
a.
To define:The variables to represent the cost of a taco and the cost of a burrito.
a.
Answer to Problem 13MCQ
The algebraic quantities x and y are variables that represent cost of one taco and cost of one burrito respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
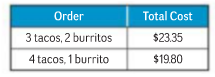
The cost of two orders at a restaurant is shown in table given below.
Concept used:
The variables are independent quantities.
Definition:
Suppose the cost of one taco is x and cost of one burrito is y.The algebraic quantities x and y are variables.
b.
To write:A system of equations to find the cost of a single taco and a single burrito.
b.
Answer to Problem 13MCQ
A system of equations to find the cost of a single taco and a single burrito is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The data table in part (a)
Concept used:
According to the given conditions we connect the variables and given quantities.
Calculations:
Conclusion:
In order-1, the total cost of 3 tacos and 2 burritos is $23.35. The cost of one taco is x and that of burrito is y. So cost of 3 tacos is $3xand of 2 burritos is $2y.Therefore, the equation that connect the variable and given quantities is
In order-2, the total cost of 4 tacos and 1burritos is $19.80. The cost of one taco is x and that of burrito is y. So cost of 3 tacos is $4xand of 2 burritos is $y.Therefore, the equation that connect the variable and given quantities is
Conclusion:
A system of equations to find the cost of a single taco and a single burrito is
c.
To solve:The system of equations in obtained in part (a).
c.
Answer to Problem 13MCQ
The solution of system of equations is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given system of equations is
Method used:
We solve equations using graphing calculator.
Graph:
The graph of given system of equations
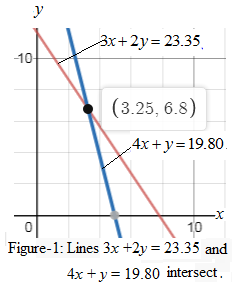
We see that lines
The solution means that cost of one taco is $ 3.35 and the cost of one burrito is $6.80.
Conclusion:
The solution of system of equations is
d.
To find:The amount to be paid by a customer to buy 2 taco and 2 burrito.
d.
Answer to Problem 13MCQ
The amount to be paid by a customer to buy 2 taco and 2 burrito is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The cost of one taco is $ 3.35 and the cost of one burrito is $6.80.
Formula used:
Cost of n items C = n× cost of one item.
Calculations:
The amount paid by customer to buy 2 tacos
The amount paid by customer to buy 2burritos
Therefore, the amount to be paid by a customer to buy 2 taco and 2 burrito is
Conclusion:
The amount to be paid by a customer to buy 2 taco and 2 burrito is
Chapter 6 Solutions
Algebra 1
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
- Using f(x) = log x, what is the x-intercept of g(x) = log (x + 4)? Explain your reasoning. Please type out answerarrow_forwardThe function f(x) = log x is transformed to produce g(x) = log (x) – 3. Identify the type of transformation and describe the change. Please type out answerarrow_forwardEach graph below is the graph of a system of three linear equations in three unknowns of the form Ax = b. Determine whether each system has a solution and, if it does, the number of free variables. A. O free variables ✓ B. no solution C. no solution D. no solution E. 1 free variable F. 1 free variablearrow_forward
- Solve the following systems of equations and show all work.y = x2 + 3y = x + 5 Please type out answerarrow_forwardSolve the following system of equations. Show all work and solutions.y = 2x2 + 6x + 1y = −4x2 + 1 Please type out answerarrow_forwardDalia buys 20 collectible gems per month. Grace sells 10 gems from her collection of 120 each month. When will Dalia have more gems than Grace? Show your work. Dear Student If You Face any issue let me know i will solve your all doubt. I will provide solution again in more detail systematic and organized way. I would also like my last 3 questions credited to mearrow_forward
- Dalia buys 20 collectible gems per month. Grace sells 10 gems from her collection of 120 each month. When will Dalia have more gems than Grace? Show your work.arrow_forwardSolve the following system of equations. Show all work and solutions.y = 2x2 + 6x + 1y = −4x2 + 1arrow_forwardSolve the following systems of equations and show all work.y = x2 + 3y = x + 5arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





