
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:Whether the pair of two molecules representconstitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
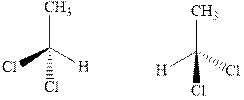
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(b)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
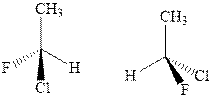
Concept introductionIn order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(c)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
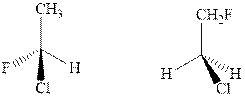
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(d)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.

Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(e)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.

Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(f)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
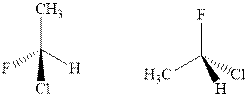
Concept introduction:The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral.
(g)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
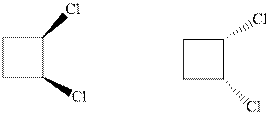
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(h)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.

Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(i)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.

Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(j)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
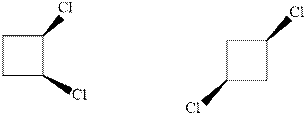
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(k)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
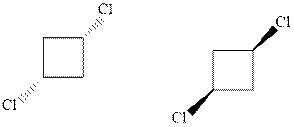
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(l)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
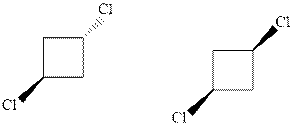
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
(m)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
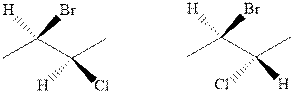
Concept introduction:The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral.
(n)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
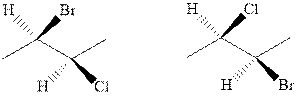
Concept introduction: The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral.
(o)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
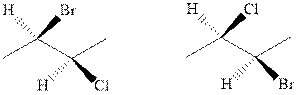
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral.
(p)
Interpretation: Whether the pair of two molecules represent constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical isomers should be identified.
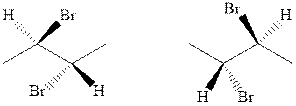
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S, Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of atomic number. The one with highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as 1 and so on and with the lowest priority group at the bottom.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Which of the following are descriptions of possible starting material for this reaction? H ? trace acid an ester a ketone an imine an aldehyde a carboxylic acid an enamine a primary amine a secondary amine a tertiary aminearrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardWhat are the reagents needed for this and the third structure I only got the top right structure rightarrow_forward
- Please label this COZY spectraarrow_forwardPlease label this HNMRarrow_forwardConsider the following gas chromatographs of Compound A, Compound B, and a mixture of Compounds A and B. Inject A B mixture Area= 9 Area = 5 Area = 3 Area Inject . མི། Inject J2 What is the percentage of Compound B in the the mixture?arrow_forward
- Rank these according to stability. CH3 H3C CH3 1 CH3 H3C 1 most stable, 3 least stable O 1 most stable, 2 least stable 2 most stable, 1 least stable O2 most stable, 3 least stable O3 most stable, 2 least stable O3 most stable, 1 least stable CH3 2 CH3 CH3 H₂C CH3 3 CH3 CHarrow_forwardConsider this IR and NMR: INFRARED SPECTRUM TRANSMITTANCE 0.8- 0.6 0.4 0.2 3000 10 9 8 00 HSP-00-541 7 CO 6 2000 Wavenumber (cm-1) сл 5 ppm 4 M Which compound gave rise to these spectra? N 1000 1 0arrow_forwardConsider this reaction (molecular weights are under each compound): HC=CH + 2 HCI --> C2H4Cl 2 MW = 26 36.5 99 If 4.4 g of HC=CH are reacted with 110 mL of a 2.3 M HCI solution, and 6.0 g of product are actually produced, what is the percent yield?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning



