
Concept explainers
1.
General Ledger
General ledger refers to the ledger that records all the transactions of the business related to the company’s assets, liabilities, owners’ equities, revenues, and expenses. Each subsidiary ledger is represented in the general ledger by summarizing the account.
Accounts payable control account and subsidiary ledger
Accounts payable account and subsidiary ledger is the ledger which is used to post the creditors transaction in one particular ledger account. It helps the business to locate the error in the creditor ledger balance. After all transactions of creditor accounts are posted, the balances in the accounts payable subsidiary ledger should be totaled, and compare with the balance in the general ledger of accounts payable. If both the balance does not agree, the error has been located and corrected.
Purchase journal
Purchase journal refers to the journal that is used to record all purchases on account. In the purchase journal, all purchase transactions are recorded only when the business purchased the goods on account. For example, the business purchased cleaning supplies on account.
Cash payments journal
Cash payments journal refers to the journal that is used to record all transaction which involves the cash payments. For example, the business paid cash to employees (salary paid to employees).
To Prepare: A single column revenue journal and cash receipt journal, and post the accounts in the accounts payable subsidiary ledger.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Purchase journal
Purchase journal of Company WTE in the month of October 2016 is as follows:
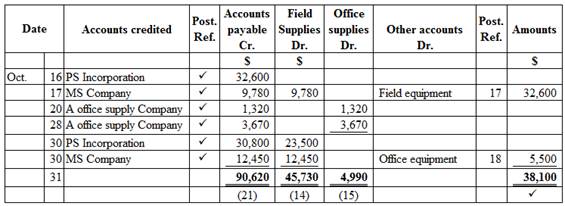
Figure (1)
Cash payment journal
Cash payment journal of Company WTE in the month of October 2016 is as follows:
Cash payment journal
| Date | Check No. | Account debited | Post Ref. | Other accounts Dr. | Accounts payable Dr. | Cash Dr. | |
| Oct. | 16 | 1 | Rent expense | 71 | 7,000 | 7,000 | |
| 18 | 2 | Field supplies | 14 | 4,570 | 4,570 | ||
| Office supplies | 15 | 650 | 650 | ||||
| 24 |
|
✓ | 32,600 | 32,600 | |||
| 26 |
|
✓ | 9,780 | 9,780 | |||
| 28 | Land | 240,000 | 240,000 | ||||
| 30 |
|
✓ | 1,320 | 1,320 | |||
| 31 | Salary expense | 61 | 32,000 | 32,000 | |||
| 31 | 284,220 | 43,700 | 327,920 | ||||
| ✓ | (21) | (11) | |||||
Table (1)
Accounts payable subsidiary ledger
| Name: A Office supply Company | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| Oct. | 20 | P1 | 1,320 | 1,320 | ||
| 28 | P1 | 3,670 | 4,990 | |||
| 30 | CP1 | 1,320 | 3,670 | |||
Table (2)
| Name: MS Company | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| Oct. | 17 | P1 | 9,780 | 9,780 | ||
| 26 | CP1 | 9,780 | - | |||
| 30 | P1 | 12,450 | 12,450 | |||
Table (3)
| Name: PS Incorporation | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| Oct. | 16 | P1 | 32,600 | 32,600 | ||
| 24 | CP1 | 32,600 | - | |||
| 30 | P1 | 30,800 | 30,800 | |||
Table (4)
2. and 3.
