
Chemistry
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780078021510
Author: Raymond Chang Dr., Kenneth Goldsby Professor
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.18QP
Consider the following gaseous sample in a cylinder fitted with a movable piston. Initially there are n moles of the gas at temperature T, pressure P, and volume V.
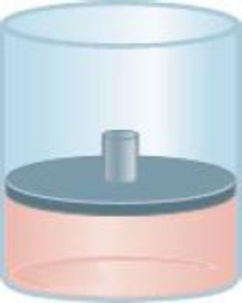
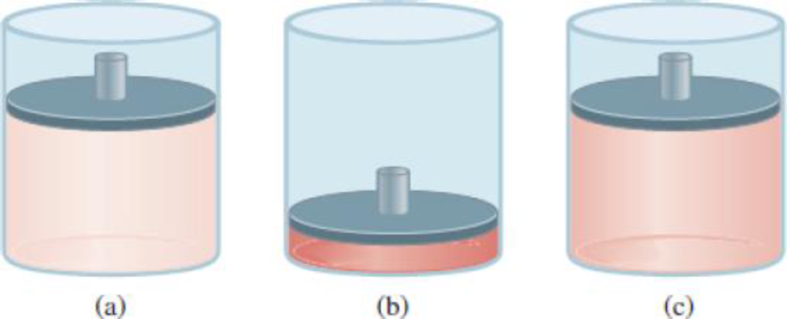
Choose the cylinder that correctly represents the gas after each of the following changes.
(1) The pressure on the piston is tripled at constant n and T. (2) The temperature is
doubled at constant n and P. (3) n moles of another gas are added at constant T and P. (4) T is halved and pressure on the piston is reduced to a quarter of its original value.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Manoharan Mariappan, FR.D.,
34) Complete the following reaction starting from hex-1-yne proceeding via different substitution reactions forming
2-heptanone.
(25 pts).
A
Sia₂BH
H₂O₂
NaOH
Br
D
Mechanism for reaction D - ether-cleavage:
10
B
Ph-MgCI, THF
H₁₂O+
D
HBr (XS)
C
TsCl, Py
CH3-CH2-CH2-ONa
In the table below, the correct structure for (2R)-3-methylpentan-2-ol (IUPAC
name)
can be represented by the letter
OH
OH
HE
> '
ÕH
C
B
OH
D
A/
E
OH
Predict the major products of the following organic reaction:
+
A Δ
?
Some important notes:
• Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below.
• If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead.
Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers.
Check
Click and drag to start drawing a structure.
Save For Later
2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use
Chapter 5 Solutions
Chemistry
Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 1PECh. 5.2 - Prob. 2PECh. 5.2 - Rank the following pressures from lowest to...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 2RCCh. 5.3 - Prob. 1RCCh. 5.4 - Calculate the volume (in liters) occupied by 2.12...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 4PECh. 5.4 - Prob. 1RCCh. 5.4 - A sample of chlorine gas occupies a volume of 946...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 6PE
Ch. 5.4 - A gas initially at 4.0 L, 1.2 atm, and 66C...Ch. 5.4 - What is the density (in g/L) of uranium...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 9PECh. 5.4 - Prob. 10PECh. 5.5 - Prob. 11PECh. 5.5 - The equation for the metabolic breakdown of...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 13PECh. 5.5 - Prob. 1RCCh. 5.6 - Prob. 14PECh. 5.6 - Prob. 15PECh. 5.6 - Prob. 1RCCh. 5.7 - Prob. 16PECh. 5.7 - Prob. 17PECh. 5.7 - Prob. 1RCCh. 5.8 - Using the data shown in Table 5.4, calculate the...Ch. 5.8 - Prob. 1RCCh. 5 - Prob. 5.1QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.2QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.3QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.4QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.5QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.6QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.7QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.8QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.9QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.10QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.11QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.12QPCh. 5 - Convert 562 mmHg to atm.Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.14QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.15QPCh. 5 - A gaseous sample of a substance is cooled at...Ch. 5 - Consider the following gaseous sample in a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.19QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.20QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.21QPCh. 5 - A sample of air occupies 3.8 L when the pressure...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.23QPCh. 5 - Under constant-pressure conditions a sample of...Ch. 5 - Ammonia burns in oxygen gas to form nitric oxide...Ch. 5 - Molecular chlorine and molecular fluorine combine...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.27QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.28QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.29QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.30QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.31QPCh. 5 - Given that 6.9 moles of carbon monoxide gas are...Ch. 5 - What volume will 5.6 moles of sulfur hexafluoride...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.34QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.35QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.36QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.37QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.38QPCh. 5 - An ideal gas originally at 0.85 atm and 66C was...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.40QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.41QPCh. 5 - Dry ice is solid carbon dioxide. A 0.050-g sample...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.43QPCh. 5 - At 741 torr and 44C, 7.10 g of a gas occupy a...Ch. 5 - Ozone molecules in the stratosphere absorb much of...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.46QPCh. 5 - A 2.10-L vessel contains 4.65 g of a gas at 1.00...Ch. 5 - Calculate the density of hydrogen bromide (HBr)...Ch. 5 - A certain anesthetic contains 64.9 percent C, 13.5...Ch. 5 - A compound has the empirical formula SF4. At 20C,...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.51QPCh. 5 - The density of a mixture of fluorine and chlorine...Ch. 5 - Consider the formation of nitrogen dioxide from...Ch. 5 - Methane, the principal component of natural gas,...Ch. 5 - When coal is burned, the sulfur present in coal is...Ch. 5 - In alcohol fermentation, yeast converts glucose to...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.57QPCh. 5 - A quantity of 0.225 g of a metal M (molar mass =...Ch. 5 - What is the mass of the solid NH4Cl formed when...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.60QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.61QPCh. 5 - Ethanol (C2H5OH) burns in air:...Ch. 5 - (a) What volumes (in liters) of ammonia and oxygen...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.64QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.65QPCh. 5 - A sample of air contains only nitrogen and oxygen...Ch. 5 - A mixture of gases contains 0.31 mol CH4, 0.25 mol...Ch. 5 - A 2.5-L flask at 15C contains a mixture of N2, He,...Ch. 5 - Dry air near sea level has the following...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.70QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.71QPCh. 5 - A sample of zinc metal reacts completely with an...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.73QPCh. 5 - A sample of ammonia (NH3) gas is completely...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.75QPCh. 5 - The volume of the box on the right is twice that...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.78QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.79QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.80QPCh. 5 - Compare the root-mean-square speeds of O2 and UF6...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.82QPCh. 5 - The average distance traveled by a molecule...Ch. 5 - At a certain temperature the speeds of six gaseous...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.85QPCh. 5 - The 235U isotope undergoes fission when bombarded...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.87QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.88QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.90QPCh. 5 - (a) A real gas is introduced into a flask of...Ch. 5 - Using the data shown in Table 5.4, calculate the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.94QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.95QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.96QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.97QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.98QPCh. 5 - When ammonium nitrite (NH4NO2) is heated, it...Ch. 5 - The percent by mass of bicarbonate (HCO3) in a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.101QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.102QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.103QPCh. 5 - A healthy adult exhales about 5.0 102 mL of a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.105QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.106QPCh. 5 - Some commercial drain cleaners contain a mixture...Ch. 5 - The volume of a sample of pure HCl gas was 189 mL...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.109QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.110QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.111QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.112QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.113QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.114QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.115QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.116QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.117QPCh. 5 - Commercially, compressed oxygen is sold in metal...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.119QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.120QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.121QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.122QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.123QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.124QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.125QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.126QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.127QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.128QPCh. 5 - Acidic oxides such as carbon dioxide react with...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.130QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.131QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.132QPCh. 5 - Atop Mt. Everest, the atmospheric pressure is 210...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.134QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.135QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.136QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.137QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.138QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.139QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.140QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.141QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.142QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.143QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.144QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.145QPCh. 5 - At what temperature will He atoms have the same...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.148QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.149QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.150QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.151QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.152QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.153QPCh. 5 - A 6.11-g sample of a Cu-Zn alloy reacts with HCl...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.155QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.156QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.157QPCh. 5 - A mixture of methane (CH4) and ethane (C2H6) is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.159QPCh. 5 - One way to gain a physical understanding of b in...Ch. 5 - Use the van der Waals constants in Table 5.4. to...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.162QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.163QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.164QPCh. 5 - Referring to Figure 5.17, we see that the maximum...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.166QPCh. 5 - A gaseous hydrocarbon (containing C and H atoms)...Ch. 5 - Three flasks (a)(c) contain gases A (red) and B...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.169QPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.170QPCh. 5 - In 2012, Felix Baumgartner jumped from a balloon...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.172IMECh. 5 - A flask with a volume of 14.5 L contains 1.25...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.174IMECh. 5 - Prob. 5.175IMECh. 5 - Prob. 5.176IMECh. 5 - Prob. 5.177IME
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Why is analysing salt content (using Mohr titration) in both regular & salt reduced tomato sauce important?arrow_forwardIn the image below, correctly name the glassware # _P ( Blank 1) and T ( Blank 2). 景 A W Blank # 1 Blank #2 1000 +19 E E D 0 0-0 G H A A K Π 12 R M N S 0-0-arrow_forwardFeedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: CN Δ + A ? NC Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. esc Check 80 MH F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 50 @ # C % 95 € Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C A DII F6 F7 F8 7 * 8 Λ & 6 F9 F10 9 0 4arrow_forward
- Incorrect Feedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: ཤིགས་བྱ རྩ་ཅད་ཀྱིས་༢༩ + Some important notes: A ^ ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. E Check 0 لا Save For La ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of All F9 Aarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + Δ A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privaarrow_forwardesc 2 Incorrect Feedback: Your answer is incorrect. Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? A O • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. . If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Check F1 ! @ X C Save For Later Submit Assignment 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility 80 et A ད 1 4 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 # $ 45 % A 6 87 & * 8 9 ) 0 + ||arrow_forward
- Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ?A Δ O • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilit ku F11arrow_forward१ eq ine teaching and × + rn/takeAssignment/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator-assignment-take [Review Topics] [References] Write an acceptable IUPAC name for the compound below. (Only systematic names, not common names are accepted by this question.) Keep the information page open for feedback reference. The IUPAC name is In progress mit Answer Retry Entire Group 5 more group attempts remaining Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support Save and Exitarrow_forwardDraw the molecules.arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-hexan-2-ol with arrows please.arrow_forward. Draw the products for addition reactions (label as major or minor) of the reaction between 2-methyl-2-butene and with following reactants : Steps to follow : A. These are addition reactions you need to break a double bond and make two products if possible. B. As of Markovnikov rule the hydrogen should go to that double bond carbon which has more hydrogen to make stable products or major product. Here is the link for additional help : https://study.com/academy/answer/predict-the-major-and-minor-products-of-2-methyl- 2-butene-with-hbr-as-an-electrophilic-addition-reaction-include-the-intermediate- reactions.html H₂C CH3 H H3C CH3 2-methyl-2-butene CH3 Same structure CH3 IENCESarrow_forwardDraw everything on a piece of paper including every single step and each name provided using carbons less than 3 please.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Step by Step Stoichiometry Practice Problems | How to Pass ChemistryMole Conversions Made Easy: How to Convert Between Grams and Moles; Author: Ketzbook;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b2raanVWU6c;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY