
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product obtained on reaction of
Concept introduction:
In an electrophilic addition reaction, there is an addition of an electrophilic reagent on a nucleophilic group. The double bond and triple bond containing compounds act as a nucleophile. The addition of electrophilic reagent on nucleophilic compound leads to the dissociation of
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed on reaction of
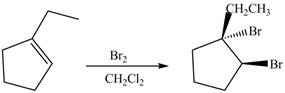
Explanation of Solution
In the reaction of
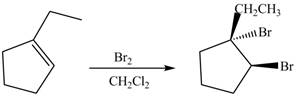
Figure 1
The product formed by reaction of
The reaction between
(b)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product obtained on reaction of
Concept introduction:
In the reactionof
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In the reaction,
The general view of
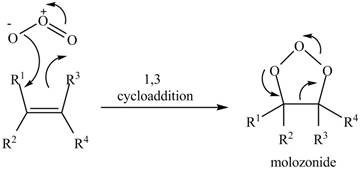
Figure 2
In the same manner,
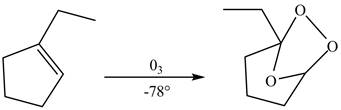
Figure 3
The product formed by the reaction between
(c)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product obtained on the reaction of
Concept introduction:
In the reactionof alkene with ozone, the oxidation of alkene takes place which leads to form molozonide product. This reaction takes place through
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
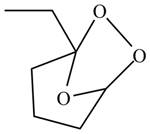
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The compound
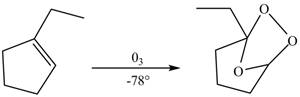
Figure 3
The molozonide formed is unstable in nature, therefore, it gets easily reduced by
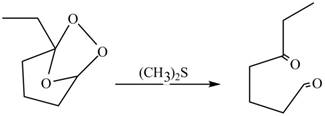
Figure 4
Therefore, the product formed by the reaction between
The reaction between
(d)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product obtained on the reaction of
Concept introduction:
In the reactionof alkene with ozone, the oxidation of alkene takes place which leads to form molozonide product. This reaction takes place through
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The compound
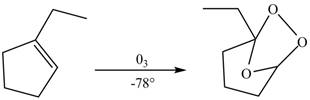
Figure 3
The molozonide formed is unstable in nature, therefore, it gets easily oxidized by
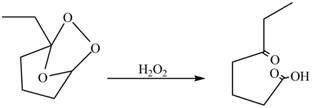
Figure 5
Therefore, the product formed by the reaction between
The reaction between
(e)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
The reaction between unsaturated alkene with
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between
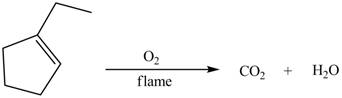
Figure 6
Therefore, the reaction between
The reaction between
(f)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
In markovnikov’s addition of
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In the reaction of
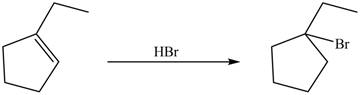
Figure 7
Therefore, the product formed by the reaction between
Thereaction between
(g)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
.In an electrophilic addition reaction, there is an addition of an electrophilic reagent on a nucleophilic group. The double bond and triple bond containing compounds act as nucleophile. The addition of electrophilic reagent on nucleophilic compound leads to the dissociation of
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In the reaction first reaction between
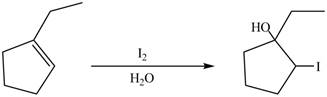
Figure 8
Therefore, the reaction between
The reaction between
(h)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
In acatalytic hydrogenation reaction, palladium is used as a catalyst which accelerates the
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In this reaction, palladium is used as a catalyst which helps in accelerating the rate of hydrogenation reaction. This reaction leads to conversion of
The product formed by the reaction between
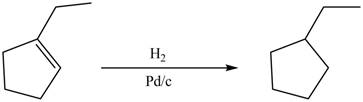
Figure 9
Theproduct formed by the reaction between
(i)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
In Anti-Markovnikov’s addition of
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed on reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In thereaction, in presence of peroxides,
The product formed by the reaction between
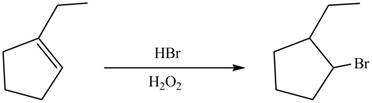
Figure 10
The product formed by the reaction between
