
Mechanics Of Materials, Si Edition
9th Edition
ISBN: 9789810694364
Author: Russell C Hibbeler
Publisher: Pearson Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.4, Problem 5.59P
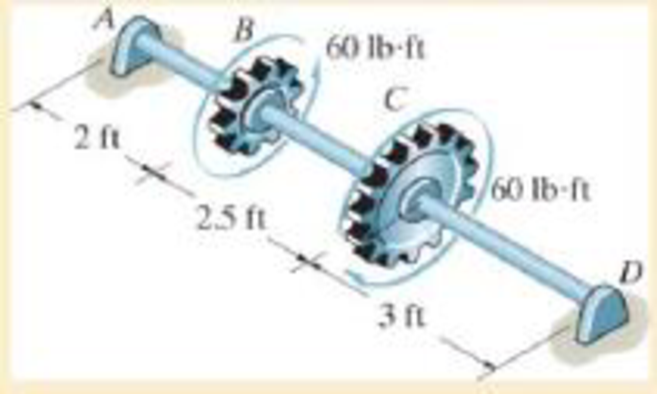
It has a diameter of 1 in. and is supported by bearings at A and D, which allow free rotation. Determine the angle of twist of B with respect to D.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
this is an old practice exam, the answer is Ax = -4, Ay = -12,Az = 32.5, Bx= 34, Bz = 5, By = 0 but how?
This is an old practice exam, the answer is Ax = Az = 0, Ay = 2000, TDE = 4750, Cx = 2000, Cy = 2000, Cz = -800 but how?
this is an old practice exam, the answer is Fmin = 290.5lb but how
Chapter 5 Solutions
Mechanics Of Materials, Si Edition
Ch. 5.3 - Determine the internal torque at each section and...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the. internal torque at each section and...Ch. 5.3 - The solid and hollow shafts are each subjected to...Ch. 5.3 - The motor delivers 10 hp to the shaft. If it...Ch. 5.3 - The solid circular shaft is subjected to an...Ch. 5.3 - The hollow circular shaft is subjected to an...Ch. 5.3 - The shaft is hollow from A to B and solid from B...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the maximum shear stress in the...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the maximum shear stress in the shaft at...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the shear stress a: point A on the...
Ch. 5.3 - The solid 50-mm-diameter shaft is subjected to the...Ch. 5.3 - The gear motor can develop 3 hp when it turns at...Ch. 5.3 - The solid shaft of radius r is subjected to a...Ch. 5.3 - The solid shaft of radius r is subjected to a...Ch. 5.3 - 5-3. The solid shaft is fixed to the support at C...Ch. 5.3 - The copper pipe has an outer diameter of 40 mm and...Ch. 5.3 - The copper pipe has an outer diameter of 2.50 in....Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.6PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.7PCh. 5.3 - The solid 30-mm-diameter shaft is used to transmit...Ch. 5.3 - The solid shaft is fixed to the support at C and...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.10PCh. 5.3 - The assembly consists of two sections of...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.12PCh. 5.3 - 5-13. If The tubular shaft is made from material...Ch. 5.3 - A steel tube having an outer diameter of 2.5 in....Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.15PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.16PCh. 5.3 - The rod has a diameter of 1 in. and a weight of 10...Ch. 5.3 - The rod has a diameter of 1 in. and a weight of 15...Ch. 5.3 - 5-19. The shaft consists of solid 80-mm-diameter...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.20PCh. 5.3 - 5-21. If the 40-mm-diameter rod is subjected to a...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.22PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.23PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.24PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.25PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.26PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.27PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.28PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.29PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.30PCh. 5.3 - The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm...Ch. 5.3 - The pump operates using the motor that has a power...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.33PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.34PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.35PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.36PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.37PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.38PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.39PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.40PCh. 5.3 - The A-36 steel tubular shaft is 2 m long and has...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.42PCh. 5.3 - The solid shaft has a linear taper from rA at one...Ch. 5.3 - *5-44. The rod has a diameter of 0.5 in. and...Ch. 5.3 - 5-45. Solve Prob. 5-44 for the maximum torsional...Ch. 5.3 - A motor delivers 500 hp to the shaft, which is...Ch. 5.4 - The 60 mm-diameter steel shaft is subjected to the...