
Concept explainers
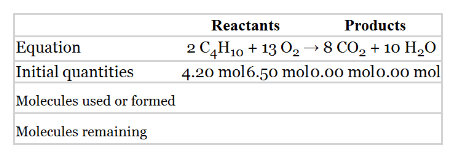
Completer the followin table using the given balanced equation and the initial quantities of reactants. Label the limiting reactant and the reactant used in excess.
| Reactants | Products | |
| Equation |
|
|
| Initial quantities | 4.20 mol 6.50 molo.00 molo.oo mol | |
| Molecules used or formed | ||
| Molecules remaining |
Interpretation:
The following table should be completed using the given information. The limiting reactant and the reactant used in excess should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Mole is the amount of the substance that contains the same number of particles or atoms or molecules. Molar mass is defined as average mass of atoms present in the chemical formula. It is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms present in the chemical formula of any compound.
Answer to Problem 88P
The limiting reactant is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
Therefore, the moles of
Therefore, 4.20 moles of
The amount of product would be formed according to the
The amount of
The amount of
Therefore, the limiting reactant is
The limiting reactant is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
MARINE BIOLOGY
Organic Chemistry
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
- Please correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardYou have started a patient on a new drug. Each dose introduces 40 pg/mL of drug after redistribution and prior to elimination. This drug is administered at 24 h intervals and has a half life of 24 h. What will the concentration of drug be after each of the first six doses? Show your work a. What is the concentration after the fourth dose? in pg/mL b. What is the concentration after the fifth dose? in pg/mL c. What is the concentration after the sixth dose? in pg/mLarrow_forward
- McLafferty Rearrangement: Label alpha (), beta (), and gamma () on the molecule. Draw mechanismarrows to describe the process of the rearrangement. What functional group is lost during the rearrangement? What new functional group is made from the ketone/aldehyde you started with? What stabilizing chemical theory causes (allows) rearrangement to happen?arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781285199030Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781285199030Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div