(j)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of ![]() with
with
Concept introduction:
In hydroboration reaction, antimarkovnikov’s addition of
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by thereaction of
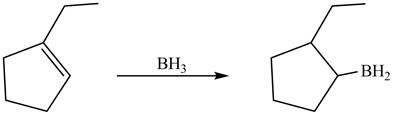
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between
The product formed by thereaction between
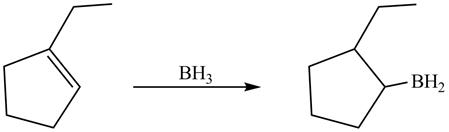
Figure 11
The product formed by the reaction between
(k)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product formed by the reaction of product of
Concept introduction:
In hydroboration reaction, antimarkovnikov’s addition of
The compound
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed on reaction of boron substitued
Explanation of Solution
In the reaction,.the hydroxide group of
The product formed by the reaction between boron substitued
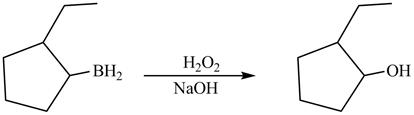
Figure 12
The product formed by thereaction between boron substitued
(l)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
Inan oxymercuration reaction,
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed on reaction of
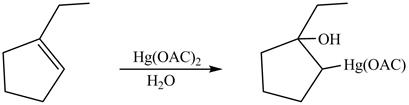
Explanation of Solution
This is an oxymercuration reaction in which
The product formed by the reaction between
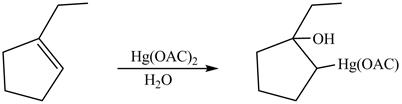
Figure 13
The product formed by thereaction between
(m)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Concept introduction:
In an oxymercuration reaction,
In demercuration reaction,
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The Principal organic product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The product formed by the reaction between
In demercuration reaction,
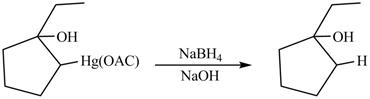
Figure 14
The product formed on reaction is
The product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
(n)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Concept introduction:
In an electrophilic addition reaction, there is an addition of an electrophilic reagent on a nucleophilic group. The double bond and triple bond containing compounds act as a nucleophile. The addition of electrophilic reagent on nucleophilic compound leads to the dissociation of
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between
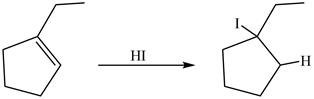
Figure 15
Principal organic product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
(o)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Concept introduction:
The reaction between an alkene,
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The Principal organic product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between ![]() in presence of
in presence of
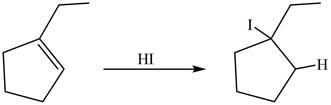
Figure 15
The product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- (a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forward
- Draw a mechanism for the following synthetic transformation including reagents and any isolable intermediates throughout the process. Please clearly indicate bond cleavage/formation using curly arrows. MeO2Carrow_forwardCHEM 310 Quiz 8 Organic Chemistry II Due: Tuesday, April 25th, at 11:59 pm. This quiz is open textbook / open notes - but you must work alone. You cannot use the internet or the solutions manual for the book. Scan in your work and record an explanation of your mechanism. You may record this any way that you like. One way would be to start an individual Zoom meeting, start recording, "share your screen" and then talk through the problem. This will be converted to an .mp4 file that you can upload into Canvas using the "record/upload media" feature. Pyridine, benzoic acid and benzene are dissolved in ethyl acetate. Design and provide a plan / flow chart for separating and isolating each of these components. Pyridine and benzene are liquids at room temperature. Benzoic acid is a solid. You have ethyl acetate, 2M NaOH, 2M HCI and anhydrous MgSO4 available, as well as all the glassware and equipment that you used in the organic lab this year. Provide accurate acid/base reactions for any…arrow_forwardCan anyone help me solve this step by step. Thank you in advaarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