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.10FPCh. 5.4 - The hollow 6061-T6 aluminum shaft has an outer and...Ch. 5.4 - A series of gears are mounted on the...Ch. 5.4 - The 80-mm-diameter shaft is made of steel. If it...Ch. 5.4 - The 80-mm-diameter shaft is made of steel. If it...Ch. 5.4 - The propellers of a ship are connected to an A-36...Ch. 5.4 - Show that the maximum shear strain in the shaft is...Ch. 5.4 - 5-49. The A-36 steel axle is made from tubes AB...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.50PCh. 5.4 - Determine the maximum allowable torque T. Also,...Ch. 5.4 - If the allowable shear stress is allow = 80 MPa,...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.53PCh. 5.4 - If gear B supplies 15 kW of power, while gears A,...Ch. 5.4 - If the shaft is made of steel with the allowable...Ch. 5.4 - *5-56. The A-36 steel axle is made from tubes AB...Ch. 5.4 - If the rotation of the 100-mm-diameter A-36 steel...Ch. 5.4 - If the rotation of the 100-mm-diameter A-36 steel...Ch. 5.4 - It has a diameter of 1 in. and is supported by...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.60PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.61PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.62PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.63PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.64PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.65PCh. 5.4 - When it is rotating at 80 rad/s. it transmits 32...Ch. 5.4 - It is required to transmit 35 kW of power from the...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.68PCh. 5.4 - If a torque of T = 50 N m is applied to the bolt...Ch. 5.4 - If a torque of T= 50N m is applied to the bolt...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.72PCh. 5.4 - If the shaft is subjected to a torque T at its...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.74PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.75PCh. 5.4 - *5-76. A cylindrical spring consists of a rubber...Ch. 5.5 - Gst = 75 GPa.Ch. 5.5 - The A992 steel shaft has a diameter of 60 mm and...Ch. 5.5 - If the shaft is fixed at its ends A and B and...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 5.80PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 5.81PCh. 5.5 - 5-82. The shaft is made from a solid steel section...Ch. 5.5 - 5-83. The motor A develops a torque at gear B of...Ch. 5.5 - If the allowable shear stresses for the magnesium...Ch. 5.5 - If a torque of T = 5 kNm is applied to end A,...Ch. 5.5 - Each has a diameter of 25 mm and they are...Ch. 5.5 - Each has a diameter of 25 mm and they are...Ch. 5.5 - It is fixed at its ends and subjected to a torque...Ch. 5.5 - 5–89. Determine the absolute maximum shear stress...Ch. 5.5 - The shaft is subjected to a torque of 800 lbft....Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 5.91PCh. 5.5 - The shaft is made of 2014-T6 aluminum alloy and is...Ch. 5.5 - The tapered shaft is confined by the fixed...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the reactions at the fixed supports A...Ch. 5.7 - 5-95. The aluminum rod has a square cross section...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 5.96PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 5.97PCh. 5.7 - If it is subjected to the torsional loading,...Ch. 5.7 - Solve Prob.5-98 for the maximum shear stress...Ch. 5.7 - determine the maximum shear stress in the shaft....Ch. 5.7 - If the shaft has an equilateral triangle cross...Ch. 5.7 - 5-102. The aluminum strut is fixed between the two...Ch. 5.7 - is applied to the tube If the wall thickness is...Ch. 5.7 - If it is 2 m long, determine the maximum shear...Ch. 5.7 - Also, find the angle of twist of end B. The shaft...Ch. 5.7 - Also, find the corresponding angle of twist at end...Ch. 5.7 - If the solid shaft is made from red brass C83400...Ch. 5.7 - If the solid shaft is made from red brass C83400...Ch. 5.7 - The tube is 0.1 in. thick.Ch. 5.7 - 5-110. For a given maximum average shear stress,...Ch. 5.7 - 5-111. A torque T is applied to two tubes having...Ch. 5.7 - By what percentage is the torsional strength...Ch. 5.7 - 5-113. Determine the constant thickness of the...Ch. 5.7 - 5-114. Determine the torque T that can be applied...Ch. 5.7 - If the allowable shear stress is allow = 8 ksi,...Ch. 5.7 - *5-116. The tube is made of plastic, is 5 mm...Ch. 5.7 - 5–117. The mean dimensions of the cross section of...Ch. 5.7 - 5–118. The mean dimensions of the cross section of...Ch. 5.7 - If it is subjected to a torque of T = 40 Nm....Ch. 5.10 - If the transition between the cross sections has a...Ch. 5.10 - 5–121. The step shaft is to be designed to rotate...Ch. 5.10 - Prob. 5.122PCh. 5.10 - 5–123. The transition