
Concept explainers
Explain how entities are transformed into tables.
Explanation of Solution
Entity:
An entity is an object that the user wants to model and store the information about an object.
- Entity normally recognizable concepts such as things, place, person, unit or any item relevance to the database.
- Employee, Lecturer, Student are some of the examples of entities.
Table:
Table is a collection of associated data, consists of rows and columns.
- These data are arranged in a structured layout within a database.
Steps for transforming entities into table:
- In the start a table for each entity is created and the name is given to that entity.
- Specify the primary key for that table.
- Columns has to created in relation for each and every attribute present in the entity.
- In the final step, normalize the table.
Example:
Consider the example of transforming entity into table is as follows:
Entity:
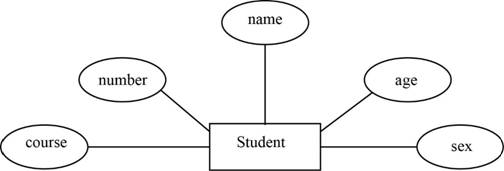
Table:

Explanation:
In the above entity diagram, the “Student” is the entity and “number”, “name”, “age”, “sex”, and “course” are the attributes of that entity.
In the above table, “number” acts as the primary key for the “Student” table. Finally normalize the data in the table.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK DATABASE CONCEPTS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Modern Database Management
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
- I need help in explaining how I can demonstrate how the Laplace & Inverse transformations behaves in MATLAB transformation (ex: LIke in graph or something else)arrow_forwardYou have made the Web solution with Node.js. please let me know what problems and benefits I would experience while making the Web solution here, as compared to any other Web solution you have developed in the past. what problems and benefits/things to keep in mind as someone just learningarrow_forwardPHP is the server-side scripting language. MySQL is used with PHP to store all the data. EXPLAIN in details how to install and run the PHP/MySQL on your computer. List the issues and challenges I may encounter while making this set-up? why I asked: I currently have issues logging into http://localhost/phpmyadmin/ and I tried using the command prompt in administrator to reset the password but I got the error LOCALHOST PORT not found.arrow_forward
- Programming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
 A Guide to SQLComputer ScienceISBN:9781111527273Author:Philip J. PrattPublisher:Course Technology Ptr
A Guide to SQLComputer ScienceISBN:9781111527273Author:Philip J. PrattPublisher:Course Technology Ptr 
 Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285196145Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos CoronelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285196145Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos CoronelPublisher:Cengage Learning





