
(a)
The
Answer to Problem 5.24P
TheJ's optimal basket is 50 units of y and
The D's optimal basket is 50 units of y and
Explanation of Solution
Budget constraint/line shows all possible combinations of two goods that can be purchased, given the level of income of the consumer and the market prices of both goods.
Indifference curve (IC) shows all possible combination of two goods that gives the same level of satisfaction to the consumer.
At the point of tangency of the budget line and the indifference curve, the consumption bundle is optimal. The slope of the IC and the budget line are equal at this point.
There are two consumers J and D and the market for goods x and y.
The utility function of J is
The
The utility function of D is
The marginal utilities
D has an income of 150.
The price of good y is
Find Optimal basket of J when
Find y by substituting
Also,
Hence J's optimal basket is 50 units of y and
Find the optimal basket od D when the price of y is
Find y by substituting
Also,
Hence D's optimal basket is 50 units of y and
(b)
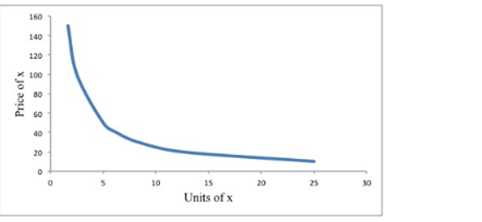
For all values of P, Separate graph for consumers
Explanation of Solution
This the J's demand for x for all values of P:
This is the D's demand for x for all values of P:
(c)
The given consumers are only consumers then aggregate demand is to be computedand plotted.
Answer to Problem 5.24P
Graph for the aggregate demand curve for x, for
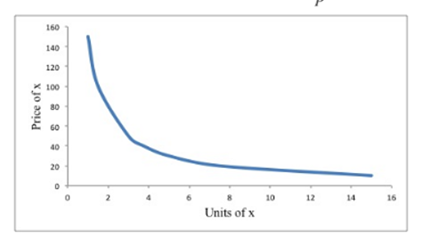
Explanation of Solution
To compute the demand D When J and D are the only consumers by adding consumer's demand for x.
Graph for the aggregate demand curve for x, Where
(d)
There is one more consumer that has the same utility function and income as consumer 2 then aggregate demand is to be plotted.
Explanation of Solution
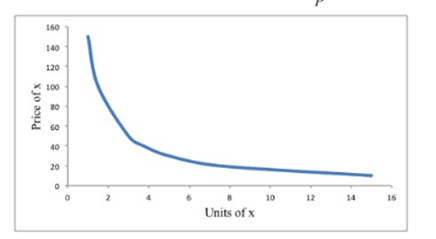
Compute aggregate demand when J, D and another consumer with the same utility function and income as D are the only consumers.
Calculate aggregate demand by adding each consumer's demand x.
Graph the aggregate demand curve for x where
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK MICROECONOMICS
- Critically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardOutline the nine (9) consumer rights as specified in the Consumer Rights Act in South Africa.arrow_forward
- In what ways could you show the attractiveness of Philippines in the form of videos/campaigns to foreign investors? Cite 10 examples.arrow_forwardExplain the following terms and provide an example for each term: • Corruption • Fraud • Briberyarrow_forwardIn what ways could you show the attractiveness of a country in the form of videos/campaigns?arrow_forward
 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning


 Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning





