
Concept explainers
All journals and general ledger;
The transactions completed by AM Express Company during March 2016, the first month of the fiscal year, were as follows:
Mar. 1. Issued Check No. 205 for March rent, $2,450.
2. Purchased a vehicle on account from McIntyre Sales Co., $26,900.
3. Purchased office equipment on account from Office Mate Inc., $1,570.
5. Issued Invoice No. 91 to Ellis Co., $7,000.
6. Received check for $7,950 from Chavez Co. in payment of invoice.
7. Issued Invoice No. 92 to Trent Co., $9,840.
9. Issued Check No. 206 for fuel expense, $820.
10. Received check for $10,000 from Sajeev Co. in payment of invoice.
10. Issued Check No. 207 to Office City in payment of $450 invoice.
Mar. 10. Issued Check No. 208 to Bastille Co. in payment of $1,890 invoice.
11. Issued Invoice No. 93 to Jarvis Co., $7,200.
11. Issued Check No. 209 to Porter Co. in payment of $415 invoice.
12. Received check for $7,000 from Ellis Co. in payment of March 5 invoice.
13. Issued Check No. 210 to McIntyre Sales Co. in payment of $26,900 invoice of
March 2.
16. Cash fees earned for March 1-16, $26,800.
16. Issued Check No. 211 for purchase of a vehicle, $28,500.
17. Issued Check No. 212 for miscellaneous administrative expense, $4,680.
18. Purchased maintenance supplies on account from Bastille Co., $2,430.
18. Received check for rent revenue on office space, $900.
19. Purchased the following on account from Master Supply Co. Maintenance supplies, $2,640, and office supplies, $1,500.
20. Issued Check No. 213 in payment of advertising expense, $8,590.
20. Used maintenance supplies with a cost of $4,400 to repair vehicles.
21. Purchased office supplies on account from Office City, $990.
24. Issued Invoice No. 94 to Sajeev Co., $9,200.
25. Received check for $14,000 from Chavez Co. in payment of invoice.
25. Issued Invoice No. 95 to Trent Co., $6,300.
26. Issued Check No. 214 to Office Mate Inc. in payment of $1,570 invoice of March 3.
27. Issued Check No. 215 to J. Wu as a personal withdrawal, $4,000.
30. Issued Check No. 216 in payment of driver salaries, $33,300.
31. Issued Check No. 217 in payment of office salaries, $21,200.
31. Issued Check No. 218 for office supplies, $600.
31. Cash fees earned for March 17-31, $29,400.
Instructions
1. Enter the following account balances in the general ledger as of March 1:
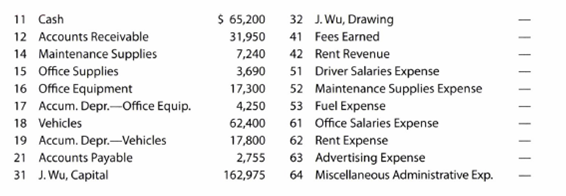
2. Journalize the transactions for March 2016, using the following journals similar to those illustrated in this chapter: single-column revenue journal (p. 35), cash receipts journal (p. 31), purchases journal (p. 37, with columns for Accounts Payable, Maintenance Supplies, Office Supplies, and Other Accounts), cash payments journal (p. 34), and two-column general journal (p. 1). Assume that the daily postings to the individual accounts in the accounts payable subsidiary ledger and the
3. Post the appropriate individual entries to the general ledger.
4. Total each of the columns of the special journals, and post the appropriate totals to the general ledger; insert the account balances.
5. Prepare a trial balance.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 5 Solutions
Working Papers, Chapters 1-17 for Warren/Reeve/Duchac's Accounting, 26th and Financial Accounting, 14th
- Can you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forwardWhich is not an objective of internal controls?A. Safeguard assetsB. Improve profitsC. Ensure accurate recordsD. Promote operational efficiency no aiarrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate answer to this financial accounting problem using appropriate methods.arrow_forward
- Please provide the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using valid calculations.arrow_forward20 Nelson and Murdock, a law firm, sells $8,000,000 of four-year, 8% bonds priced to yield 6.6%. The bonds are dated January 1, 2026, but due to some regulatory hurdles are not issued until March 1, 2026. Interest is payable on January 1 and July 1 each year. The bonds sell for $8,388,175 plus accrued interest. In mid-June, Nelson and Murdock earns an unusually large fee of $11,000,000 for one of its cases. They use part of the proceeds to buy back the bonds in the open market on July 1, 2026 after the interest payment has been made. Nelson and Murdock pays a total of $8,456,234 to reacquire the bonds and retires them. Required1. The issuance of the bonds—assume that Nelson and Murdock has adopted a policy of crediting interest expense for the accrued interest on the date of sale.2. Payment of interest and related amortization on July 1, 2026.3. Reacquisition and retirement of the bonds.arrow_forward13 Which of the following is correct about the difference between basic earnings per share (EPS) and diluted earnings per share? Question 13 options: Basic EPS uses comprehensive income in its calculation, whereas diluted EPS does not. Basic EPS is not a required disclosure, whereas diluted EPS is required disclosure. Basic EPS uses total common shares outstanding, whereas diluted EPS uses the weighted-average number of common shares. Basic EPS is not adjusted for the potential dilutive effects of complex financial structures, whereas diluted EPS is adjusted.arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning



