
Concept explainers
Plot the shear diagram, bending moment diagram, axial force diagram, and the qualitative deflected shape of the frame.
Explanation of Solution
Write the condition for static instability, determinacy and indeterminacy of plane frames as follows:
Here, number of members is m, number of external reactions is r, the number of joints is j, and the number of elastic hinges is
Find the degree of static indeterminacy (i) using the equation;
Refer to the Figure in the question;
The number of members (m) is 3.
The number of external reactions (r) is 3.
The number of joints (j) is 4.
The number of elastic hinges
Substitute the values in Equation (2);
Show the free-body diagram of the entire frame as in Figure 1.
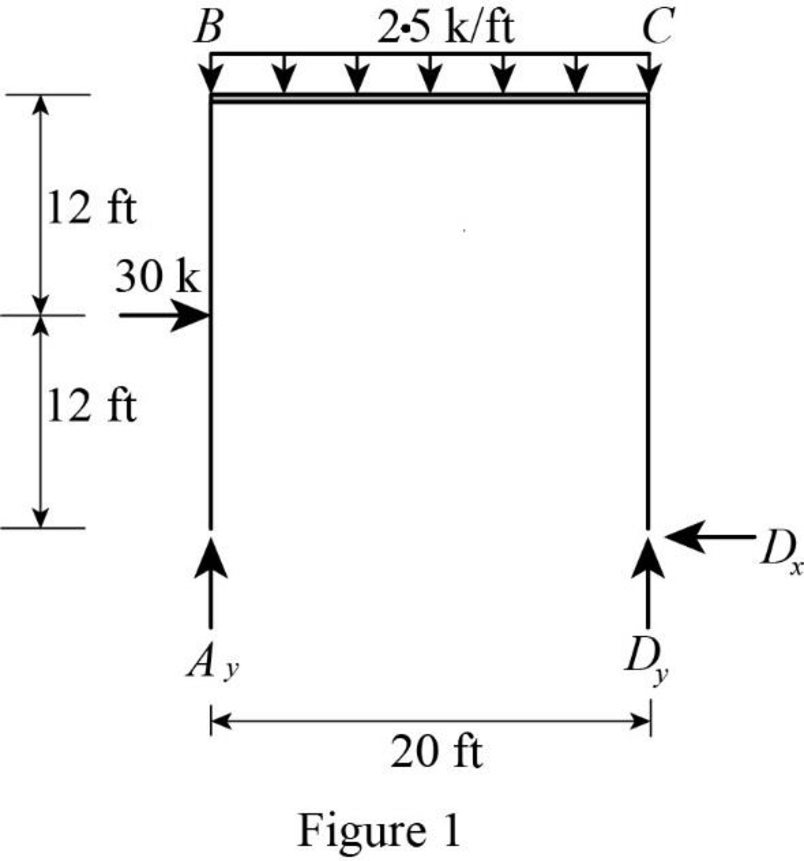
Refer Figure 1,
Find the vertical reaction at point D by taking moment about point A.
Find the vertical reaction at point A by resolving the vertical component of forces.
Find the horizontal reaction at point D by resolving the horizontal component of forces.
Show the free-body diagram of the members and joints of the entire frame as in Figure 2.
