
Mechanics of Materials
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605460
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Pearson Education (US)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.10, Problem 126P
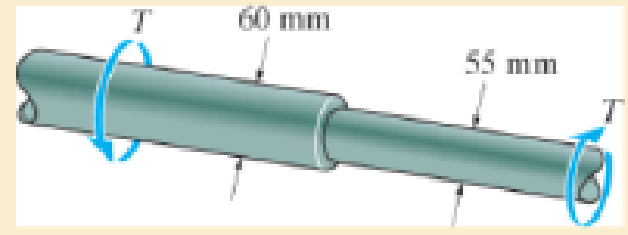
Determine the radius of the elastic core produced in the smaller diameter segment. Neglect the stress concentration at the fillet.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED.
12: A steel cantilever beam 16 ft 8 in in length is subjected to a concentrated load of 320 lb acting at the freeend of the bar. A commercially available rolled steel section, designated as W12x32, is used for the beam. Assume that the total depth of the beam is 12 in, and the neutral axis of the section is in the middle. Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses. (Properties of commercially available rolled steel section provided in the table. Z = section modulus). ANS: σT = σC = 1,572.482 lb/in2
CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED.
14: Two ½-in x 8-in cover plates are welded to two channels 10 in high to formthe cross section of the beam shown in Fig. 8-59. Loads are in a vertical plane and bendingtakes place about a horizontal axis. The moment of inertia of each channel about ahorizontal axis through the centroid is 78.5 in4. If the maximum allowable elastic bendingstress is 18,000 lb/in2, determine the maximum bending moment that may be developedin the beam.ANS: 1,236,000 lb-in.
CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED.
11: A beam of circular cross section is 7 in in diameter. It is simply supported at each end and loaded by twoconcentrated loads of 20,000 lb each, applied 12 in from the ends of the beam. Determine the maximum bending stressin the beam. ANS: σ = 7,127.172 lb/in2
Chapter 5 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 5.3 - The solid circular shaft is subjected to an...Ch. 5.3 - The hollow circular shaft is subjected to an...Ch. 5.3 - The shaft is hollow from A to B and solid from B...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the maximum shear stress in the...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the maximum shear stress in the shaft at...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the shear stress a: point A on the...Ch. 5.3 - The solid 50-mm-diameter shaft is subjected to the...Ch. 5.3 - The gear motor can develop 3 hp when it turns at...Ch. 5.3 - The solid shaft of radius r is subjected to a...Ch. 5.3 - The solid shaft of radius r is subjected to a...
Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 3PCh. 5.3 - The copper pipe has an outer diameter of 40 mm and...Ch. 5.3 - The copper pipe has an outer diameter of 2.50 in....Ch. 5.3 - The link acts as part of the elevator control for...Ch. 5.3 - The assembly consists of two sections of...Ch. 5.3 - A steel tube having an outer diameter of 2.5 in....Ch. 5.3 - The rod has a diameter of 1 in. and a weight of 10...Ch. 5.3 - The rod has a diameter of 1 in. and a weight of 15...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 20PCh. 5.3 - The 60-mm-diameter solid shaft is subjected to the...Ch. 5.3 - The 60-mm-diameter solid shaft is subjected to the...Ch. 5.3 - The solid shaft is subjected to the distributed...Ch. 5.3 - If the tube is made from a material having an...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 29PCh. 5.3 - The motor delivers 50 hp while turning at a...Ch. 5.3 - The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 35PCh. 5.4 - The 60 mm-diameter steel shaft is subjected to the...