
Concept explainers
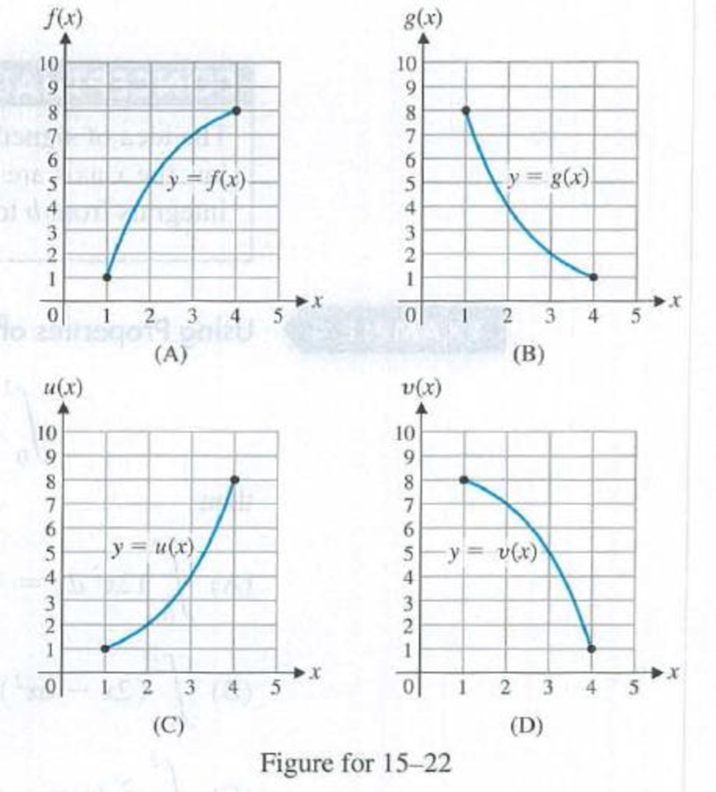
Problems 15–22 involve estimating the area under the curves in Figures A–D from x = 1 to x = 4. For each figure, divide the interval [1, 4] into three equal subintervals.
19. Replace the question marks with L3 and R3 as appropriate. Explain your choice.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Calculus for Business Economics Life Sciences and Social Sciences Plus NEW
- 2. A microwave manufacturing firm has determined that their profit function is P(x)=-0.0014x+0.3x²+6x-355 , where is the number of microwaves sold annually. a. Graph the profit function using a calculator. b. Determine a reasonable viewing window for the function. c. Approximate all of the zeros of the function using the CALC menu of your calculator. d. What must be the range of microwaves sold in order for the firm to profit?arrow_forwardSolve by DrWz WI P L B dy Sind Ⓡ de max ⑦Ymax dx Solve by Dr ③Yat 0.75m from A w=6KN/M L=2 W2=9 kN/m P= 10 KN Solve By Drarrow_forwardA clothing manufacturer's profitability can be modeled by p (x)=-x4 + 40x² - 144, where .x is the number of items sold in thousands and p (x) is the company's profit in thousands of dollars. a. Sketch the function on your calculator and describe the end behavior. b. Determine the zeros of the function. c. Between what two values should the company sell in order to be profitable? d. Explain why only two of the zeros are considered in part c.arrow_forward
- CCSS REASONING The number of subscribers using pagers in the United States can be modeled by f(x) = 0.015x4 -0.44x³ +3.46x² - 2.7x+9.68 where x is the number of years after 1990 and f(x) is the number of subscribers in millions. a. Graph the function. b. Describe the end behavior of the graph. c. What does the end behavior suggest about the number of pager subscribers? d. Will this trend continue indefinitely? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardHow to find the radius of convergence for the series in the image below? I'm stuck on how to isolate the x in the interval of convergence.arrow_forwarddjdjjdjdk4jr i need help on part C,arrow_forward
- Determine the exact signed area between the curve g(x): x-axis on the interval [0,1]. = tan2/5 secx dx andarrow_forwardSet up the partial fraction expansion of the function below. Do not explicitly solve for the variables 5 x²(x − 2)(x − 3)³ (24 - 81)² -arrow_forwardEvaluate the integral below: (4w (4w8) sec(4w) tan(4w) dwarrow_forward
- Evaluate the integral 7 x²√22-16 dxarrow_forwardQuestion 2. An American option on a stock has payoff given by F = f(St) when it is exercised at time t. We know that the function f is convex. A person claims that because of convexity, it is optimal to exercise at expiration T. Do you agree with them?arrow_forwardQuestion 4. We consider a CRR model with So == 5 and up and down factors u = 1.03 and d = 0.96. We consider the interest rate r = 4% (over one period). Is this a suitable CRR model? (Explain your answer.)arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning


