
Concept explainers
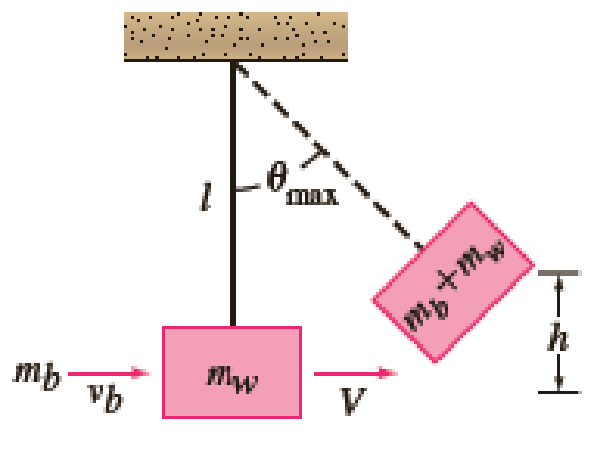
The ballistic pendulum Historically, in order to maintain quality control over munitions (bullets) produced by an assembly line, the manufacturer would use a ballistic pendulum to determine the muzzle velocity of a gun, that is, the speed of a bullet as it leaves the barrel. Invented in 1742 by the English engineer Benjamin Robins, the ballistic pendulum is simply a plane pendulum consisting of a rod of negligible mass to which a block of wood of mass mw is attached. The system is set in motion by the impact of a bullet which is moving horizontally at the unknown velocity vb; at the time of the impact, which we take as t = 0, the combined mass is mw + mb, where mb is the mass of the bullet imbedded in the wood. In (7) of this section, we saw that in the case of small oscillations, the angular displacement θ(t) of a plane pendulum shown in Figure 5.3.3 is given by the linear DE
Intuitively, the horizontal velocity V of the combined mass (wood plus bullet) after impact is only a fraction of the velocity vb of the bullet, that is,
Now recall, a distance s traveled by a particle moving along a circular path is related to the radius l and central angle θ by the formula s = lθ. By differentiating the last formula with respect to time t, it follows that the angular velocity ω of the mass and its linear velocity v are related by v = lω. Thus the initial angular velocity ω0 at the time t at which the bullet impacts the wood block is related to V by V = lω0 or
- (a) Solve the initial-value problem
- (b) Use the result from part (a) to show that
- (c) Use Figure 5.3.11 to express cos θmax in terms of l and h. Then use the first two terms of the Maclaurin series for cos θ to express θmax in terms of l and h. Finally, show that vb is given (approximately) by
- (d) Use the result in part (c) to find vb and mb = 5 g, mw = 1 kg, and h = 6 cm.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 5 Solutions
A First Course in Differential Equations with Modeling Applications (MindTap Course List)
- 4 Consider f(x) periodic function with period 2, coinciding with (x) = -x on the interval [,0) and being the null function on the interval [0,7). The Fourier series of f: (A) does not converge in quadratic norm to f(x) on [−π,π] (B) is pointwise convergent to f(x) for every x = R П (C) is in the form - 4 ∞ +Σ ak cos(kx) + bk sin(kx), ak ‡0, bk ‡0 k=1 (D) is in the form ak cos(kx) + bk sin(kx), ak 0, bk 0 k=1arrow_forwardTIP the aren't, the data are not sym 11 Suppose that the average salary at a certain company is $100,000, and the median salary is $40,000. a. What do these figures tell you about the shape of the histogram of salaries at this company? b. Which measure of center is more appro- priate here? c. Suppose that the company goes through a salary negotiation. How can people on each side use these summary statistics to their advantage? 6360 be 52 PART 1 Getting Off to a Statistically Significant Sarrow_forwardSolve the equation.arrow_forward
- y of 45 home- televisions u find that 010020 le own one, ee, and 1 owns y histogram of 4 Suppose that you have a loaded die. You roll it several times and record the outcomes, which are shown in the following figure. Histogram for Loaded Die 444% 34.00 48% 6% 2% Frequency 20 20 15 155 10 5- ம 0 1 2 3 4 Outcome 5 6 a. Make a relative frequency histogram of these results. b. You can make a relative frequency histo- gram from a frequency histogram; can you go the other direction?arrow_forward7. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 6.1.505.XP. Evaluate the integral. (Use C for the constant of integration.) 21z³e² dz | 21 Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER 8. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 6.1.020. Evaluate the integral. 36 In y dy ₤36 25 Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER 9. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 6.1.009. Evaluate the integral. (Use C for the constant of integration.) In(7x In(7x + 1) dxarrow_forward10. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 6.1.506.XP. Evaluate the integral. √xy dy Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWER 11. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 6.1.023. Evaluate the integral. 1/2 7 cos-1 x dx Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWER 12. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 6.1.507.XP. Evaluate the integral. L² 0 (In x)² x3 dx Need Help? Read Itarrow_forward
- Calculate the mean for Study Hours and Test Scores. Compute the covariance between the two variables using the formula: Calculate the standard deviation for Study Hours (X) and Test Scores (Y). Determine the correlation coefficient Interpret the results: What does the calculated r-value indicate about the relationship between study hours and test scores?arrow_forwardDirections: Use the equation A = Pet to answer each question and be sure to show all your work. 1. If $5,000 is deposited in an account that receives 6.1% interest compounded continuously, how much money is in the account after 6 years? 2. After how many years will an account have $12,000 if $6,000 is deposited, and the account receives 3.8% interest compounded continuously? 3. Abigail wants to save $15,000 to buy a car in 7 years. If she deposits $10,000 into an account that receives 5.7% interest compounded continuously, will she have enough money in 7 years? 4. Daniel deposits $8,000 into a continuously compounding interest account. After 18 years, there is $13,006.40 in the account. What was the interest rate? 5. An account has $26,000 after 15 years. The account received 2.3% interest compounded continuously. How much was deposited initially?arrow_forwardIf m<RST=(12x-1) m<RSU(9x-15) and m<UST=53arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