To
2. and 3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the general ledger for given accounts as follows:
| Account: Cash Account no. 11 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 31 | CP1 | 327,920 | 327,920 | |||
Table (5)
| Account: Field supplies Account no. 14 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 18 | CP1 | 4,570 | 4,570 | |||
| 31 | P1 | 47,530 | 52,100 | ||||
Table (6)
| Account: Office supplies Account no. 15 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 18 | CP1 | 650 | 650 | |||
| 31 | P1 | 4,990 | 5,460 | ||||
Table (7)
| Account: Prepaid rent Account no. 16 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 31 | J1 | 15,000 | 15,000 | |||
Table (8)
| Account: Field equipment Account no. 17 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 16 | P1 | 32,600 | 32,600 | |||
| 31 | J1 | 15,000 | 17,600 | ||||
Table (9)
| Account: Office equipment Account no. 18 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 31 | P1 | 5,500 | 5,500 | ||||
Table (10)
| Account: Land Account no. 19 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 23 | CP1 | 240,000 | 240,000 | |||
Table (11)
| Account: Accounts payable Account no. 21 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 31 | P1 | 90,620 | 90,620 | |||
| 31 | CP1 | 43,700 | 46,920 | ||||
Table (12)
| Account: Salary expense Account no. 61 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 31 | CP1 | 32,000 | 32,000 | |||
Table (13)
| Account: Rent expense Account no. 71 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 16 | CP1 | 7,000 | 7,000 | |||
Table (14)
| Journal Page 01 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Oct. | 31 | Prepaid rent | 16 | 15,000 | |
| Field equipment | 17 | 15,000 | |||
| (To record leasing of field equipment) | |||||
Table (15)
4.
To prepare: The accounts payable creditor balances.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Accounts payable creditor balance
Accounts payable creditor balance is as follows:
| Company WTE | |
| Accounts payable creditor balances | |
| October 31, 2016 | |
| Amount ($) | |
| A Office supply Company | 3,670 |
| MS Company | 12,450 |
| PS Incorporation | 30,800 |
| Total accounts receivable | 46,920 |
Table (16)
Accounts payable controlling account
Ending balance of accounts payable controlling account is as follows:
| Company WTE | |
| Accounts payable (Controlling account) | |
| October 31, 2016 | |
| Amount ($) | |
| Opening balance | 0 |
| Add: | |
| Total credits (from purchase journal) | 90,620 |
| 90,620 | |
| Less: | |
| Total debits (from cash payment journal) | (43,700) |
| Total accounts payable | 46,920 |
Table (17)
In this case, accounts payable subsidiary ledger is used to identify, and locate the error by way of cross-checking the creditor balance and accounts payable controlling account. From the above calculation, we can understand that both balances of accounts payable is agree, hence there is no error in the recording and posing of transactions.
5.
To discuss: The reason for using subsidiary ledger for the field equipment.
5.
Explanation of Solution
A subsidiary ledger for the field equipment helps the company to track the cost of each piece of equipment, location, useful life, and other necessary data. This information is used for safeguarding the equipment and determining depreciation of equipment.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Working Papers, Chapters 1-17 for Warren/Reeve/Duchac's Accounting, 26th and Financial Accounting, 14th
