
Concept explainers
This serial problem began in Chapter 1 and continues through most of the book. If previous chapter segments were not completed, the serial problem can begin at this point.
SP 5 Santana Rey created Business Solutions on October 1, 2019. The company has been successful, and its list of customers has grown. To accommodate the growth, the accounting system is modified to set up separate accounts for each customer. The following chart of accounts includes the account number used for each account and any balance as of December 31, 2019. Santana Rey decided to add a fourth digit with a decimal point to the 106 account number that had been used for the single
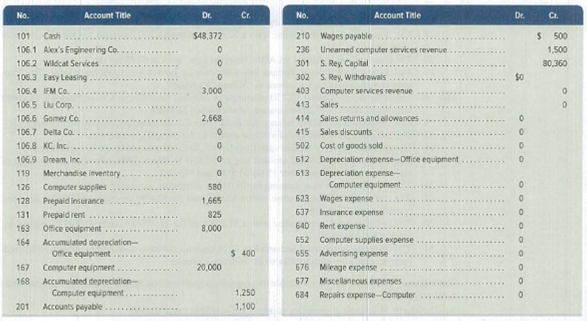
In response to requests from customers, S. Rey will begin sell1ng computer software. The company will extend credit terms of 1/10, n/30, FOB shipping point, to all customers who purchase this merchandise. However, no cash discount is available on consulting fees. Additional accounts (Nos. 119, 413, 414, 415, and 502) are added to its general ledger to accommodate the company's new merchandising activities. Its transactions for January through March follow.



The following additional facts are available for preparing adjustments on March 31 prior to financial statement preparation.
- a. The March 31 amount of computer supplies still available totals $2,005.
- b. Prepaid insurance coverage of $555 expired during this three-month period.
- c. Lyn Addie has not been paid for seven days of work at the rate of $125 per day.
- d. Prepaid rent of $2,475 expired during this three-month period.
- e.
Depreciation on the computer equipment for January 1 through March 31 is $1,250. - f. Depreciation on the office equipment for January 1 through March 31 is $400.
- g. The March 31 amount of merchandise inventory still available totals $704.
Required
- 1. Prepare
journal entries to record each of the January through March transactions. - 2. Post the journal entries in part 1 to the accounts in the company's general ledger. Note: Begin with the ledger’s post-closing adjusted balances as of December 31,2019.
- 3. Prepare a 6-column work sheet (similar to the one shown in Exhibit 3.13) that includes the unadjusted
trial balance , the March 31 adjustments (a) through (g), and the adjusted trial balance. Do not prepare closing entries and do not journalize the adjustments or post them to the ledger. - 4. Prepare an income statement (from the adjusted trial balance in part 3) for the three months ended March 31, 2020. (a) Use a single-step format. List all expenses without differentiating between selling expenses and general and administrative expenses. (b) Use a multiple-step format that begins with gross sales (service revenues plus gross product sales) and includes separate categories for net sales, cost of goods sold, selling expenses, and general and administrative expenses. Categorize the following accounts as selling expenses: Wages Expense, Mileage Expense, and Advertising Expense. Categorize the remaining expenses as general and administrative.
- 5. Prepare a statement of owner’s equity (from the adjusted trial balance in part 3) for the three months ended March 31, 2020.
- 6. Prepare a classified
balance sheet (from the adjusted trial balance) as of March 3 1, 2020.
Prepare journal entries to record the transactions from January to March.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Prepare journal entries to record the transactions from January to March.
| Date | Account title and explanation | PR | Amount | |
| Debit | Credit | |||
| 2020 | ||||
| 4-Jan | Wages Expense | 623 | $125 | |
| Wages Payable | 210 | $500 | ||
| Cash | 101 | $625 | ||
| (To record the Paid employee) | ||||
| 5-Jan | Cash | 101 | $25,000 | |
| Person R, Capital | 301 | $25,000 | ||
| (To record the Additional investment by owner.) | ||||
| 7-Jan | Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $5,800 | |
| Accounts Payable - Corporation K | 201 | $5,800 | ||
| (To record the Purchase of merchandise on credit) | ||||
| 9-Jan | Cash | 101 | $2,668 | |
| Accounts Receivable— Company G | 106.6 | $2,668 | ||
| (To record the Collected accounts receivable) | $5,500 | |||
| 11-Jan | Accounts Receivable—Company AE | 106.1 | $5,500 | |
| Unearned Computer Services Revenue | 236 | $1,500 | ||
| Computer Services Revenue | 403 | $7,000 | ||
| ( To record the Completed work on project) | ||||
| 13-Jan | Accounts Receivable—Corporation L | 106.5 | $5,200 | |
| Sales | 413 | $5,200 | ||
| (To record the merchandise sold on credit.) | ||||
| 13-Jan | Cost of Goods Sold | 502 | $3,560 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $3,560 | ||
| ( To Record the cost of January 13 sale) | ||||
| 15-Jan | Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $600 | |
| Cash | 101 | $600 | ||
| ( To record the freight paid on incoming merchandise) | ||||
| 16-Jan | Cash | 101 | $4,000 | |
| Computer Services Revenue | 403 | $4,000 | ||
| (To record the cash collected revenue from customer) | ||||
| Jan. 17 | Accounts Payable - Corporation K | 201 | $5,800 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $58 | ||
| Cash | 101 | $5,742 | ||
| (To record the payment of account payable within discount period) | ||||
| 20-Jan | Sales Returns and Allowances | 414 | $500 | |
| Accounts Receivable—Corporation L | 106.5 | $500 | ||
| ( To record the defective goods returned from customers) | ||||
| 22-Jan | Cash | 101 | $4,653 | |
| Sales Discounts | 415 | $47 | ||
| Accounts Receivable—Corporation L | 106.5 | $4,700 | ||
| (To record the Collections from accounts receivable) | ||||
| 24-Jan | Accounts Payable | 201 | $496 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $496 | ||
| (To record the return of merchandise for credit) | ||||
| 26-Jan | Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $9,000 | |
| Accounts Payable - Corporation K | 201 | $9,000 | ||
| ( To record the purchase of merchandise for resale) | ||||
| 26-Jan | Accounts Receivable—Incorporation KC | 106.8 | $5,800 | |
| Sales | 413 | $5,800 | ||
| (To record the merchandise sold on credit) | ||||
| 26-Jan | Cost of Goods Sold | 502 | $4,640 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $4,640 | ||
| ( To record the cost of January 26 sales) | ||||
| 31-Jan | Wages Expense | 623 | $1,250 | |
| Cash | 101 | $1,250 | ||
| ( To record the payment of employee wages) | ||||
| 1-Feb | Prepaid Rent | 131 | $2,475 | |
| Cash | 101 | $2,475 | ||
| ( To record the payment of three months’ rent in advance) | ||||
| 3-Feb | Accounts Payable | 201 | $8,504 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $90 | ||
| Cash | 101 | $8,414 | ||
| (To record the payment of account payable within discount period) | ||||
| 5-Feb | Advertising Expense | 655 | $600 | |
| Cash | 101 | $600 | ||
| ( To record the payment for advertising expense) | ||||
| 11-Feb | Cash | 101 | $5,500 | |
| Accounts Receivable—Alex’s Eng. Co. | 106.1 | $5,500 | ||
| ( To record the collection of cash from customers) | ||||
| 15-Feb | Person R, Withdrawals | 302 | $4,800 | |
| Cash | 101 | $4,800 | ||
| (To record the withdrawals of owner) | ||||
| 23-Feb | Accounts Receivable—Corporation D | 106.7 | $3,220 | |
| Sales | 413 | $3,220 | ||
| ( To record the sale of merchandise on credit) | ||||
| 23-Feb | Cost of Goods Sold | 502 | $2,660 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $2,660 | ||
| ( To record the cost of February 23 sales) | ||||
| 26-Feb | Wages Expense | 623 | $1,000 | |
| Cash | 101 | $1,000 | ||
| ( To record the payment of wages to employee) | ||||
| 27-Feb | Mileage Expense | 676 | $192 | |
| Cash | 101 | $192 | ||
| (To record the Reimbursement of business mileage) | ||||
| 8-Mar | Computer Supplies | 126 | $2,730 | |
| Accounts Payable-Company H | 201 | $2,730 | ||
| ( To record the purchase of supplies on credit) | ||||
| 9-Mar | Cash | 101 | $3,220 | |
| Accounts Receivable—Corporation D | 106.7 | $3,220 | ||
| ( To record the collection of accounts receivable) | ||||
| 11-Mar | Repairs Expense–Computer | 684 | $960 | |
| Cash | 101 | $960 | ||
| (To record the payment for computer repairs) | ||||
| 16-Mar | Cash | 101 | $5,260 | |
| Computer Services Revenue | 403 | $5,260 | ||
| ( To record the collection cash revenue from customer) | ||||
| 19-Mar | Accounts Payable | 201 | $3,830 | |
| Cash | 101 | $3,830 | ||
| ( To record the payment of accounts payable ($1,100 + $2,730)) | ||||
| 24-Mar | Accounts Receivable—Company EL | 106.3 | $9,047 | |
| Computer Services Revenue | 403 | $9,047 | ||
| (To record the billed customer for services) | ||||
| 25-Mar | Accounts Receivable—Company WS | 106.2 | $2,800 | |
| Sales | 413 | $2,800 | ||
| ( To record the sale of merchandise on credit) | ||||
| 25-Mar | Cost of Goods Sold | 502 | $2,002 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $2,002 | ||
| ( To record the cost of sales of March 25 ) | ||||
| 30-Mar | Accounts Receivable—Company IFM | 106.4 | $2,220 | |
| Sales | 413 | $2,220 | ||
| ( To record the sale of merchandise on credit) | ||||
| 30-Mar | Cost of Goods Sold | 502 | $1,048 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $1,048 | ||
| ( To record the cost of sales of March 30 ) | ||||
| 31-Mar | Mileage Expense | 676 | $128 | |
| Cash | 101 | $128 | ||
| (To record the Reimbursement of business mileage) | ||||
Table (1)
2.
Post the journal entries to the accounts in the general ledger of Company BS.
Explanation of Solution
Account: A record, that documents or records the change in assets, liabilities, or equity for a particular period, is referred to as an account.
| Cash No. 101 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | $48,372 | ||||
| 4-Jan | $625 | $47,747 | |||
| 5-Jan | $25,000 | $72,747 | |||
| 9-Jan | $2,668 | $75,415 | |||
| 15-Jan | $600 | $74,815 | |||
| 16-Jan | $4,000 | $78,815 | |||
| 17-Jan | $5,742 | $73,073 | |||
| 22-Jan | $4,653 | $77,726 | |||
| 31-Jan | $1,250 | $76,476 | |||
| 1-Feb | $2,475 | $74,001 | |||
| 3-Feb | $8,414 | $65,587 | |||
| 5-Feb | $600 | $64,987 | |||
| 11-Jan | $5,500 | $70,487 | |||
| 15-Feb | $4,800 | $65,687 | |||
| 26-Feb | $1,000 | $64,687 | |||
| 27-Feb | $192 | $64,495 | |||
| 9-Mar | $3,220 | $67,715 | |||
| 11-Mar | $960 | $66,755 | |||
| 16-Mar | $5,260 | $72,015 | |||
| 19-Mar | $3,830 | $68,185 | |||
| 31-Mar | $128 | $68,057 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Company AE No. 106.1 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 11-Jan | $5,500 | $5,500 | |||
| 11-Feb | $5,500 | $0 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Company WS No. 106.2 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 25-Mar | $2,800 | $2,800 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Company EL No. 106.3 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 24-Mar | $9,047 | $9,047 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Company IFM No. 106.4 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $3,000 | |||
| 30-Mar | $2,220 | $5,220 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Corporation L No. 106.5 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 13-Jan | $5,200 | $5,200 | |||
| 20-Jan | $500 | $4,700 | |||
| 22-Jan | $4,700 | $0 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Company G 106.6 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $2,668 | |||
| 9-Jan | $2,668 | $0 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Company D No. 106.7 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 23-Feb | $3,220 | $3,220 | |||
| 9-Mar | $3,220 | $0 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Incorporation KC No. 106.8 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 26-Jan | $5,800 | $0 | $5,800 | ||
| Accounts Receivable—Incorporation D No. 106.8 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| Merchandise inventory—Incorporation D No. 119 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 7-Jan | $5,800 | $5,800 | |||
| 13-Jan | $3,560 | $2,240 | |||
| 15-Jan | $600 | $2,840 | |||
| 17-Jan | $58 | $2,782 | |||
