
Concept explainers
Reminder Round all answers to two decimal places unless otherwise indicated.
Parallax Angle If we view a star now, and then view it again
| Star | Parallax angle | Distance |
| Markab |
|
|
| Al Na’ir |
|
|
| Alderamin |
|
|
| Altair |
|
|
| Vega |
|
|
| Rasalhague |
|
|
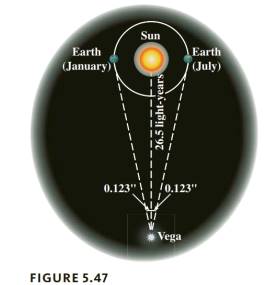
a. Make a power function model of the data for
b. If one star has a parallax angle that is twice that of a second, how do their distances compare?
c. The star Mergez has a parallax angle of
d. The star Sabik is
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Webassign Printed Access Card For Crauder/evans/noell's Functions And Change: A Modeling Approach To College Algebra, 6th Edition, Single-term
- 3. Let M = (a) - (b) 2 −1 1 -1 2 7 4 -22 Find a basis for Col(M). Find a basis for Null(M).arrow_forwardSchoology X 1. IXL-Write a system of X Project Check #5 | Schx Thomas Edison essay, x Untitled presentation ixl.com/math/algebra-1/write-a-system-of-equations-given-a-graph d.net bookmarks Play Gimkit! - Enter... Imported Imported (1) Thomas Edison Inv... ◄›) What system of equations does the graph show? -8 -6 -4 -2 y 8 LO 6 4 2 -2 -4 -6 -8. 2 4 6 8 Write the equations in slope-intercept form. Simplify any fractions. y = y = = 00 S olo 20arrow_forwardEXERCICE 2: 6.5 points Le plan complexe est rapporté à un repère orthonormé (O, u, v ).Soit [0,[. 1/a. Résoudre dans l'équation (E₁): z2-2z+2 = 0. Ecrire les solutions sous forme exponentielle. I b. En déduire les solutions de l'équation (E2): z6-2 z³ + 2 = 0. 1-2 2/ Résoudre dans C l'équation (E): z² - 2z+1+e2i0 = 0. Ecrire les solutions sous forme exponentielle. 3/ On considère les points A, B et C d'affixes respectives: ZA = 1 + ie 10, zB = 1-ie 10 et zc = 2. a. Déterminer l'ensemble EA décrit par le point A lorsque e varie sur [0, 1. b. Calculer l'affixe du milieu K du segment [AB]. C. Déduire l'ensemble EB décrit par le point B lorsque varie sur [0,¹ [. d. Montrer que OACB est un parallelogramme. e. Donner une mesure de l'angle orienté (OA, OB) puis déterminer pour que OACB soit un carré.arrow_forward
- 2 Use grouping to factor: 10x + 13x + 3 = 0 Identify A B and C in the chart below feach responce inarrow_forward2 Use grouping to factor: 10x² + 13x + 3 = 0 Identify A, B, and C in the chart below. (each rearrow_forward2 Use grouping to factor: 10x + 13x + 3 = 0 Identify A B and C in the chart below feach responce inarrow_forward
- Use grouping to fully factor: x³ + 3x² - 16x - 48 = 0 3 2arrow_forwardName: Tay Jones Level Two Date: Algebra 3 Unit 3: Functions and Equations Practice Assessment Class: #7-OneNote 1. The function f(x) = x² is transformed in the following functions. List the vertex for each function, circle whether the function opens up or down, and why. All three parts must be correct to receive Level 2 points. You can receive points for a, b, and c. a) g(x) = -2(x+5)² Vertex: Opens Up Opens Down Why? ais negative -2 Vertex: b) g(x) = (x + 2)² - 3 c) g(x) = -4(x + 2)² + 2 Opens Up Opens Down Vertex: Opens Up Opens Down Why? 4 Ca is negative) Why? his positive 2. The graph of the function f(x) is shown below. Find the domain, range, and end behavior. Then list the values of x for which the function values are increasing and decreasing. f(x) Domain: End Behavior: As x → ∞o, f(x) -> -6 As x, f(x) -> Range: Where is it Increasing? (002] Where is it Decreasing? (1,00)arrow_forwardShow what to do on the graph visually please!arrow_forward
- The county's new asphalt paving machine can surface 1 km of highway in 10 h. A much older machine can surface 1 km in 18 h. How long will it take them to surface 21 km of highway if they start at opposite ends and work day and night?arrow_forward3. Write a system of linear equations in slope intercept form that has exactly one solution at the point (3, 4), such that one line has positive slope (but not 1) and the other line has negative slope (but not "1). Also write your system of equations with both equations written in standard form with out any fractions 8- 7 8 5 4 3 -2- + -8-7-6-5-4-3-2-1 1 2 3 -1 2 - ° 4 -5 - -8arrow_forward2. Write a system of linear equations in slope-intercept form has exactly one solution at the point (3, 4), such that both lines have negative slope (but neither one has slope of 1). Also write your system of equations with both equations written in standard form without any fractions. B 0 5 4 3 -2 1 -8-7-6-5-4-3-2 -1 12 3 -1 2 -3 -5 6 -7 -8arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell  Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning