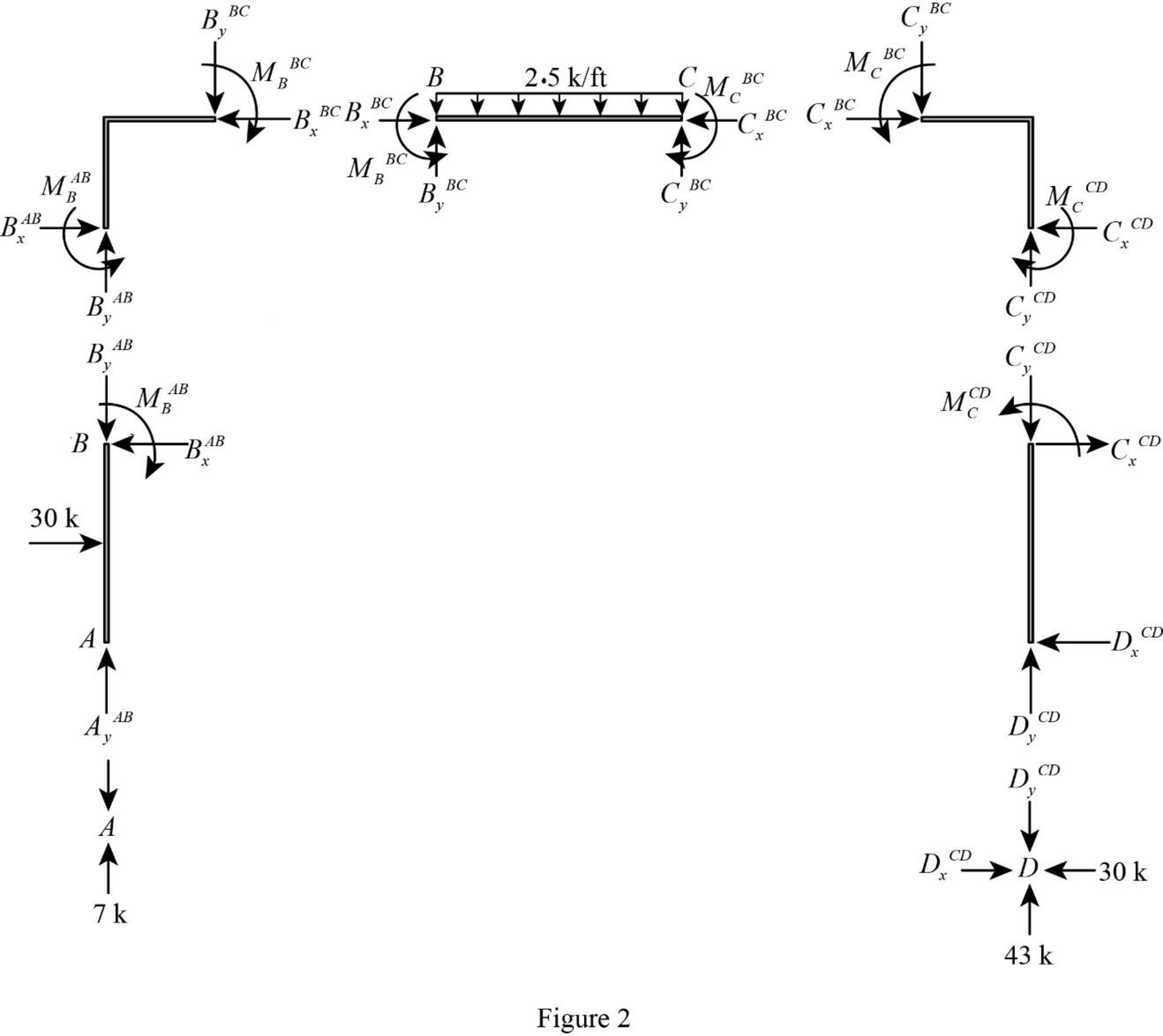
Consider point A:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Consider the member AB:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Take moment about the point B.
Consider the point B:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Take moment about the point B.
Consider the member BC:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Take moment about the point C.
Consider the point C:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Take moment about the point C.
Consider the point D:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Plot the moment end forces of the frame as in Figure 3.