- C2 X✓ fx Σ N A B 1 Product ☑ Order Quantity C D E F G H K L Product ID ✓ Unit Price Gross Sales Formulas for Columns C, D, & E Product Product ID Unit Price 2 Carry-on Suitcase 3 Carry-on Suitcase 4 Bluetooth Headphones 5 Carry-on Suitcase 6 Travel Pillow 7 Travel Umbrella 8 Battery Pack 9 Travel Pillow 10 Travel Pillow 11 Battery Pack 23 #N/A #N/A #N/A Travel Umbrella B07NQKQ19S $12.51 #N/A #N/A #N/A Bluetooth Headphones B01NAJGGA2 $35.39 12 Battery Pack 13 Travel Pillow 14 Bluetooth Headphones 15 Battery Pack 16 Bluetooth Headphones 17 Travel Umbrella 18 Carry-on Suitcase 19 Bluetooth Headphones 20 Travel Umbrella 21 Bluetooth Headphones 22 Travel Umbrella 23 Battery Pack 24 Bluetooth Headphones 25 Carry-on Suitcase 26 Travel Pillow 27 Battery Pack 28 Carry-on Suitcase 29 Carry-on Suitcase 30 Battery Pack 31 Carry-on Suitcase 32 Travel Pillow 33 Bluetooth Headphones 34 Bluetooth Headphones 22226-22 22272122227222432-29 10 9 23 27 27 23 #N/A #N/A #N/A Battery Pack B00Z9QVE4Q $34.98…arrow_forwardCan you explain the process for solving this financial accounting question accurately?arrow_forwardPlease give me answer with accounting questionarrow_forward
- EXERCISE 3-5 Treasury Stock Held by Subsidiary LO 8 Pool Company purchased 90% of the outstanding common stock of Spruce Company on December 31, 2019, for cash. At that time the balance sheet of Spruce Company was as follows: Required: Current assets Plant and equipment Land Total assets Liabilities Common stock, $20 par value Other contributed capital Retained earnings Total Less treasury stock at cost, 5,000 shares Total equities $1,050,000 990,000 170,000 $2,210,000 $ 820,000 900,000 440,000 150,000 2,310,000 100,000 $2,210,000 Prepare the elimination entry required for the preparation of a consolidated balance sheet workpa- per on December 31, 2019, assuming: (1) The purchase price of the stock was $1,400,000. Assume that any difference between the book value of net assets and the value implied by the purchase price relates to subsidiary land. (2) The purchase price of the stock was $1,160,000. Assume that the subsidiary land has a fair value of $180,000, and the other assets and…arrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting problem using accurate calculation methods.arrow_forwardB2 A 1 DATE VALUE X✓ fx 2 1 3 9 4 548 56 3835 40468 VALUE B C D E F G H MEASURE Current Date (TODAY) VALUE FORMULA MEASURE VALUE FORMULA Current Time (NOW) #N/A #N/A Use E6 "Problem Date" for green cells in col. E & I Cumulative full days this year #N/A Year to date fraction (YEARFRAC) #N/A Use E6 "Problem Date" for green cells in col. E & I Month to date fraction of year #N/A 10/8/2019 Day of the week #N/A 6 Problem Date 7 Year (YEAR) 8 Date Value Fractional Date Month (MONTH) 9 40468.25 Day (DAY) 10 40468.375 11 40468.625 12 13 14 15 DATE DATA CLEANUP and MANIPULATION End of month Start of month Start of next month First day of the year #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A TIP: Use custom date format to display as the name of the day (dddd) Name of month Workdays in current month #N/A #N/A 30 workdays (excluding weekends) from today Days between today and 30 workdays from now #N/A #N/A 16 Target $2,000 17 18 DATE REVENUE MONTH DAY OF WEEK Hit Target? MONTH DAY OF WEEK FORMULAS for…arrow_forward
- Please provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using valid techniques.arrow_forwardB2 A 1 DATE VALUE X✓ fx 2 1 3 9 4 548 56 3835 40468 VALUE B C D E F G H MEASURE Current Date (TODAY) VALUE FORMULA MEASURE VALUE FORMULA Current Time (NOW) #N/A #N/A Use E6 "Problem Date" for green cells in col. E & I Cumulative full days this year #N/A Year to date fraction (YEARFRAC) #N/A Use E6 "Problem Date" for green cells in col. E & I Month to date fraction of year #N/A 10/8/2019 Day of the week #N/A 6 Problem Date 7 Year (YEAR) 8 Date Value Fractional Date Month (MONTH) 9 40468.25 Day (DAY) 10 40468.375 11 40468.625 12 13 14 15 DATE DATA CLEANUP and MANIPULATION End of month Start of month Start of next month First day of the year #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A TIP: Use custom date format to display as the name of the day (dddd) Name of month Workdays in current month #N/A #N/A 30 workdays (excluding weekends) from today Days between today and 30 workdays from now #N/A #N/A 16 Target $2,000 17 18 DATE REVENUE MONTH DAY OF WEEK Hit Target? MONTH DAY OF WEEK FORMULAS for…arrow_forwardI need help finding the correct solution to this financial accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forward
- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning  Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning