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 10FPCh. 5.4 - The hollow 6061-T6 aluminum shaft has an outer and...Ch. 5.4 - A series of gears are mounted on the...Ch. 5.4 - The 80-mm-diameter shaft is made of steel. If it...Ch. 5.4 - The 80-mm-diameter shaft is made of steel. If it...Ch. 5.4 - The propellers of a ship are connected to an A-36...Ch. 5.4 - Show that the maximum shear strain in the shaft is...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the angle of twist of end B with respect...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the maximum allowable torque T. Also,...Ch. 5.4 - If the allowable shear stress is allow = 80 MPa,...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the angle of twist of the end A.Ch. 5.4 - The hydrofoil boat has an A992 steel propeller...Ch. 5.4 - Also, calculate the absolute maximum shear stress...Ch. 5.4 - If a torque of T = 50 N m is applied to the bolt...Ch. 5.4 - If a torque of T= 50N m is applied to the bolt...Ch. 5.4 - If the motor delivers 4 MW of power to the shaft...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the angle of twist at the free end A of...Ch. 5.5 - Gst = 75 GPa.Ch. 5.5 - The shaft is made of L2 tool steel, has a diameter...Ch. 5.5 - Each has a diameter of 25 mm and they are...Ch. 5.5 - Each has a diameter of 25 mm and they are...Ch. 5.5 - It is fixed at its ends and subjected to a torque...Ch. 5.5 - 5–89. Determine the absolute maximum shear stress...Ch. 5.7 - If the yield stress for brass is Y = 205 MPa,...Ch. 5.7 - By what percentage is the shaft of circular cross...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 97PCh. 5.7 - Also, find the angle of twist of end B. The shaft...Ch. 5.7 - Also, find the corresponding angle of twist at end...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 110PCh. 5.7 - Determine the average shear stress in the tube if...Ch. 5.7 - By what percentage is the torsional strength...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 114PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 115PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 119PCh. 5.10 - Prob. 121PCh. 5.10 - If the radius of the fillet weld connecting the...Ch. 5.10 - Prob. 125PCh. 5.10 - Determine the radius of the elastic core produced...Ch. 5.10 - Prob. 128PCh. 5.10 - Determine the torque T needed to form an elastic...Ch. 5.10 - Determine the torque applied to the shaft.Ch. 5.10 - Prob. 131PCh. 5.10 - Determine the ratio of the plastic torque Tp to...Ch. 5.10 - Determine the applied torque T, which subjects the...Ch. 5.10 - Determine the radius of its elastic core if it is...Ch. 5.10 - Plot the shear-stress distribution acting along a...Ch. 5.10 - If the material obeys a shear stress-strain...Ch. 5.10 - It is made of an elastic perfectly plastic...Ch. 5.10 - Prob. 139PCh. 5.10 - Prob. 140PCh. 5.10 - Prob. 142PCh. 5.10 - Prob. 143PCh. 5 - The shaft is made of A992 steel and has an...Ch. 5 - The shaft is made of A992 steel and has an...Ch. 5 - Determine the shear stress at the mean radius p =...Ch. 5 - If the thickness of its 2014-T6-aluminum skin is...Ch. 5 - Determine which shaft geometry will resist the...Ch. 5 - If couple forces P = 3 kip are applied to the...Ch. 5 - If the allowable shear stress for the aluminum is...Ch. 5 - Determine the angle of twist of its end A if it is...Ch. 5 - This motion is caused by the unequal belt tensions...