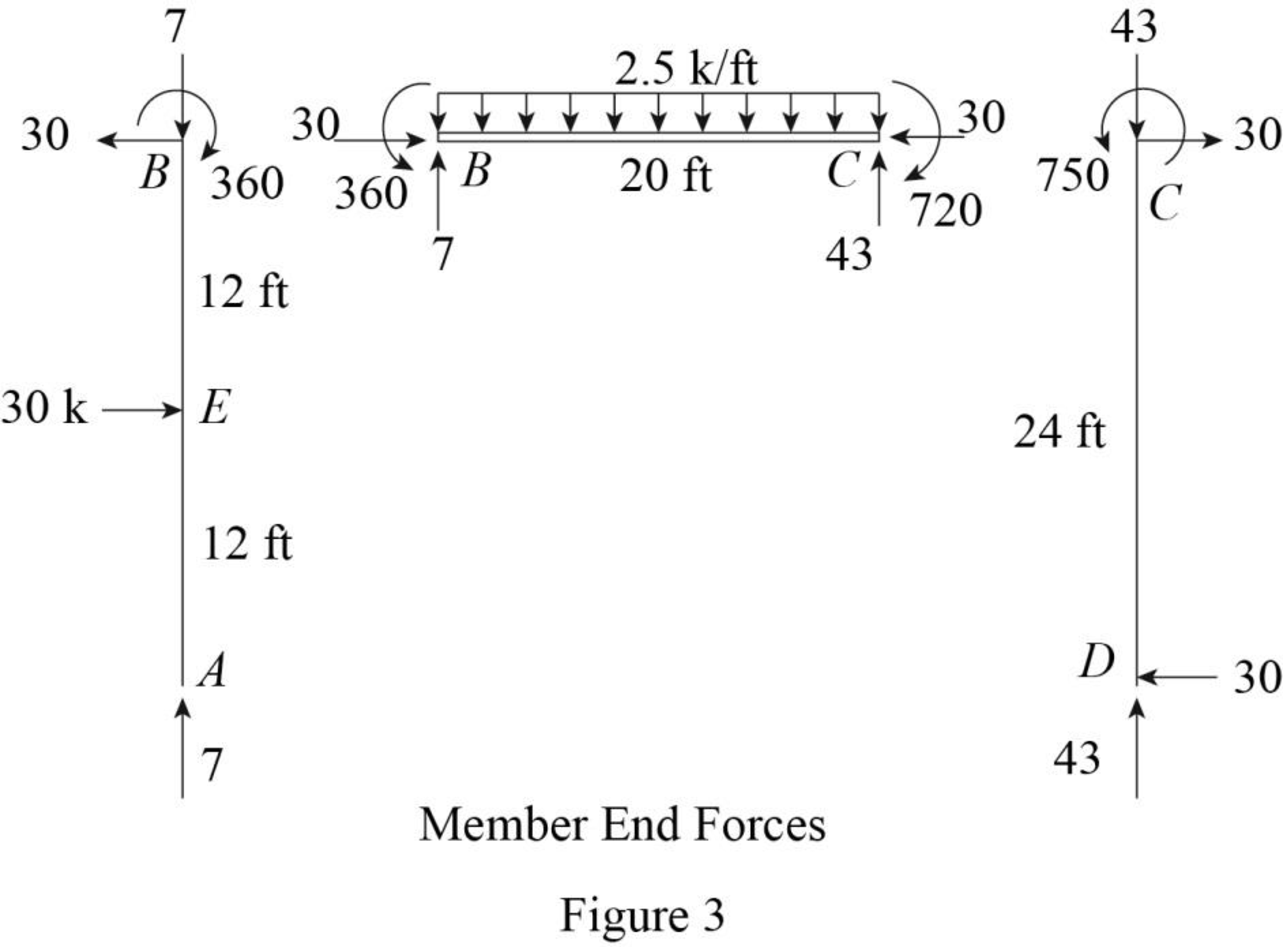
Refer to the moment end force diagram plot the shear diagram, bending moment diagram, and the axial force diagrams.