at the cross sections of the...Ch. 5.10 - *5–124. The steel used for the step shaft has an...Ch. 5.10 - 5–125. The step shaft is subjected to a torque of...Ch. 5.10 - Determine the radius of the elastic core produced...Ch. 5.10 - Assume that the material becomes fully plastic.Ch. 5.10 - diameter is subjected to a torque of 100 in.kip....Ch. 5.10 - Determine the torque T needed to form an elastic...Ch. 5.10 - Determine the torque applied to the shaft.Ch. 5.10 - 5–131. An 80-mm-diameter solid circular shaft is...Ch. 5.10 - Determine the ratio of the plastic torque Tp to...Ch. 5.10 - 5–133. If the step shaft is elastic-plastic as...Ch. 5.10 - 5–134. The solid shaft is made from an...Ch. 5.10 - 5–135. A 1.5-in.-diameter shaft is made from an...Ch. 5.10 - *5–136. The tubular shaft is made of a...Ch. 5.10 - 5–137. The shaft is made from a strain-hardening...Ch. 5.10 - 5–138. The tube is made of elastic-perfectly...Ch. 5.10 - Determine the torque required to cause a maximum...Ch. 5.10 - *5–140. The 2-m-long tube is made of an...Ch. 5.10 - is made from an elastic perfectly plastic material...Ch. 5.10 - 5–142. The 2-m-long lube is made from an...Ch. 5 - The shaft is made of A992 steel and has an...Ch. 5 - The shaft is made of A992 steel and has an...Ch. 5 - Determine the shear stress at the mean radius p =...Ch. 5 - If the thickness of its 2014-T6-aluminum skin is...Ch. 5 - Determine which shaft geometry will resist the...Ch. 5 - If couple forces P = 3 kip are applied to the...Ch. 5 - If the allowable shear stress for the aluminum is...Ch. 5 - Determine the angle of twist of its end A if it is...Ch. 5 - This motion is caused by the unequal belt tensions...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- This is an exam review question. The answer is Pmin = 622.9 lb but whyarrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardThis is an old practice exam. Fce = 110lb and FBCD = 62 lb but whyarrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 4mm, for w2 h2 = 6mm, and for w3 is h3 =6.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=29 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E100xx). 163 mm S 133 mm 140 mm Please solve the question above I solved the question but I'm sure the answer is wrong the link : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1w5UD2EPDiaKSx3W33aj Rv0olChuXtrQx/view?usp=sharingarrow_forward
- Q2: (15 Marks) A water-LiBr vapor absorption system incorporates a heat exchanger as shown in the figure. The temperatures of the evaporator, the absorber, the condenser, and the generator are 10°C, 25°C, 40°C, and 100°C respectively. The strong liquid leaving the pump is heated to 50°C in the heat exchanger. The refrigerant flow rate through the condenser is 0.12 kg/s. Calculate (i) the heat rejected in the absorber, and (ii) the COP of the cycle. Yo 8 XE-V lo 9 Pc 7 condenser 5 Qgen PG 100 Qabs Pe evaporator PRV 6 PA 10 3 generator heat exchanger 2 pump 185 absorberarrow_forwardQ5:(? Design the duct system of the figure below by using the balanced pressure method. The velocity in the duct attached to the AHU must not exceed 5m/s. The pressure loss for each diffuser is equal to 10Pa. 100CFM 100CFM 100CFM ☑ ☑ 40m AHU -16m- 8m- -12m- 57m 250CFM 40m -14m- 26m 36m ☑ 250CFMarrow_forwardA mass of ideal gas in a closed piston-cylinder system expands from 427 °C and 16 bar following the process law, pv1.36 = Constant (p times v to the power of 1.36 equals to a constant). For the gas, initial : final pressure ratio is 4:1 and the initial gas volume is 0.14 m³. The specific heat of the gas at constant pressure, Cp = 0.987 kJ/kg-K and the specific gas constant, R = 0.267 kJ/kg.K. Determine the change in total internal energy in the gas during the expansion. Enter your numerical answer in the answer box below in KILO JOULES (not in Joules) but do not enter the units. (There is no expected number of decimal points or significant figures).arrow_forward
- my ID# 016948724. Please solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 please find the forces for Fx=0: fy=0: fz=0: please help me to solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 please solve the proble step by step find the forces fx=o: fy=0; fz=0; and find shear moment and the bending moment diagran please draw the diagram for the shear and bending momentarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Solids: Lesson 53 - Slope and Deflection of Beams Intro; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I7lTq68JRmY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY