
(a)
To show:
At interior optimum, the
Explanation of Solution
In
Budget constraint/line shows all probable combinations of two products that can be bought.
given the level of earning of the consumer and the market values of both products.
Indifference curve (IC) displays all probable combination of two goods that gives the same level of satisfaction to the consumer.
The consumption bundle is optimalat the point of tangency of the budget line and the indifference curve. The slope of the IC and the budget line are equal at this point.
Consumer's marginal utility functions
The Consumer has income I.
Let the prices of x and ybe denoted as Px and Py.
The interior optimum basket is specified by the solution:
Usingabove equation to find the demand for x as follows:
(b)
To calculate:
The value of Px for which consumer would ever purchase any X.
Answer to Problem 5.16P
Explanation of Solution
Utility function refers to measure preferences over set of product and services. it is majorly used in economics. A function is to satisfy consumers for all grouping of products consumed.
Marginal utility (MU) can be defined as the extra benefit added from the consumption of one more unit of a product or service.
The demand curve is the graph display the demand for products or service an alteration with a change in
Given
I =100, and
Since
The maximum value for which the consumer would buy can be calculated as −
From Equ (1), x = 0 (as it can't ne negative)
(c)
If
Explanation of Solution
Pattern of consumption is the expenses pattern of income groups in the categories of products like food, clothing and optional items.
The budget constraint traces the highest indifference curve accessible; the consumer is defined to be optimizing consumption.
Suppose that
Find out the optimal consumption basket of x and y.
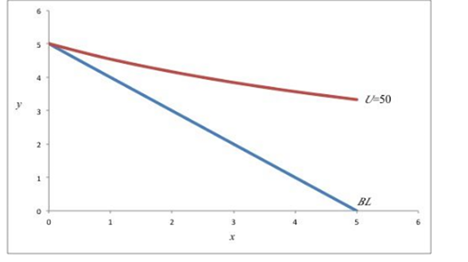
The utility function
This implies that the consumer could have a positive level of utility with purchases of y and no units of x.
The Utility is maximized in the graph
Since this corresponds to a corner point optimum where,
(d)
The marginal rate of substitution ofx for y with the ratio
Explanation of Solution
Marginal rate of substitution is used in economics. In this,the consumer gets some amount of one product in return for another product. It keeps the same level of utility.
The corner point has the price ratio
To compare this ratio to the marginal rate of substitution of x and y, use the equation for the marginal rate of substitution.
As the marginal rate of substitution of x for y is a smaller amount than the price ratio of 1 and the marginal rate of substitution of x for y is diminishing as xrises.
This confirms that the consumer would decrease utility if a positive amount of x were purchased.
(e)
If income remains at 100 then the demand schedule for x for all values Px is to be determinedand location dependsupon thevalue of Py is to be checked.
Explanation of Solution
Demand curve is the graph showing the demand for goods or service changes with change in price.
Let us draw the demand schedule for x for all values of Px when I =100 which is given by the equation is
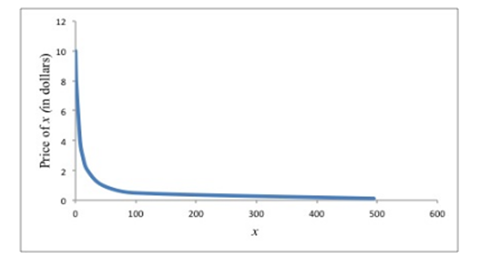
The demand curve for x is downward sloping and bowed towards the origin.
As the demand schedule equation
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK MICROECONOMICS
- 3. Consider a call on the same underlier (Cisco). The strike is $50.85, which is the forward price. The owner of the call has the choice or option to buy at the strike. They get to see the market price S1 before they decide. We assume they are rational. What is the payoff from owning (also known as being long) the call? What is the payoff from selling (also known as being short) the call? Payoff from Call with Strike of k=$50.85 S1 Long $100 $95 $90 $85 $80 $75 $70 $65 $60 $55 $50.85 $50 $45 $40 $35 $30 $25 Shortarrow_forward4. Consider a put on the same underlier (Cisco). The strike is $50.85, which is the forward price. The owner of the call has the choice or option to buy at the strike. They get to see the market price S1 before they decide. We assume they are rational. What is the payoff from owning (also known as being long) the put? What is the payoff from selling (also known as being short) the put? Payoff from Put with Strike of k=$50.85 S1 Long $100 $95 $90 $85 $80 $75 $70 $65 $60 $55 $50.85 $50 $45 $40 $35 $30 $25 Shortarrow_forwardThe following table provides information on two technology companies, IBM and Cisco. Use the data to answer the following questions. Company IBM Cisco Systems Stock Price Dividend (trailing 12 months) $150.00 $50.00 $7.00 Dividend (next 12 months) $7.35 Dividend Growth 5.0% $2.00 $2.15 7.5% 1. You buy a futures contract instead of purchasing Cisco stock at $50. What is the one-year futures price, assuming the risk-free interest rate is 6%? Remember to adjust the futures price for the dividend of $2.15.arrow_forward
- 5. Consider a one-year European-style call option on Cisco stock. The strike is $50.85, which is the forward price. The risk-free interest rate is 6%. Assume the stock price either doubles or halves each period. The price movement corresponds to u = 2 and d = ½ = 1/u. S1 = $100 Call payoff= SO = $50 S1 = $25 Call payoff= What is the call payoff for $1 = $100? What is the call payoff for S1 = $25?arrow_forwardMC The diagram shows a pharmaceutical firm's demand curve and marginal cost curve for a new heart medication for which the firm holds a 20-year patent on its production. Assume this pharmaceutical firm charges a single price for its drug. At its profit-maximizing level of output, it will generate a total profit represented by OA. areas J+K. B. areas F+I+H+G+J+K OC. areas E+F+I+H+G. D. - it is not possible to determine with the informatio OE. the sum of areas A through K. (...) Po P1 Price F P2 E H 0 G B Q MR D ōarrow_forwardPrice Quantity $26 0 The marketing department of $24 20,000 Johnny Rockabilly's record company $22 40,000 has determined that the demand for his $20 60,000 latest CD is given in the table at right. $18 80,000 $16 100,000 $14 120,000 The record company's costs consist of a $240,000 fixed cost of recording the CD, an $8 per CD variable cost of producing and distributing the CD, plus the cost of paying Johnny for his creative talent. The company is considering two plans for paying Johnny. Plan 1: Johnny receives a zero fixed recording fee and a $4 per CD royalty for each CD that is sold. Plan 2: Johnny receives a $400,000 fixed recording fee and zero royalty per CD sold. Under either plan, the record company will choose the price of Johnny's CD so as to maximize its (the record company's) profit. The record company's profit is the revenues minus costs, where the costs include the costs of production, distribution, and the payment made to Johnny. Johnny's payment will be be under plan 2 as…arrow_forward
- Which of the following is the best example of perfect price discrimination? A. Universities give entry scholarships to poorer students. B. Students pay lower prices at the local theatre. ○ C. A hotel charges for its rooms according to the number of days left before the check-in date. ○ D. People who collect the mail coupons get discounts at the local food store. ○ E. An airline offers a discount to students.arrow_forwardConsider the figure at the right. The profit of the single-price monopolist OA. is shown by area D+H+I+F+A. B. is shown by area A+I+F. OC. is shown by area D + H. ○ D. is zero. ○ E. cannot be calculated or shown with just the information given in the graph. (C) Price ($) B C D H FIG шо E MC ATC A MR D = AR Quantityarrow_forwardConsider the figure. A perfectly price-discriminating monopolist will produce ○ A. 162 units and charge a price equal to $69. ○ B. 356 units and charge a price equal to $52 for the last unit sold only. OC. 162 units and charge a price equal to $52. OD. 356 units and charge a price equal to the perfectly competitive price. Dollars per Unit $69 $52 MR 162 356 Output MC Darrow_forward
- The figure at right shows the demand line, marginal revenue line, and cost curves for a single-price monopolist. Now suppose the monopolist is able to charge a different price on each different unit sold. The profit-maximizing quantity for the monopolist is (Round your response to the nearest whole number.) The price charged for the last unit sold by this monopolist is $ (Round your response to the nearest dollar.) Price ($) 250 225- 200- The monopolist's profit is $ the nearest dollar.) (Round your response to MC 175- 150 ATC 125- 100- 75- 50- 25- 0- °- 0 20 40 60 MR 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 Quantityarrow_forwardThe diagram shows a pharmaceutical firm's demand curve and marginal cost curve for a new heart medication for which the firm holds a 20-year patent on its production. At its profit-maximizing level of output, it will generate a deadweight loss to society represented by what? A. There is no deadweight loss generated. B. Area H+I+J+K OC. Area H+I D. Area D + E ◇ E. It is not possible to determine with the information provided. (...) 0 Price 0 m H B GI A MR MC D Outparrow_forwardConsider the figure on the right. A single-price monopolist will produce ○ A. 135 units and charge a price equal to $32. B. 135 units and generate a deadweight loss. OC. 189 units and charge a price equal to the perfectly competitive price. ○ D. 189 units and charge a price equal to $45. () Dollars per Unit $45 $32 MR D 135 189 Output MC NGarrow_forward
 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning





