The bond pays the coupons annually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is one installment. Hence, annual coupon payment is $70.
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 13 years after twelve years from now. As the coupon payment is annual, the annual periods to maturity is 13 years
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 9 percent per year. As the calculations is annual, the yield to maturity is 9 percent.
Hence, the current price of the bond is $850.2619.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after one year:
The bond pays the coupons annually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is one installment. Hence, annual coupon payment is $70.
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 12 years after twelve years from now. As the coupon payment is annual, the annual periods to maturity is 12 years.
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 9 percent per year. As the calculations is annual, the yield to maturity is 9 percent.
Hence, the price of the bond is $856.7855 after one year.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after three years:
The bond pays the coupons annually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is one installment. Hence, annual coupon payment is $70.
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 10 years after twelve years from now. As the coupon payment is annual, the annual periods to maturity is 10 years.
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 9 percent per year. As the calculations is annual, the yield to maturity is 9 percent.
Hence, the price of the bond is $871.6468 after three years.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after eight years:
The bond pays the coupons annually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is one installment. Hence, annual coupon payment is $70.
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 5 years after twelve years from now. As the coupon payment is annual, the annual periods to maturity is 5 years.
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 9 percent per year. As the calculations is annual, the yield to maturity is 9 percent.
Hence, the price of the bond is $922.2068 after eight years.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after twelve years:
The bond pays the coupons annually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is one installment. Hence, annual coupon payment is $70.
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 5 years after twelve years from now. As the coupon payment is annual, the annual periods to maturity is 5 years.
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 9 percent per year. As the calculations is annual, the yield to maturity is 9 percent.
Hence, the price of the bond is $981.6514 after twelve years.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after thirteen years:
The thirteenth year is the year of maturity for Bond Y. In this year, the bondholder will receive the face value of the bond. Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,000 after thirteen years.
Table indicating the bond prices of Bond X and Bond Y at different maturities:
Table 1
| Time to maturity (Years) | Bond X | Bond Y |
| 13 | $1,167.1529 | $850.2619 |
| 12 | $1,158.8536 | $856.7855 |
| 10 | $1,140.4715 | $871.6468 |
| 5 | $1,082.004 | $922.2068 |
| 1 | $1,018.6915 | $981.6514 |
| 0 | $1,000.0000 | $1,000.0000 |
Graphical representation of the bond prices of Bond X and Bond Y from Table 1:
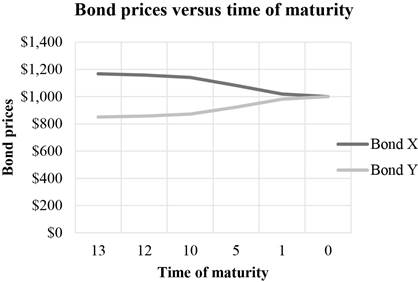
Explanation of the graph:
The graph indicates a “pull to par” effect on the prices of the bonds. The face value of both the bonds is $1,000. Although Bond X is at a premium and Bond Y is at a discount, both the bonds will reach their par values at the time of maturity. The effect of reaching the face value or par value from a discount or premium is known as “pull to par”.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essentials of Corporate Finance
- . If a stock pays an annual dividend of $3 and the required rate of return is 10%, what is its value using the dividend discount model? A) $30B) $25C) $33D) $300arrow_forward7. Calculate the present value of $1,000 received in 3 years at 8% discount rate. need a ai ...??arrow_forward6. If sales are $100,000 and net income is $20,000, what is the profit margin? need a helpful..???arrow_forward
- 5. Calculate WACC for a company with 50% debt (cost 6%) and 50% equity (cost 10%). Need a helpfully...???arrow_forward2. A bond pays $50 annual interest with a face value of $1,000. What is the coupon rate? need a helfuarrow_forward3. If EPS is $5 and the stock price is $50, what is the P/E ratio? Need a helpful..?????arrow_forward
- 1. Calculate the future value of $1,000 invested at 5% interest for 2 years. no gpt ..???arrow_forward4. A savings account earns an annual interest rate of 2%. If you deposit $1,000, how much interest will you earn in one year? correct solution????arrow_forward1. If a stock's current price is $50 and it increases by 10%, what is the new price? Need a helpful..???arrow_forward
- 2. A bond has a face value of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 5%. What is the annual interest payment? need a helpful????arrow_forward4. A savings account earns an annual interest rate of 2%. If you deposit $1,000, how much interest will you earn in one year? step by step solution???arrow_forward5. If a stock's dividend yield is 4% and the stock price is $50, what is the annual dividend payment per share? no gpt???arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