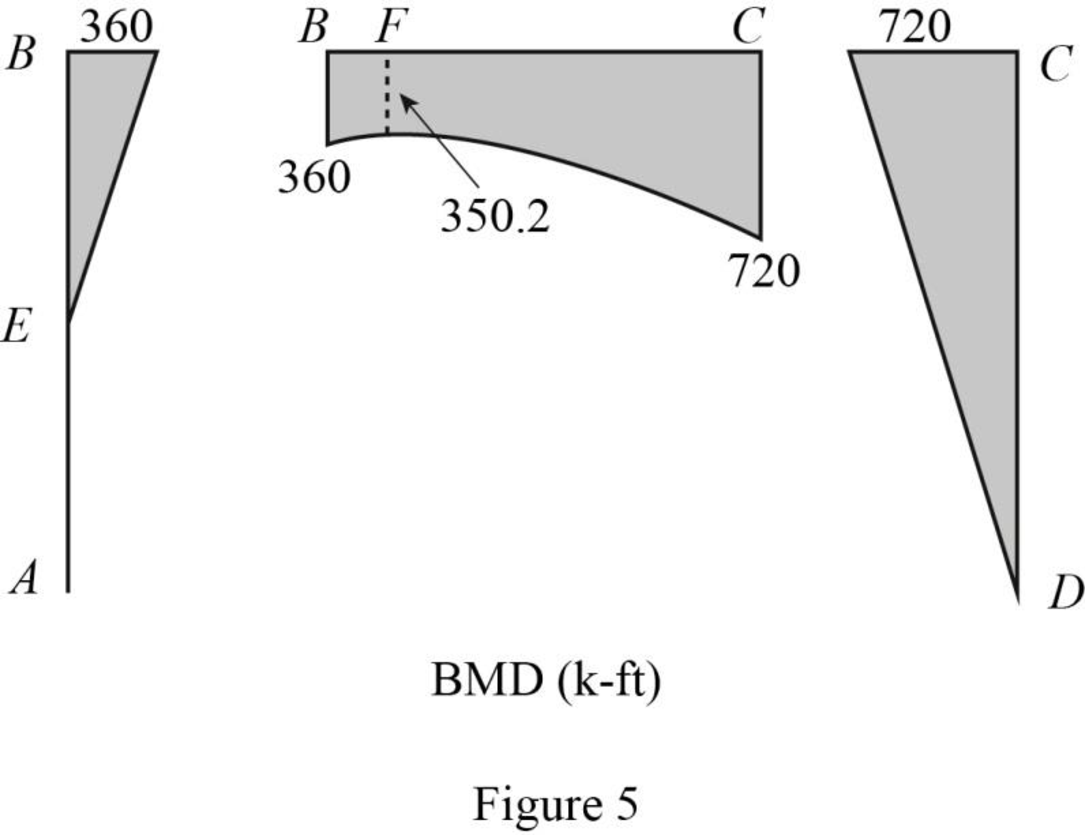
Refer to the shear force diagram, the maximum bending moment occurs at point F where the shear force changes sign.
Use similar triangle concept for the region BC:
Plot the shear force diagram as in Figure 4.
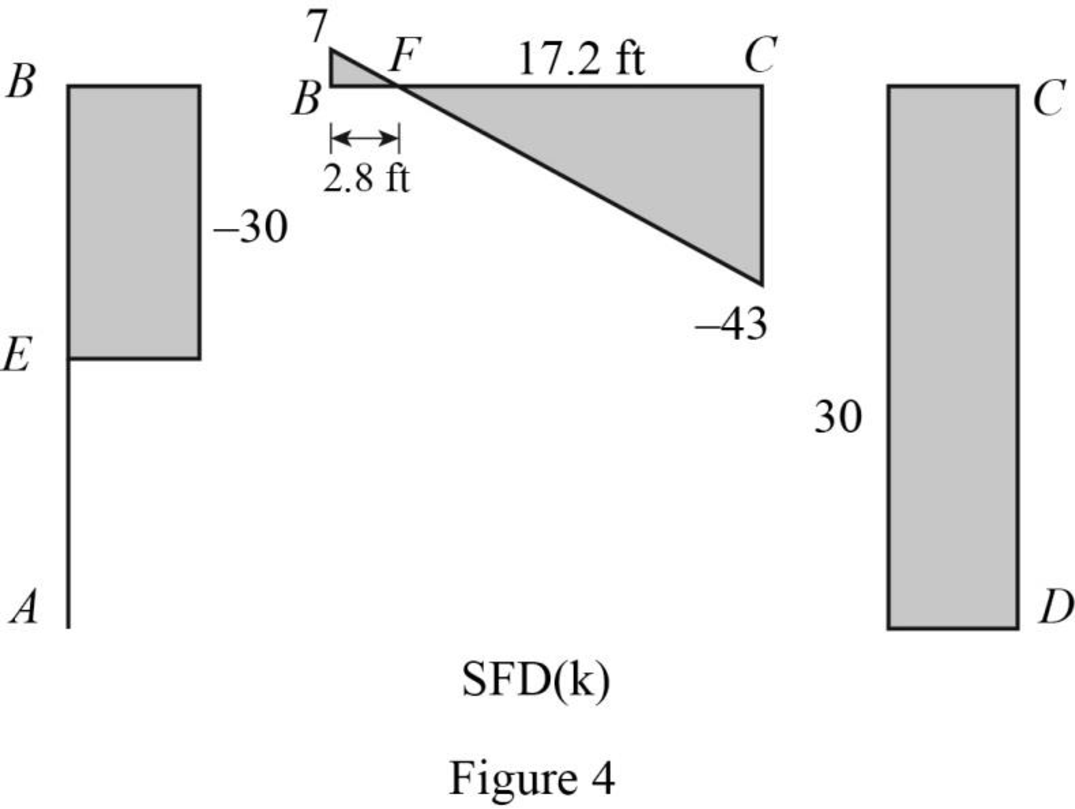
Find the bending moment at point F.
Plot the bending moment diagram as in Figure 5.
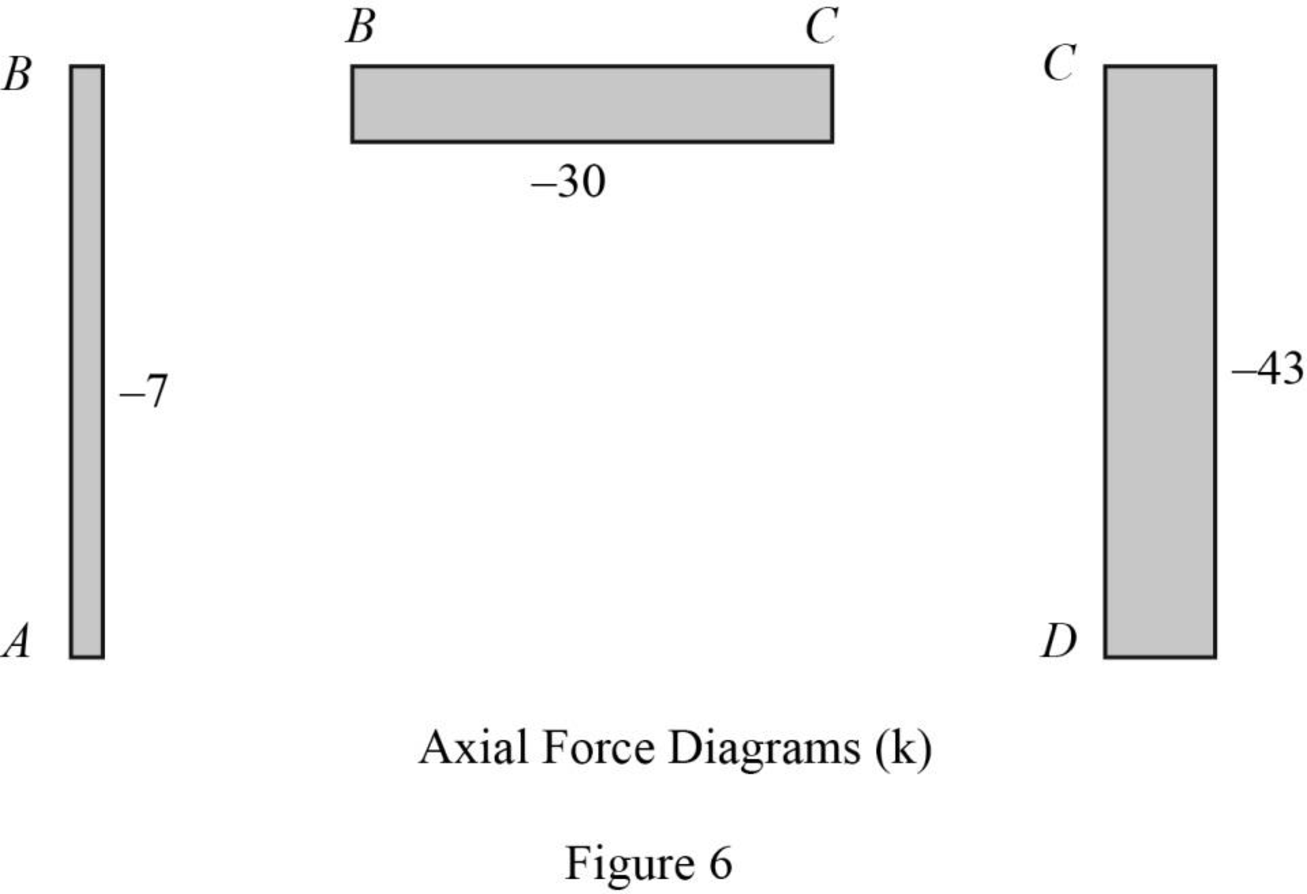
Plot the axial force diagram as in Figure 6.
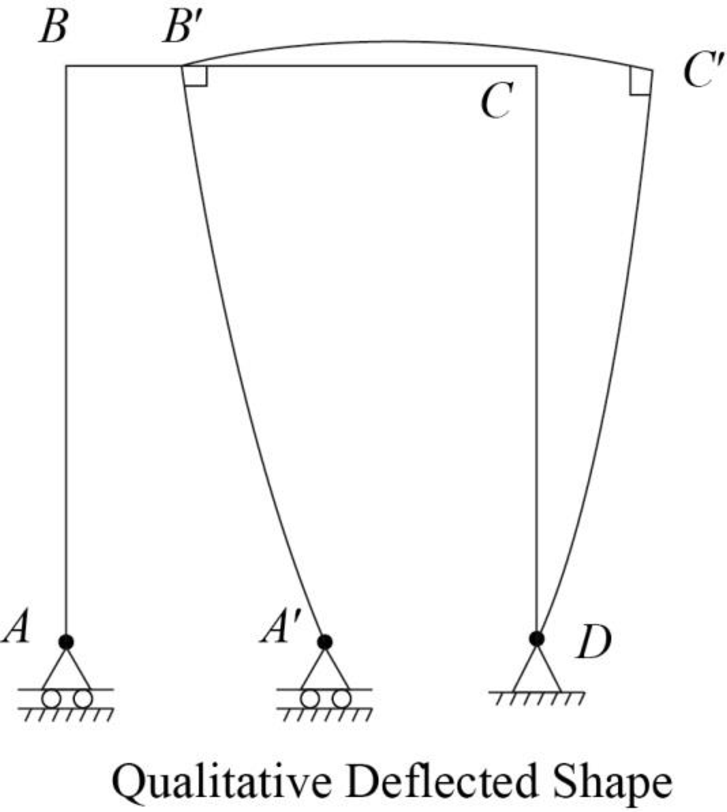
Plot the qualitative deflected shape as in Figure 7.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Structural Analysis, Si Edition
- Hi! I would like helping hand in computing all the materials needed for masonry works (CHB walls) on the ground floor. I’ve already computed the other structural elements — please refer to the attached image.arrow_forwardHi! Kindly help me compute the following based on the attached elevation plan and floor plan: Total Perimeter of the building – to be used for layouting. Total Length of Batter Board – include all sides where batter boards will be installed. Number and spacing of Stakes – assuming a stake is placed every 1.2 meters along the perimeter. Please show the complete solution and