
Concept explainers
Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
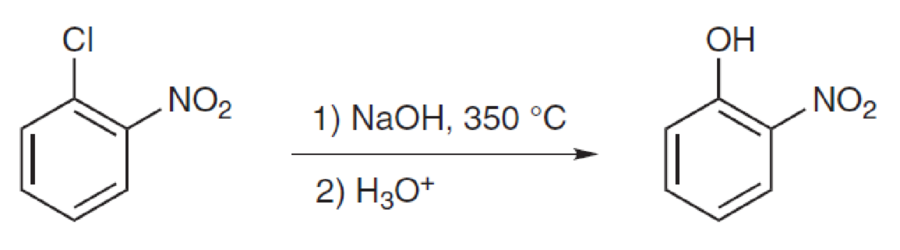
Interpretation:
Mechanism for the given transformation has to be proposed.
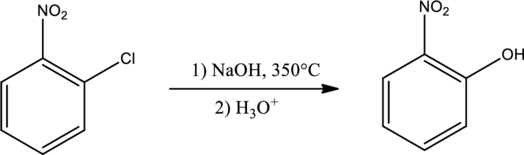
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is,
Mechanism:
Looking into the reaction it is found that the nucleophile is a strong one namely hydroxide and the reactant has all the three important criteria to undergo
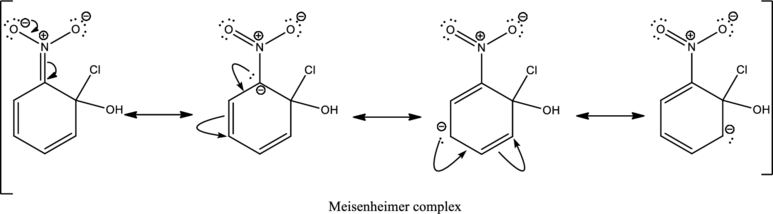
First step is the attack of nucleophile on the carbon atom that bears that chlorine atom which is a leaving group resulting in formation of Meisenheimer complex.
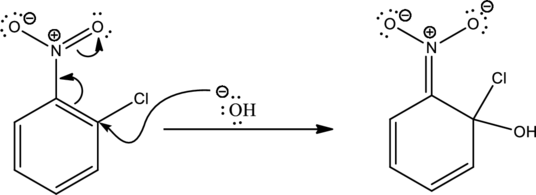
The formed Meisenheimer complex has the following resonance structures.
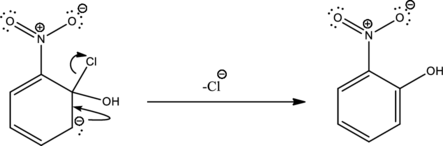
Second step is the expelling of the leaving group to give the product.
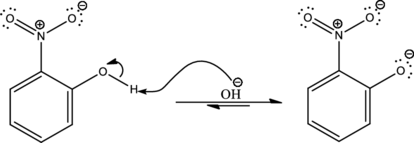
As the given condition is basic, deprotonation takes place.
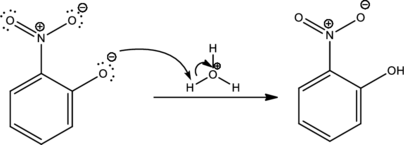
Under acidic condition the formed ion is protonated to give the product. This is the reason for using acid in order to complete the reaction.
Complete mechanism can be given as shown below,
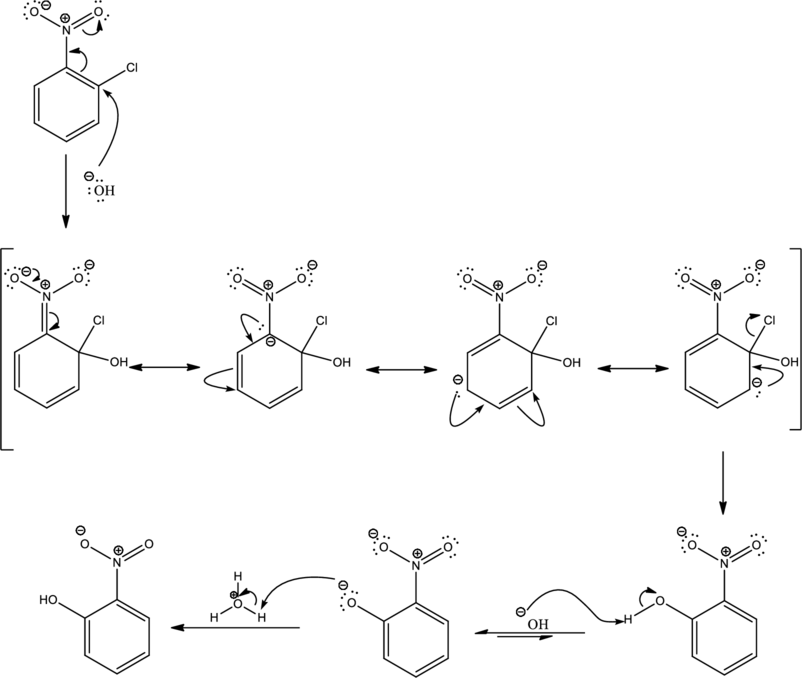
Mechanism for the given transformation is proposed.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry As a Second Language: Second Semester Topics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
- help 20arrow_forwardProvide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