| 24-Jan | $496 | $2,286 | |||
| 26-Jan | $9,000 | $11,286 | |||
| 26-Jan | $4,640 | $6,646 | |||
| 3-Feb | $90 | $6,556 | |||
| 23-Feb | $2,660 | $3,896 | |||
| 25-Mar | $2,002 | $1,894 | |||
| 30-Mar | $1,048 | $846 | |||
| Compute supplies No. 126 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $580 | |||
| 8-Mar | Balance | $2,730 | $3,310 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance No. 128 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $1,665 | |||
| Prepaid Rent No. 131 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $825 | |||
| 1-Feb | $2,475 | $3,300 | |||
| Office equipment No. 163 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $8,000 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation- Office equipment No. 164 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $400 | |||
| Computer equipment No. 167 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $20,000 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation- Computer equipment No. 168 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $1,250 | |||
| Accounts payable No. 201 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $1,100 | |||
| 7-Jan | Balance | $5,800 | $6,900 | ||
| 17-Jan | Balance | $5,800 | $1,100 | ||
| 24-Jan | Balance | $496 | $604 | ||
| 26-Jan | Balance | $9,000 | $9,604 | ||
| 3-Feb | Balance | $8,504 | $1,100 | ||
| 8-Mar | Balance | $2,730 | $3,830 | ||
| 9-Mar | Balance | $3,830 | $0 | ||
| Wages payable No. 210 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $500 | |||
| 4-Jan | $500 | $0 | |||
| Unearned computer services revenue No. 236 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $1,500 | |||
| 11-Jan | $1,500 | $0 | |||
| Person R, Capital No. 301 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $80,360 | |||
| 5-Jan | $25,000 | $105,360 | |||
| Person R, Withdrawals No. 302 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 15-Feb | $4,800 | $4,800 | |||
| Computer services revenue No. 403 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 11-Jan | $7,000 | $7,000 | |||
| 16-Jan | $4,000 | $11,000 | |||
| 16-Mar | $5,260 | $16,260 | |||
| 24-Mar | $9,047 | $25,307 | |||
| Sales No. 413 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 13-Jan | $5,200 | $5,200 | |||
| 26-Jan | $5,800 | $11,000 | |||
| 23-Feb | $3,220 | $14,220 | |||
| 25-Mar | $2,800 | $17,020 | |||
| 30-Mar | $2,220 | $19,240 | |||
| Sales returns and allowances No. 414 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 20-Jan | $500 | $500 | |||
| Sales discounts No. 415 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 20-Jan | $47 | $0 | $47 | ||
| Cost of goods sold No. 502 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 13-Jan | $3,560 | $3,560 | |||
| 26-Jan | $4,640 | $8,200 | |||
| 23-Feb | $2,660 | $10,860 | |||
| 25-Mar | $2,002 | $12,862 | |||
| 30-Mar | $1,048 | $13,910 | |||
| Depreciation expense - Office equipment No. 612 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Depreciation expense - Computer equipment No. 613 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Wages expense No. 623 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 4-Jan | $125 | $125 | |||
| 31-Jan | $1,250 | $1,375 | |||
| 26-Feb | $1,000 | $2,375 | |||
| Insurance expense No. 637 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Rent expense No. 640 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Computer supplies expense No. 652 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Advertising expense No. 655 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 5-Feb | $600 | $600 | |||
| Mileage expense No. 676 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 27-Feb | $192 | $192 | |||
| 31-Mar | $128 | $320 | |||
| Miscellaneous Expenses No. 677 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Repairs Expense—Computer No. 684 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 11-Mar | $960 | $960 | |||
3.
Prepare a partial worksheet of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2020.
Explanation of Solution
Worksheet: A worksheet is the summarized form of accounting information which is made in order to ensure that the accounts are made properly.
Prepare a partial worksheet of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2020.
