
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the given
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to possess a symmetry element if the molecule is unchanged in appearance after applying the symmetry operation corresponding to the symmetry element.
There are different types of symmetries such as rotational, reflectional, inversion, and improper rotation.
A molecule has rotational symmetry only if you rotate less than one full turn; it is the same as the original shape.
For example,
The cyclobutane has rotational symmetry; it is same as the original shape after
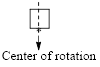
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the given ketone compound exhibit reflectional symmetry has to be checked.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to possess a symmetry element if the molecule is unchanged in appearance after applying the symmetry operation corresponding to the symmetry element.
There are different types of symmetries such as rotational, reflectional, inversion, and improper rotation.
Reflectional symmetry is also known as line symmetry is a type of balance in which a center line called line of symmetry (plane of symmetry) divides an object in half so that one side mirrors the other.
Plane of symmetry: When structure of the compound can be cut into two equal halves along the plane. Then such plane is called as plane of symmetry.
Example for a molecule which has reflectional symmetry is,
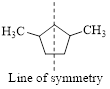
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the compound is chiral or achiral and if it is a chiral compound its enantiomer has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to possess a symmetry element if the molecule is unchanged in appearance after applying the symmetry operation corresponding to the symmetry element.
There are different types of symmetries such as rotational, reflectional, inversion, and improper rotation.
Reflectional symmetry is also known as line symmetry is a type of balance in which a center line called line of symmetry divides an object in half so that one side mirrors the other.
A molecule has rotational symmetry only if you rotate less than one full turn; it is the same as the original shape.
Chiral center: A chiral center is defined as the tetrahedral carbon atom in an organic molecule that is connected to four non-identical groups/substituents. It is sometimes known as a stereo genic center.
Chirality: The geometric property of molecules where the structure of the molecule and its mirror image are not superimposable is known as chirality. Chiral molecules are optically active and they can rotate the plane polarized light.
Chirality is not dependent on the presence or absence of rotational symmetry. It is only dependent on the presence or absence of reflectional symmetry.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, WITH SOL. MAN/ STUDY
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





