
Concept explainers
The following
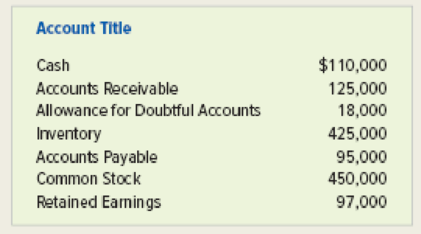
Tile, Etc. had the following transactions in 2018:
- 1. Purchased merchandise on account for $580,000.
- 2. Sold merchandise that cost $420,000 for $890,000 on account.
- 3. Sold for $245,000 cash merchandise that had cost $160,000.
- 4. Sold merchandise for $190,000 to credit card customers. The merchandise had cost $96,000. The credit card company charges a 4 percent fee.
- 5. Collected $620,000 cash from
accounts receivable . - 6. Paid $610,000 cash on accounts payable.
- 7. Paid $145,000 cash for selling and administrative expenses.
- 8. Collected cash for the full amount due from the credit card company (see item 4).
- 9. Loaned $60,000 to J. Parks. The note had an 8 percent interest rate and a one-year term to maturity.
- 10. Wrote off $7,500 of accounts as uncollectible.
- 11. Made the following
adjusting entries :- (a) Recorded uncollectible accounts expense estimated at 1 percent of sales on account.
- (b) Recorded seven months of accrued interest on the note at December 31, 2018 (see item 9).
Required
- a. Organize the transaction data in accounts under an
accounting equation. - b. Prepare an income statement, a statement of changes in stockholders’ equity, a
balance sheet , and a statement ofcash flows for 2018.
a.
Organize the transaction data in accounts under an accounting equation.
Explanation of Solution
Percentage of sales method: Credit sales are recorded by debiting (increasing) accounts receivable account. The bad debts is a loss incurred out of credit sales, hence uncollectible accounts can be estimated as a percentage of credit sales or total sales.
It is a method of estimating the bad debts (expected loss on extending credit), by multiplying the expected percentage of uncollectible with the total amount of net credit sale (or total sales) for a specific period. Under percentage of sales method, estimated bad debts would be treated as a bad debt expense of the particular period.
Horizontal statements model: The model that represents all the financial statements, balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows in one table in a horizontal form, is referred to as, horizontal statements model.
Organize the transaction data in accounts under an accounting equation.
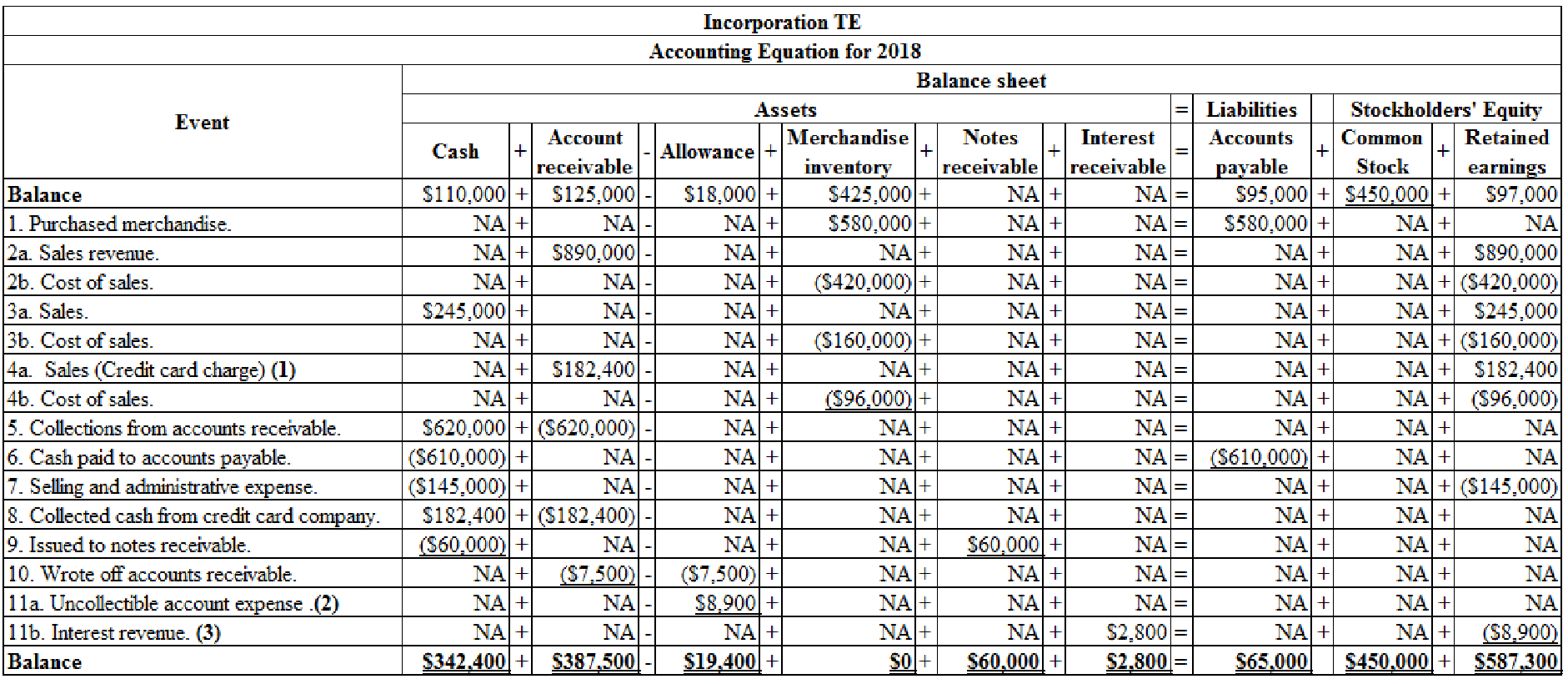
Table (1)
Working note:
(1) Calculate the amount of credit card sales made to customers:
The merchandise sold to credit card customers for $190,000 and the company charges a fee of 4% on sales. So, the credit card expense is
(2) Calculate the amount for uncollectible accounts expense:
Calculate the amount of interest receivable:
Given: The loan amount is $60,000 and the rate of interest is 8%. So the total interest income is calculated as follows:
b.
Prepare an income statement, statement of changes in stockholders’ equity, a balance sheet, and a statement of cash flows for 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare the income statement.
| Incorporation TE | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Revenue | ||
| Sales revenue | $1,325,000 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | $676,000 | |
| Gross profit | $649,000 | |
| Less: Operating Expenses | ||
| Credit card expenses | $7,600 | |
| Selling and administrative expenses | $145,000 | |
| Uncollectible accounts expense | $8,900 | |
| Total operating income | ($161,500) | |
| Operating income | $487,500 | |
| Add: Non-operating items | ||
| Interest revenue | $2,800 | |
| Net income | $490,300 | |
Table (2)
Statement of changes in the stockholders’ equity: This statement reflects whether the components of stockholders’ equity have increased or decreased during the period.
Prepare the statement of changes in stockholders’ equity.
| Incorporation TE | ||
| Statement of changes in stockholders’ equity | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Beginning common stock | $450,000 | |
| Add: Common stocks issued | $0 | |
| Ending common stock | $450,000 | |
| Beginning retained earnings | $97,000 | |
| Add: Net income | $490,300 | |
| Less: Dividends | ($0) | |
| Ending retained earnings | $587,300 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | $1,037,300 | |
Table (3)
Balance sheet: Balance Sheet is one of the financial statements that summarize the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Prepare the balance sheet.
| Incorporation TE | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| As of December 31, 2018 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $342,400 | |
| Accounts receivable | $387,500 | |
| Less: Allowance for doubtful accounts | $19,400 | $368,100 |
| Merchandise inventory | $329,000 | |
| Interest receivable | $2,800 | |
| Notes receivable | $60,000 | |
| Total assets | $1,102,300 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts payable | $65,000 | |
| Total liabilities | $65,000 | |
| Stockholders’ equity | ||
| Common stock | $450,000 | |
| Retained earnings | $587,300 | |
| Total stockholders' equity | $1,037,300 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $1,102,300 | |
Table (4)
Statement of cash flows: This statement reports all the cash transactions involves for inflow and outflow of cash, and the result of these transactions is reported as an ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
Prepare the statement of cash flows.
| Incorporation TE | ||
| Statement of cash flow | ||
| For the year December 31, 2018 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Cash flow from operating activities: | ||
| Inflow from customers (4) | $1,047,400 | |
| Outflow for inventory | ($610,000) | |
| Outflow for expenses | ($145,000) | |
| Net cash flow from operating activities | $292,400 | |
| Cash flow from investing activities | ||
| Outflow for notes receivable | ($60,000) | |
| Net cash flow from investing activities | ($60,000) | |
| Cash flow from financing activities | $0 | |
| Net change in cash | $232,400 | |
| Add: Beginning cash balance | $110,000 | |
| Ending cash balance | $342,400 | |
Table (5)
Working note:
(4) Calculate the amount of inflow from customers.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- Please explain this financial accounting problem by applying valid financial principles.arrow_forwardI need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardCronix Metal Works manufactures a single product that sells for $88 per unit. Variable costs are $56 per unit, and fixed costs total $145,000 per month. Calculate the operating income if the selling price is raised to $91 per unit, advertising expenditures are increased by $20,000 per month, and monthly unit sales volume becomes 5,800 units.arrow_forward
- Please explain the accurate process for solving this financial accounting question with proper principles.arrow_forwardCan you explain the correct approach to solve this general accounting question?arrow_forwardI need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forward
- Please explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forwardNamita's Salon purchased equipment for $12,000 on January 1. The equipment has an estimated useful life of 5 years and a salvage value of $2,000. Calculate the annual depreciation expense using the straight-line method and the book value at the end of year 3.arrow_forwardI am searching for a clear explanation of this financial accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning


