
Concept explainers
(a)
To Calculate: The maximum and minimum values of applied force for which the block does not slip.
(a)
Answer to Problem 63P
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Mass of the block,
Mass of the wedge,
Coefficient of static friction,
Angle of wedge,
Formula Used:
Newton’s second law of motion:
Where, m is the mass and a is the acceleration.
Calculation:
Free-body diagram:
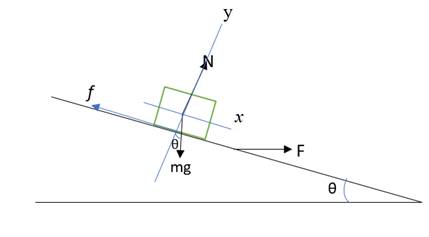
Maximum force,
Minimum force,
Where,
For the block,
Substitute (3) in (1) to find the minimum acceleration:
Substitute the values and solve:
For maximum force, reverse the direction of f
Substitute the values and solve:
Conclusion:
The maximum and minimum values of applied force for which the block does not slip are 84 N and 1.6 N respectively.
(b)
To Calculate: The maximum and minimum values of applied force for which the block does not slip.
(b)
Answer to Problem 63P
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Mass of the block,
Mass of the wedge,
Coefficient of static friction,
Angle of wedge,
Formula Used:
From previous part:
Calculation:
Substitute the values and solve for minimum force:
For maximum force, reverse the direction of f
Substitute the values and solve:
Conclusion:
The maximum and minimum values of applied force for which the block does not slip are 37.5 N and 5.8 N respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- Consider the circuit shown in the figure below. (Assume L = 5.20 m and R2 = 440 Ω.) (a) When the switch is in position a, for what value of R1 will the circuit have a time constant of 15.4 µs? (b) What is the current in the inductor at the instant the switch is thrown to position b?arrow_forwardCan someone helparrow_forwardCan someone help mearrow_forward
- A particle in a box between x=0 and x=6 has the wavefunction Psi(x)=A sin(2πx). How muchenergy is required for the electron to make a transition to Psi(x)= A’ sin(7π x/3). Draw anapproximate graph for the wavefunction. Find A and A'arrow_forwardA proton is moving with 10^8 m/s speed. Find the De Broglie wavelength associated with theproton and the frequency of that wave.arrow_forwardFind the wavelength of the photon if a (Li--) electron makes a transition from n=4 to n=3. Findthe Bohr radius for each state.arrow_forward
- A photon with wavelength 3000 nm hits a stationary electron. After the collision electron isscattered to 60 degrees. Find the wavelength and frequency of the scattered photon.arrow_forwardA metal has threshold frequency 10^15. Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the ejectedelectron if a laser beam with wavelength 1.5 10^-7 m is projected on the metal.arrow_forwardDetermine the direction of the vector V, B, or ♬ that is missing from the pair of vectors shown in each scenario. Here, u is the velocity vector of a moving positive charge, B is a constant and uniform magnetic field, and F is the resulting force on the moving charge. 1. 2. 3. B OB F 4. ↑F F 5. 怔 ↑ ↑F Answer Bank 6. ↑ TE Farrow_forward
- Two point charges (+9.80 nC and -9.80 nC) are located 8.00 cm apart. Let U=0 when all of the charges are separated by infinite distances. What is the potential energy if a third point charge q=-4.20 nC is placed at point b? 8.00 cm 8.00 cm 4.00 +4.00 +4.00- cm cm cm HJarrow_forward! Required information Two chloride ions and two sodium ions are in water, the "effective charge" on the chloride ions (CI¯) is −2.00 × 10-21 C and that of the sodium ions (Na+) is +2.00 x 10-21 C. (The effective charge is a way to account for the partial shielding due to nearby water molecules.) Assume that all four ions are coplanar. CT Na+ Na+ 30.0° 45.0% с сг L. where a = 0.300 nm, b = 0.710 nm, and c = 0.620 nm. What is the direction of electric force on the chloride ion in the lower right-hand corner in the diagram? Enter the angle in degrees where positive indicates above the negative x-axis and negative indicates below the positive x-axis.arrow_forwardA pendulum has a 0.4-m-long cord and is given a tangential velocity of 0.2 m/s toward the vertical from a position 0 = 0.3 rad. Part A Determine the equation which describes the angular motion. Express your answer in terms of the variable t. Express coefficients in radians to three significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ vec (t)=0.3 cos (4.95t) + 0.101 sin (4.95t) Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 6 attempts remainingarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





