
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The electrophilic group for the given reaction is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one
Answer to Problem 5.1P
In the given reaction, iodine cation is behaving as an electrophile.
Explanation of Solution
In acid catalyzed hydration reaction, nucleophile goes to the more substituted carbon of the
In the given reaction, addition of electrophile over carbon-carbon double bond takes place. This will result in the formation of intermediate that is carbocation. Thus, the addition of electrophile is at less substituted carbon of the alkene to give the desired product as shown below.
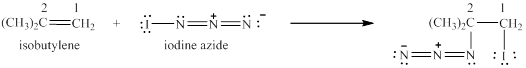
Figure 1
In this case, azide ion is behaving as a nucleophile, whereas iodine cation is behaving as an electrophile.
In the given reaction, iodine cation is behaving as an electrophile.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the given reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons are known as a nucleophile. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving group by attacking the electron deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 5.1P
The product formed by the given reaction is shown below.
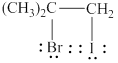
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is,
![]()
Figure 2
The electronegativity of bromine is higher than iodine, thus due to which in iodine bromide iodine will act as an electrophile, whereas bromide ion will act as a nucleophile. The given reaction will follow Markovnikov’s rule to form the desired product as shown below.

Figure 3
The product formed by the given reaction is shown in Figure 3.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- Assign the functional group bands on the IR spectra.arrow_forwardFind the pH of a 0.120 M solution of HNO2. Find the pH ignoring activity effects (i.e., the normal way). Find the pH in a solution of 0.050 M NaCl, including activityarrow_forwardPlease help me answer these three questions. Required info should be in data table.arrow_forward
- Draw the major organic substitution product or products for (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane reacting with the given nucleophile. Clearly drawn the stereochemistry, including a wedged bond, a dashed bond and two in-plane bonds at each stereogenic center. Omit any byproducts. Bri CH3CH2O- (conc.) Draw the major organic product or products.arrow_forwardTartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forward
- Order the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forwardOrdene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forwardCan I please get all final concentrations please!arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