breakdown of your computation. Thank you!arrow_forwardE D (B) (<) 2945 3725 250 2225 Car Port 5000 2500 Pool Area 2 3925 3465 2875 13075 Staff Room Bar Counter 1 GROUND FLOOR PLAN SCALE 1:100 Hallway 3 1560 4125 3125 $685 Laundry & Service Area 5 A Common T&B Kitchen & Dining Arear B Living Area 2425 Terrace E 2 12150 1330 2945 4150 5480 1800 3725 1925 3800 3465 2 3 9150 4125 3575 3925 Terrace Toilet & Bathroom Toilet Bathroom Bedroom 1 Bedroom 2 SECOND FLOOR PLAN SCALE Hallway 1:100 OPEN TO BELOW E B A 3 3725 2150 1330 2945 5480 4150 1925 ⑨ 2 9150 3800 4125 3465 3575 3925 Terrace R Toilet & Bathroom Toilet & Bathroom SECOND FLOOR PLAN SCALE Hallway 1:100 OPEN TO BELOW +arrow_forward
- Q2/ In a design of a portable sprinkler system, the following information is given: • • The sprinklers are distributed in a square pattern with radius of the wetted circle of the sprinkler=15 m Consumption rate = 10 mm/day Efficiency of irrigation = 60% Net depth of irrigation (NDI)= 80 mm. Find the following: 1-Sprinkler application rate if HRS = 11. 2-Number of pipes required for irrigation. (50 Marks) 3-Discharge of sprinkler, diameter of nozzle, and the working head pressure if C=0.90. 4-Diameter of the sprinkler pipe for Slope=0. 5-Pressure head at the inlet and at the dead end of the sprinkler pipe for Slope=0. (F² + L²)((SF)² + L²) L² 2L² ≤ D² L² + S² ≤ D² A, = * 1000 S*L ≤D² N W Af m-11-P L' Hf = 1.14*109 * 1.852 * L *F,where c=120 D4.87 Source main pipe 180 m 540 m N 1 1 √m-1 F = im/Nm+1 = + + m+1 2N 6N2 i=1 Nozzle diameter (mm) 3< ds 4.8 4.8< ds 6.4 6.4arrow_forwardMiniatry of Higher scent Research University of Ke Faculty of Engineering Cell Engineering Department 2024-2025 Mid Exam-1 st Attempt Time Date: 17/04/2025 Notes: Answer all questions. Not all figures are to scale. Assume any values if you need them. Q1/ A farm with dimensions and slopes (50 Marks) = shown in the figure below. If you asked to design a border irrigation system and if you know that Net depth of irrigation - 96mm .Manning coefficient = 0.15, Time of work in the farm is 6 hours/day. Design consumption use of water from the crop (ET) 16 mm/day, Width of the agricultural machine equal to 2.5m, Equation of infiltration - D= 12-05 and Efficiency of irrigation= 60%. You can neglect the recession lag time. Find the width and number of the borders, Irrigation interval and time required to irrigate the whole farm, Depth of flow in the inlet of border Number of borders that irrigated in one day and The neglected recession lag time Slope of irrigation % Maximum border width 0-0.1 30…arrow_forwardPLease make sure to show all work and all steps for the image find the magnitude and stressesarrow_forwardShowing all work and steps find the magnituded and stress ,arrow_forwardWhat is the value of the influence line for the reaction at support A for the beam shown at 5 m to the right of A? Select the reaction at support B to be the redundant. a. 0 kN b. -0.167 kN c. 0.425 kN d. 1.0 kNarrow_forwardDetermine the force in member AB of the truss shown due to a temperature drop of 25°C in Members AB, BC, and CD and a temperature increase of 60°C in member EF. Use the method of consistent deformations. a. 37.34 k b. 0 k c. 28 k d. 46.67 karrow_forwardWhat is the approximate axial force in girder EF of the frame shown? Use the portal method. a. 32 kN b. 60 kN c. 12 kN d. 20kNarrow_forwardDetermine the vertical reaction at C for the beam shown and support settlements of 1" at B and ¼" at C. a. 27.0 k b. 28.3 k c. 43.7 k d. 21.0 karrow_forwardWhat is the horizontal reaction component at D for the frame shown? a. 75.00 kN b. 91.67 kN c. 70.31 kN d. 4.69 kNarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
