
Concept explainers
Interpretation:Stereocenters in the indicated chiral molecules should be marked and any one of the stereoisomers should be drawn along with absolute stereochemistry as R or S.
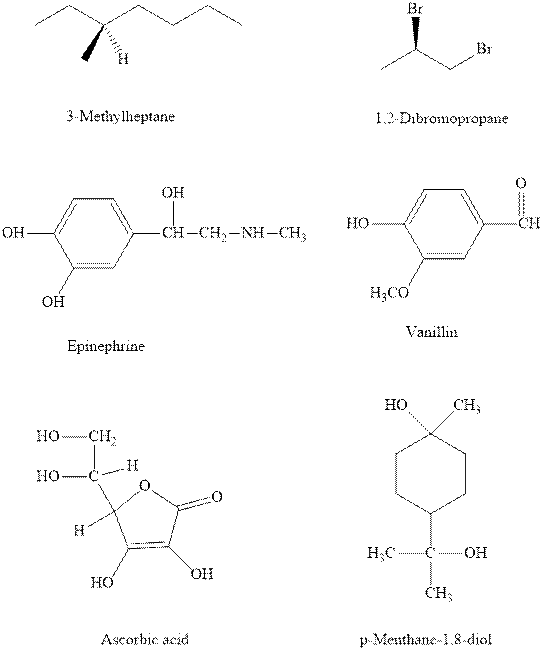
Concept introduction:Chiral carbon is any stereocenter attached to four different alkyl substituents. It is also known as stereocenter. If any two of the substituent happen to be similar the center is regarded as achiral. However, the most essential criteria that help to distinguish a chiral or non-chiral system is presence of any symmetry element. If any plane center or axis of symmetry is identified it makes molecule achiral and optically inactive.
In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of
If the groups read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
The Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK STUDY GUIDE/SOLUTIONS MANUAL FOR OR
- Draw the products of this reduction of a ketone with sodium borohydride. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicableIgnore any inorganic byproducts. 1) NaBH4 2) HCI/H2O Select to Drawarrow_forwardWhy do you think people who live at high altitudes are advised to add salt to water when boiling food like pasta? What mole fraction of NaCl is needed to raise the boiling point of H2O by 3˚C? Does the amount of salt added to water (typically about one teaspoon to four quarts of water) substantially change the boiling point? (Kb (H2O) = 0.51˚C/molal.)arrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward
- pls help asaparrow_forward9. Consider the following galvanic cell: Fe (s) | Fe(NO3)2 (aq) || Sn(NO3)2 (aq) | Sn (s) a. Write an equation for the half reactions occurring at the anode and cathode. b. Calculate the standard cell potential Show all of your work. c. Draw and label the galvanic cell, including the anode and cathode, direction of electron flow, and direction of ion migration.arrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward
- 11. Use the equation below to answer the following questions: 2 Al(s) + 3 Cd(NO3)2 (aq) → 2 Al(NO3)3 (aq) + 3 Cd(s) a. What is the net ionic equation for the reaction? b. Which species is a spectator ion in this reaction? Define a spectator ion. c. Identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent.arrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,



