
Concept explainers
(a)
The minimum possible speed of the bob if the bob is at the top of the circle.
(a)
Answer to Problem 141P
The minimum possible speed of the bob if the bob is at the top of the circle is
Explanation of Solution
The bob as a particle in uniform circular motion, it exerts a centripetal acceleration towards the peg.
The free body diagram of the bob at the top of the circle is shown in the Figure 1.
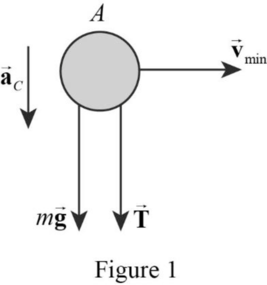
From the free body diagram, write the expression for net force in the vertical direction.
Here,
The minimum speed of the bob occurs corresponds to a tension of zero in the cord.
Substitute,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the minimum possible speed of the bob if the bob is at the top of the circle is
(b)
The distance from a point B moved by the bob if the string breaks at point A.
(b)
Answer to Problem 141P
The distance from a point B moved by the bob if the string breaks at point A is
Explanation of Solution
Let C be the point at the same height as B reached by the bob when the string breaks. Assume the bob is in the x direction and moving with constant acceleration.
Consider the Figure 2.
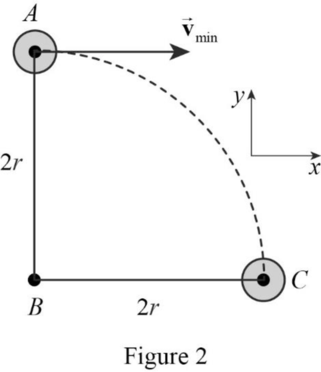
Write the expression for distance in the x-direction
Here,
Substitute,
Write the expression for distance in the y-direction
Here,
Substitute,
Use equation (VI) in (IV).
Conclusion:
Therefore, the distance from a point B moved by the bob if the string breaks at point A is
(c)
The minimum value of
(c)
Answer to Problem 141P
The minimum value of
Explanation of Solution
The system of the bob and Earth as an isolated system for energy with no non conservative forces acting, then the total energy is zero.
Here,
Use
Here,
Substitute,
Since
Conclusion:
Therefore, the minimum value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS-CONNECT ACCESS
- Please help, everytime I try to input the data only one point shows on the graph. Graph of centripetal force, Fc, versus V E2 from Activity 1. Include a line of best fit and record the equation of the line.arrow_forwardBased on your graph, explain how centripetal force is affected when the hanging mass changes. Does your graph verify the relationship in the equation r = x^i + y^j = r cos ωt I + r sin ωt^j?arrow_forwardDid your experiment results in Data Table 3 verify, to within a reasonable experimental error, the condition of equilibrium of Equation 6: Στanti-clockwise = Στclockwise? Support your response with experimental data. My data shows that they are not equal to each other. So what does this mean? Thanks!arrow_forward
- Please help, everytime I try to input the data only one point shows on the graph. Graph of centripetal force, Fc, versus V E2 from Activity 1. Include a line of best fit and record the equation of the line.arrow_forwardExplain how your experiment met the condition for equilibrium in Equation 4: ΣFvertical = ΣFy = 0.arrow_forwardCan i get answer and solution for this question and can you teach me What we use to get the answer.arrow_forward
- Can i get answer and solution and can you teach me how to get it.arrow_forwardConsider a image that is located 30 cm in front of a lens. It forms an upright image 7.5 cm from the lens. Theillumination is so bright that that a faint inverted image, due to reflection off the front of the lens, is observedat 6.0 cm on the incident side of the lens. The lens is then turned around. Then it is observed that the faint,inverted image is now 10 cm on the incident side of the lens.What is the index of refraction of the lens?arrow_forward2. In class, we discussed several different flow scenarios for which we can make enough assumptions to simplify the Navier-Stokes equations enough to solve them and obtain an exact solution. Consulting the cylindrical form of the Navier-Stokes equations copied below, please answer the following questions. др a 1 a + +0x- + +O₂ = Pgr + μl 18²v, 2 ave ²v₁] az2 + at or r de r Əz dr ar Vodvz др [18 + + +Or + +Vz = Pgz +fl at ar r 20 ôz ôz dr ave дов V,Ve ave +Or + + = pge at dr r 80 Əz + az2 a.) In class, we discussed how the Navier-Stokes equations are an embodiment of Newton's 2nd law, F = ma (where bolded terms are vectors). Name the 3 forces that we are considering in our analysis of fluid flow for this class. др a 10 1 ve 2 av 2200] + +μ or 42 30 b.) If we make the assumption that flow is "fully developed" in the z direction, which term(s) would go to zero? Write the term below, describe what the term means in simple language (i.e. do not simply state "it is the derivative of a with…arrow_forward
- 1. Consult the form of the x-direction Navier-Stokes equation below that we discussed in class. (For this problem, only the x direction equation is shown for simplicity). Note that the equation provided is for a Cartesian coordinate system. In the spaces below, indicate which of the following assumptions would allow you to eliminate a term from the equation. If one of the assumptions provided would not allow you to eliminate a particular term, write "none" in the space provided. du ди at ( + + + 매일) du ди = - Pgx dy др dx ²u Fu u + fl + ax2 ay² az2 - дх - Əz 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Assumption Flow is in the horizontal direction (e.g. patient lying on hospital bed) Flow is unidirectional in the x-direction Steady flow We consider the flow to be between two flat, infinitely wide plates There is no pressure gradient Flow is axisymmetric Term(s) in equationarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardwhy did the expert subtract the force exerted by the hand and the elbow by the force due to the weight of the hand and forearm and force exerted by the tricep. Does the order matter and how do you determine what to put first. Question 4 AP, CHAPTER 13 FROM BASIC BIOMECHANICS 8TH EDITIONarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