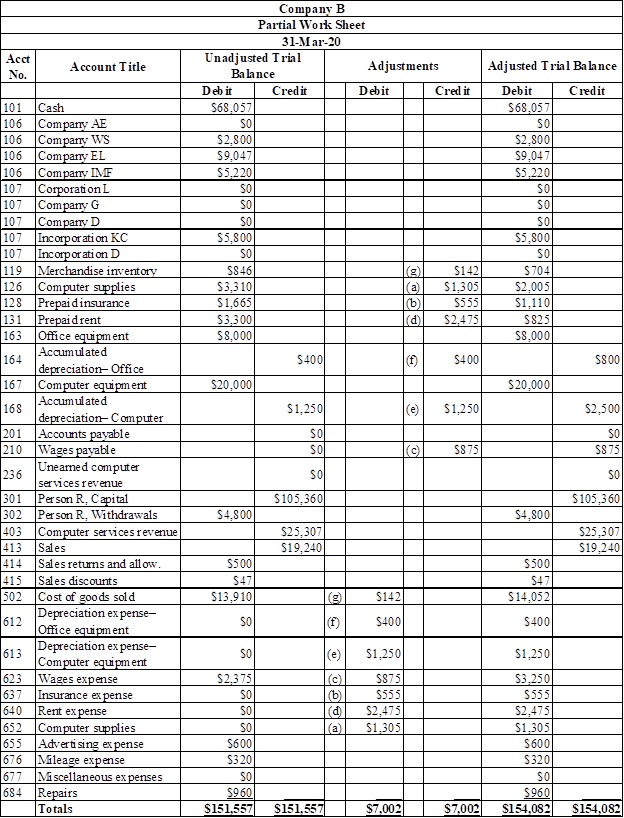
Table (2)
4.
Prepare a single step income statement of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2020.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Single-step income statement: This statement displays the total revenues as one line item from which the total expenses including cost of goods sold is subtracted to arrive at the net profit /net loss for the period.
Prepare a statement of income of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2020.
| Company BS | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the three months ended March 31, 2020 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Revenues | ||
| Computer services revenue | $25,307 | |
| Net sales () | $18,693 | |
| Total revenues | $44,000 | |
| Expenses | ||
| Cost of goods sold | $14,052 | |
| Depreciation expense—Office equipment | $400 | |
| Depreciation expense—Computer equipment | $1,250 | |
| Wages expense | $3,250 | |
| Insurance expense | $555 | |
| Rent expense | $2,475 | |
| Computer supplies expense | $1,305 | |
| Advertising expense | $600 | |
| Mileage expense | $320 | |
| Repairs expense—Computer | $960 | |
| Total expenses | ($25,167) | |
| Net income | $18,833 | |
Table (3)
The net income of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2020 is $18,833.
5.
Prepare a statement of owner’s equity of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2020.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a statement of owner’s equity of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2020.
| Company BS | ||
| Statement of owner’s equity | ||
| For the three months ended March 31, 2020 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Person R, Capital, December 31, 2019 | $80,360 | |
| Add: Investments by owner | 25,000 | |
| Net income | 18,833 | |
| $124,193 | ||
| Less: Withdrawals by owner | ($4,800) | |
| Person R, Capital, as on March 31, 2020 | $119,393 | |
Table (4)
The owner’s equity of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2020 is $119,393.
6.
Prepare a classified balance sheet of Company BS as of March 31, 2020.
Explanation of Solution
Classified balance sheet: The main elements of balance sheet assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity are categorized or classified further into sections in a classified balance sheet. Assets are further classified as current assets, long-term investments, property, plant, and equipment (PPE), and intangible assets.
Prepare a classified balance sheet as of March 31, 2020.
| Company BS | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| As of March 31, 2020 | ||
| Assets | Amount | Amount |
| Current assets | ||
| Cash | $68,057 | |
| Accounts receivable | $22,867 | |
| Merchandise inventory | $704 | |
| Computer supplies | $2,005 | |
| Prepaid insurance | $1,110 | |
| Prepaid rent | $825 | |
| Total current assets | $95,568 | |
| Plant assets | ||
| Office equipment | $8,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation—Office equipment | ($800) | $7,200 |
| Computer equipment | $20,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation—Computer equipment | ($2,500) | $17,500 |
| Total plant assets | $24,700 | |
| Total assets | $120,268 | |
| Liabilities and Stockholder's Equity | ||
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities | ||
| Wages payable | $875 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| Person R, Capital | $119,393 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $120,268 | |
Table (5)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
- Can you explain this financial accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this financial accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forward
- Please provide the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forwardI am searching for the right answer to this financial accounting question using proper techniques.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this financial accounting question using the right financial principles.arrow_forward
- Can you solve this financial accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forwardCan you show me the correct approach to solve this financial accounting problem using suitable standards?arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forward
- I need assistance with this financial accounting problem using valid financial procedures.arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forward
 Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning





