
Metropolitan Hospital has estimated its average monthly bed needs as
where
Assume that no new hospital additions are expected in the area in the foreseeable future. The following monthly seasonal adjustment factors have been estimated, using data from the past five years:
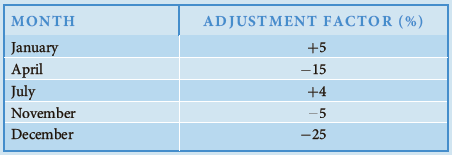
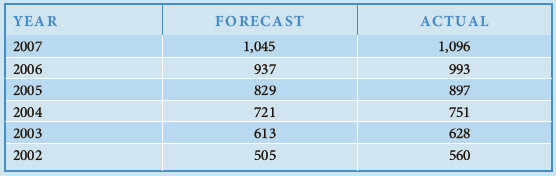
Forecast Metropolitan’s beddemand for January, April, July, November, and December 2007.- If the following actual and forecast values for June bed demands have been recorded, what seasonal adjustment factor would you recommend be used in making future June forecasts?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 5 Solutions
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies and Tactics (MindTap Course List)
- Elasticity Problems Cross Price Elasticity (Exy) (QDX-QDo/[(QDN+QDDA)/2] (P-POR/[(PNE+POB)/2]¯¯ 11. QD of good A falls from 100 to 90 as the price of good B rose from $10 to $20. Calculate coefficient: (90-100) [(90+100) 21-10/95-105 - -.158 (20-10)/[(20+10)/2] 10/15 .667 Cite Elasticity: inclastic Typs of good: complement 12. QD of good A rose from 300 to 400 as the price good K increased from $1 to $2. Calculate coefficient Cite Elasticity: Ixps of reed: 13. QD for good I falls from 2000 to 1500 units as price of good Krose from $10 to $15. Calculate coefficient: Cite Elasticity: Type of good: 14. QD for good X rose from 100 to 101 units as price of good Y increases from, $8 to $15. Calculate coefficient: Cite Elasticity: Type of paed: Page 124 (368) Value of Coefficient Description Positive (0) Negative (L*0) Type of Good(s) Substitute Quantity Demanded of W changes in same direction a change in price if Z Quantity Demanded of W changes in opposite direction as change in price if Z…arrow_forwardUse production theory to graphically illustrate the case in which a medical innovation improves health without any change in the consumption of medical care.arrow_forwardAccording to Lee et al. (2009), the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio comparing the current dialysis treatment to the next least cost dialysis treatment is $61,294 per life year and $129,090 per QALY. Can you account for the different estimates?arrow_forward
- You are employed as an economic consultant to the regional planning office of a large metropolitan area, and your task is to estimate the demand for hospital services in the area. Your estimates indicate that the own-price elasticity of demand equals 0.25, the income elasticity of demand equals 0.45, the cross-price elasticity of demand for hospital services with respect to the price of nursing home services equals 0.1, and the elasticity of travel time equals −0.37. Use this information to project the impact of the following changes on the demand for hospital services. Average travel time to the hospital diminishes by 5 percent due to overall improvements in the public transportation system. The price of nursing home care decreases by 10 percent. Average real income decreases by 10 percent. The hospital is forced to increase its price for services by 2 percent.arrow_forwardThe commissioner of health is concerned about the increasing number of reported cases of preventable childhood diseases, such as polio and rubella. It appears that a growing number of young children are not being vaccinated against childhood diseases as they should be. Two proposals to address the problem are sitting on the commissioner’s desk. The programs have equal costs, but the commissioner has funding for only one. The first proposal involves providing free vaccinations at clinics around the country. The benefits from a free vaccination program are likely to be experienced immediately in terms of a drop in the number of reported cases of illness. The second program calls for educating young married couples about the benefits of vaccination. The benefits in this instance will not be felt for some years. The commissioner wants to use cost-benefit analysis to determine which proposal should be implemented. Explain to the commissioner the critical role the discount rate plays in…arrow_forwardWhich of the following Nobel Prize Winners’ primary work in investments was consistent with market efficiency? Mark each “Yes” or “No.” You can search the internet for more information about their Nobel Prizes. Eugene Fama Harry Markowitz William Sharpe Robert Shillerarrow_forward
- not use ai pleasearrow_forwardNot use ai pleasearrow_forwardExercise 6 Imagine that you head production of a multinational food processing company. The ongoing uncer- tainty about costs means that you are unsure of the future cost of one of your inputs, x2. Your firm's production function is y = f(x1, x2) = x²x²² The output price p is 1000, x1 = 27, and wx₁ = 60. 1. Suppose the current input price is Wx2 = 50. Solve for the optimal choice of x2. 2. Now suppose that the probability the input price remains 50 is 0.65 and the probability that Wx2 60 is 0.35. Solve for the optimal choice of x2. Round down to the nearest integer. = 3. Finally, suppose the costs do actually rise, i.e., Wx2 = 60. Calculate the difference in profit from the uncertainty in (2) vs. the certainty in (1).arrow_forward
- Not use ai please letarrow_forwardQuestions from textbook: Santerre, Rexford, E., and Neun, Stephan P. Health Economics: Theories, Insights, and Industry Studies, 6th Edition, ISBN 13: 978-1-111-822729. Mason, OH: South-Western, Cengage Learning, 2013. 1. Suppose a health expenditure function is specified in the following manner: E = 500 + 0.2Y where E represents annual health care expenditures per capita and Y stands for income per capita. a. Using the slope of the health expenditure function, predict the change in per capita health care expenditures that would result from a $1,000 increase in per capita income. b. Compute the level of per capita health care spending when per capita income takes on the following dollar values: 0; 1,000; 2,000; 4,000; and 6,000. c. Using the resulting values for per capita health care spending in part B, graph the associated health care expenditure function. d. Assume that the fixed amount of health care spending decreases to $250. Graph the new and original health care functions on…arrow_forwardGraph shows the daily market price of jeans when the tax on sellers is set to zero per pair supposed the government institutes attacks of $20.30 per pair to be paid by the seller what is the quantity after taxarrow_forward
 Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning