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- using the theorem of three moments, find all the reactions and supportsarrow_forward(An ellipsoidal trapping region for the Lorenz equations) Show that there is a certain ellipsoidal region E of the form rx2 + σy2 + σ(z − 2r)2 ≤ C such that all trajectories of the Lorenz equations eventually enter E and stay in there forever. For a much stiffer challenge, try to obtain the smallest possible value of C with this property.arrow_forwardA) In a factory, an s-type pitot tube was used to calculate the velocity of dry air for a point inside a stack. Calculate the velocity at that point (ft/sec) using following conditions: ● • • Pressure = 30.23 ± 0.01 in Hg (ambient) Pitot tube coefficient = 0.847 ± 0.03 Temperature = 122 ± 0.1 F (stack) Temperature = 71.2 ± 0.1 F (ambient) AP = 0.324 ± 0.008 in H2O (pitot tube) • AP = 0.891 ± 0.002 in H2O (stack) B) Find the dominant error(s) when determining precision for the problem. C) For part A, what is the precision in ft/sec for the velocity?arrow_forward
- Q1/ For what value of x do the power series converge: 8 (-1)n-1. x2n-1 2n-1 x3 x5 = X n=1 3 Q2/ Find the Interval of convergence and Radius of convergence of the series: 8 n Σ 3+1 n=1 (x)"arrow_forwardExample-1: l D A uniform rotor of length 0.6 m and diameter 0.4 m is made of steel (density 7810 kg/m³) is supported by identical short bearings of stiffness 1 MN/m in the horizontal and vertical directions. If the distance between the bearings is 0.7 m, determine the natural frequencies and plot whirl speed map. Solution: Barrow_forwardfind the laplace transform for the flowing function 2(1-e) Ans. F(s)=- S 12) k 0 Ans. F(s)= k s(1+e) 0 a 2a 3a 4a 13) 2+ Ans. F(s)= 1 s(1+e") 3 14) f(t)=1, 0arrow_forwardFind the solution of the following Differential Equations Using Laplace Transforms 1) 4y+2y=0. y(0)=2. y'(0)=0. 2) y+w²y=0, (0)=A, y'(0)=B. 3) +2y-8y 0. y(0)=1. y'(0)-8. 4)-2-3y=0, y(0)=1. y'(0)=7. 5) y-ky'=0, y(0)=2, y'(0)=k. 6) y+ky'-2k²y=0, y(0)=2, y'(0) = 2k. 7) '+4y=0, y(0)=2.8 8) y+y=17 sin(21), y(0)=-1. 9) y-y-6y=0, y(0)=6, y'(0)=13. 10) y=0. y(0)=4, y' (0)=0. 11) -4y+4y-0, y(0)=2.1. y'(0)=3.9 12) y+2y'+2y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=-3. 13) +7y+12y=21e". y(0)=3.5. y'(0)=-10. 14) "+9y=10e". y(0)=0, y'(0)=0. 15) +3y+2.25y=91' +64. y(0)=1. y'(0) = 31.5 16) -6y+5y-29 cos(2t). y(0)=3.2, y'(0)=6.2 17) y+2y+2y=0, y(0)=0. y'(0)=1. 18) y+2y+17y=0, y(0)=0. y'(0)=12. 19) y"-4y+5y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=2. 20) 9y-6y+y=0, (0)-3, y'(0)=1. 21) -2y+10y=0, y(0)=3, y'(0)=3. 22) 4y-4y+37y=0, y(0)=3. y'(0)=1.5 23) 4y-8y+5y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=1. 24) ++1.25y-0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=-0.5 25) y 2 cos(r). y(0)=2. y'(0) = 0. 26) -4y+3y-0, y(0)=3, y(0) 7. 27) y+2y+y=e y(0)=0. y'(0)=0. 28) y+2y-3y=10sinh(27), y(0)=0. y'(0)=4. 29)…arrow_forwardAuto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardThe 120 kg wheel has a radius of gyration of 0.7 m. A force P with a magnitude of 50 N is applied at the edge of the wheel as seen in the diagram. The coefficient of static friction is 0.3, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25. Find the acceleration and angular acceleration of the wheel.arrow_forwardAuto Controls Using MATLAB , find the magnitude and phase plot of the compensators NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forward4-81 The corner shown in Figure P4-81 is initially uniform at 300°C and then suddenly exposed to a convection environment at 50°C with h 60 W/m². °C. Assume the = 2 solid has the properties of fireclay brick. Examine nodes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 and deter- mine the maximum time increment which may be used for a transient numerical calculation. Figure P4-81 1 2 3 4 1 cm 5 6 1 cm 2 cm h, T + 2 cmarrow_forwardAuto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY