
Accounting for uncollectible accounts—two cycles using the percent of revenue allowance method
The following transactions apply to Jova Company for 2018, the first year of operation:
- 1. Issued $10,000 of common stock for cash.
- 2. Recognized $210,000 of service revenue earned on account.
- 3. Collected $162,000 from
accounts receivable . - 4. Paid operating expenses of $125,000.
- 5. Adjusted accounts to recognize uncollectible accounts expense. Jova uses the allowance method of accounting for uncollectible accounts and estimates that uncollectible accounts expense will be 1 percent of sales on account.
The following transactions apply to Jova for 2019:
- 1. Recognized $320,000 of service revenue on account.
- 2. Collected $335,000 from accounts receivable.
- 3. Determined that $2,150 of the accounts receivable were uncollectible and wrote them off.
- 4. Collected $800 of an account that had previously been written off.
- 5. Paid $205,000 cash for operating expenses.
- 6. Adjusted the accounts to recognize uncollectible accounts expense for 2019. Jova estimates uncollectible accounts expense will be 0.5 percent of sales on account.
Required
Complete the following requirements for 2018 and 2019. Complete all requirements for 2018 prior to beginning the requirements for 2019.
- a. Identify the type of each transaction (asset source, asset use, asset exchange, or claims exchange).
- b. Show the effect of each transaction on the elements of the financial statements, using a horizontal statements model like the one shown here. Use + for increase, − for decrease, and NA for not affected. Also, in the Cash Flow column, indicate whether the item is an operating activity (OA), investing activity (IA), or financing activity (FA). The first transaction is entered as an example. (Hint: Closing entries do not affect the statements model.)
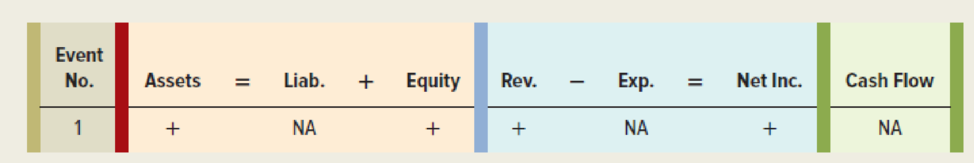
- c. Organize the transaction data in accounts under an
accounting equation. - d. Prepare the income statement, statement of changes in stockholders’ equity,
balance sheet , and statement ofcash flows .
a)
Identify whether the given transactions are asset source, asset use, asset exchange, or claims exchange for the year 2018 and 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Identify the type of each transaction for 2018:
| Event Number (2018) | Type of Transaction |
| 1. Issued common stock for cash. | Asset Source |
| 2. Service revenue earned on account. | Asset Source |
| 3. Collection of accounts receivable. | Asset Exchange |
| 4. Payment made for operating expenses. | Asset Use |
| 5. Adjusted the accounts to recognize uncollectible accounts expense. | Asset Use |
Table (1)
Identify the type of each transaction for 2019:
| Event Number (2019) | Type of Transaction |
| 1. Recognized service revenue on account. | Asset Source |
| 2. Collection of accounts receivable. | Asset Exchange |
| 3. Accounts receivable were uncollectible and written off. | Asset Exchange |
| 4. a. Allowance made for doubtful accounts. | Asset Exchange |
| 4.b. Cash collected for accounts receivable | Asset exchange |
| 5. Payment made for operating expenses. | Asset use |
| 6. Adjusted the accounts to recognize uncollectible accounts expense. | Asset use |
Table (2)
Asset source transactions are the transactions that results in an increase of both the asset and claims on assets.
Asset use transactions are the transactions that results in a decrease of both the asset and claims on assets.
Asset exchange transactions are the transactions that results in increase in one asset and decrease in the other asset.
Claim exchange transactions are the transactions that decreases one claim and increases other claims; the total claims remains unchanged.
b)
Show the effect of each transaction on the elements of the financial statements for 2018 and 2019 using horizontal statement model.
Explanation of Solution
Horizontal statements model: The model that represents all the financial statements, balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows in one table in a horizontal form, is referred to as, horizontal statements model.
Effect of each transaction on the elements using horizontal statement model for 2018:
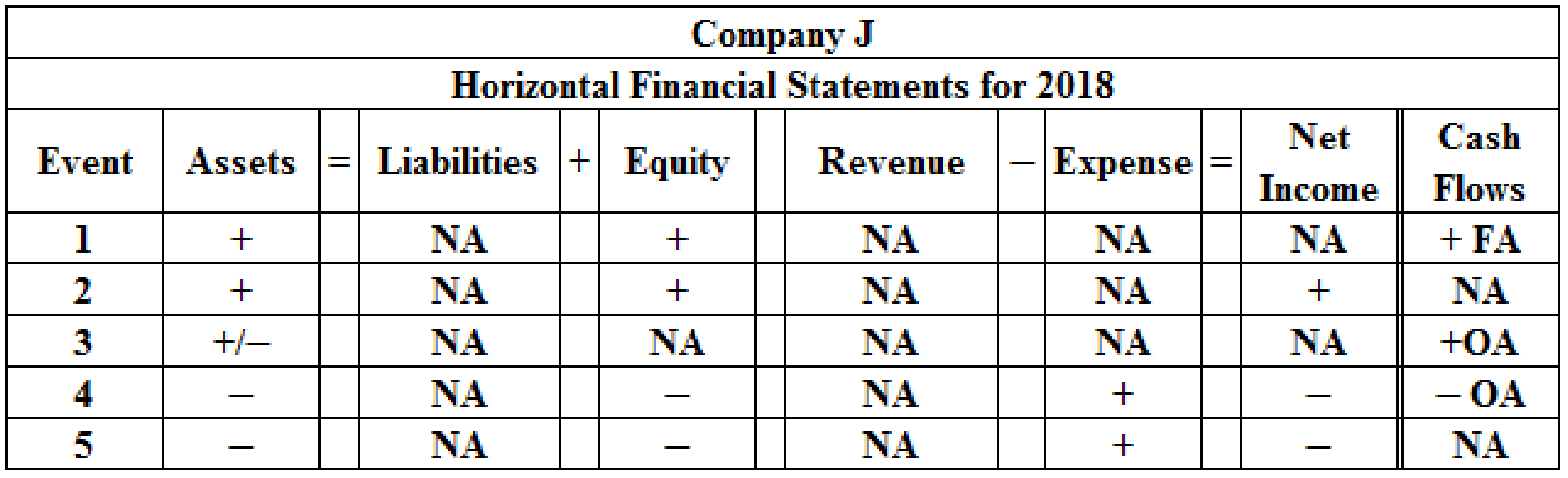
Table (3)
Effect of each transaction on the elements using horizontal statement model for 2019:
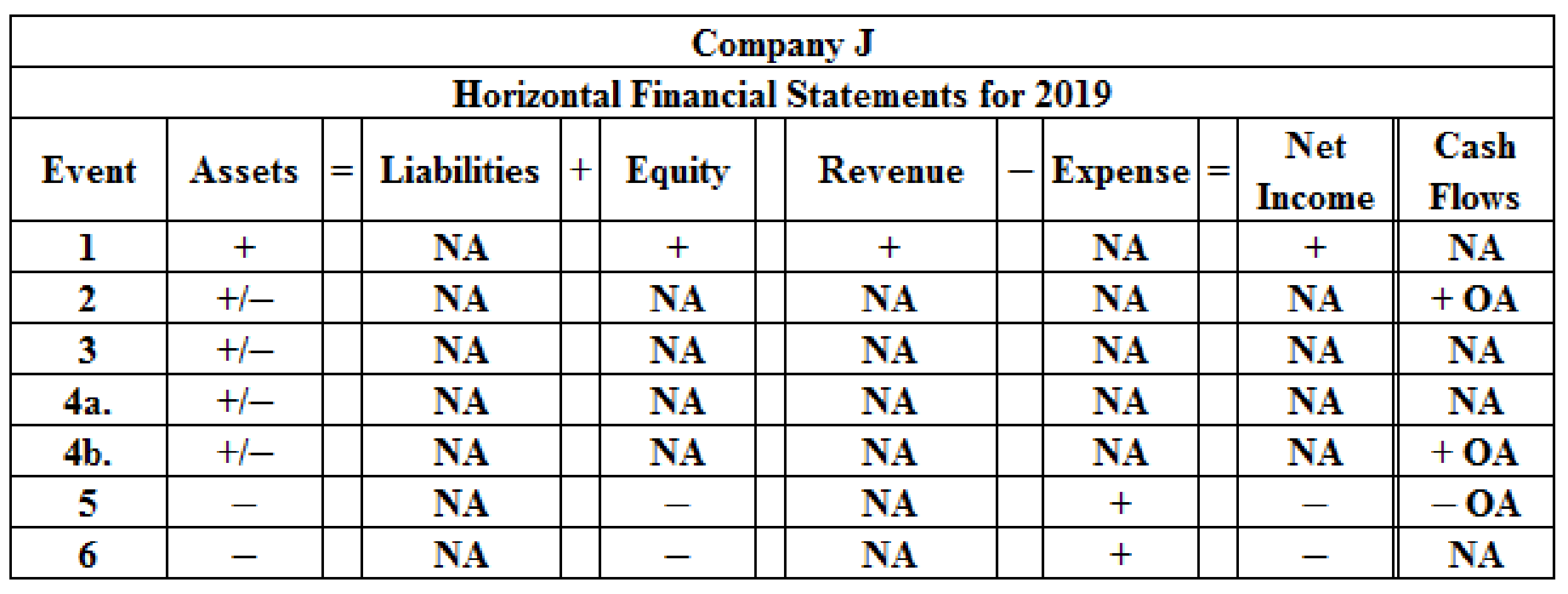
Table (4)
c.
Organize the transactions in accounts under an accounting equation for 2018 and 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation: Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relation between resources or assets of a business and claims on the resources by the creditors, and the owners.
Organize the transactions in accounts under an accounting equation for 2018:
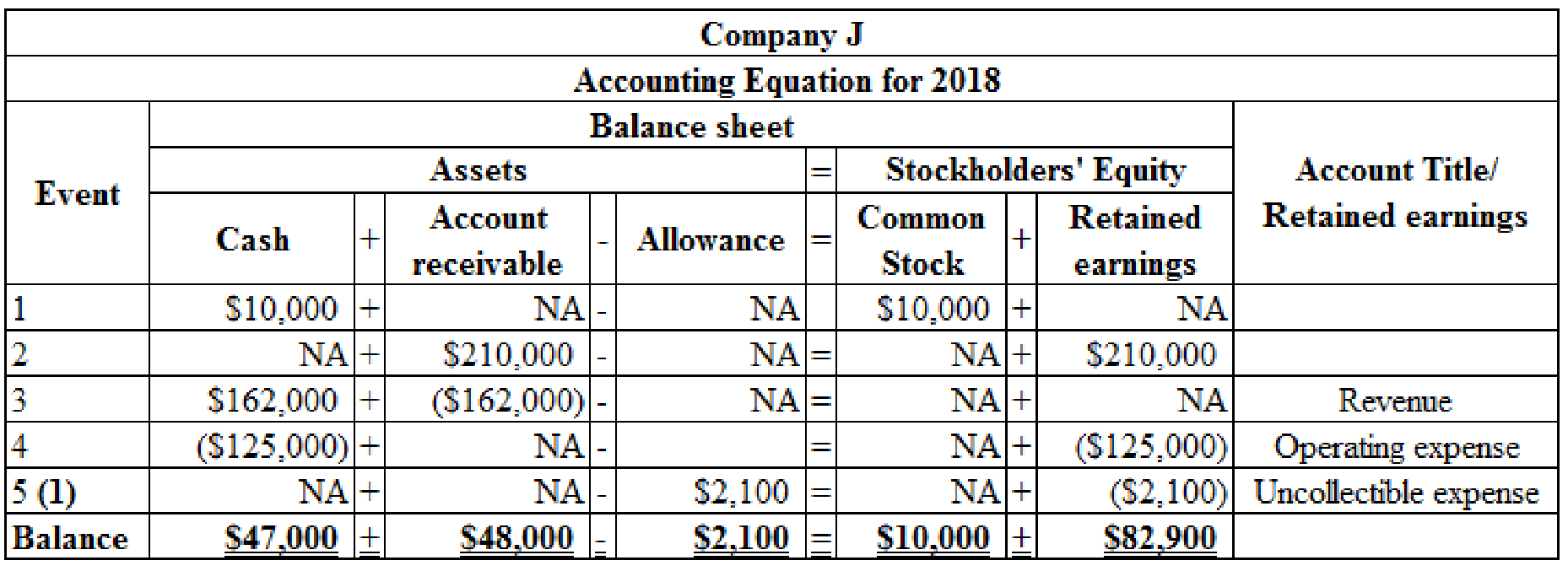
Table (5)
Organize the transactions in accounts under an accounting equation for 2019:
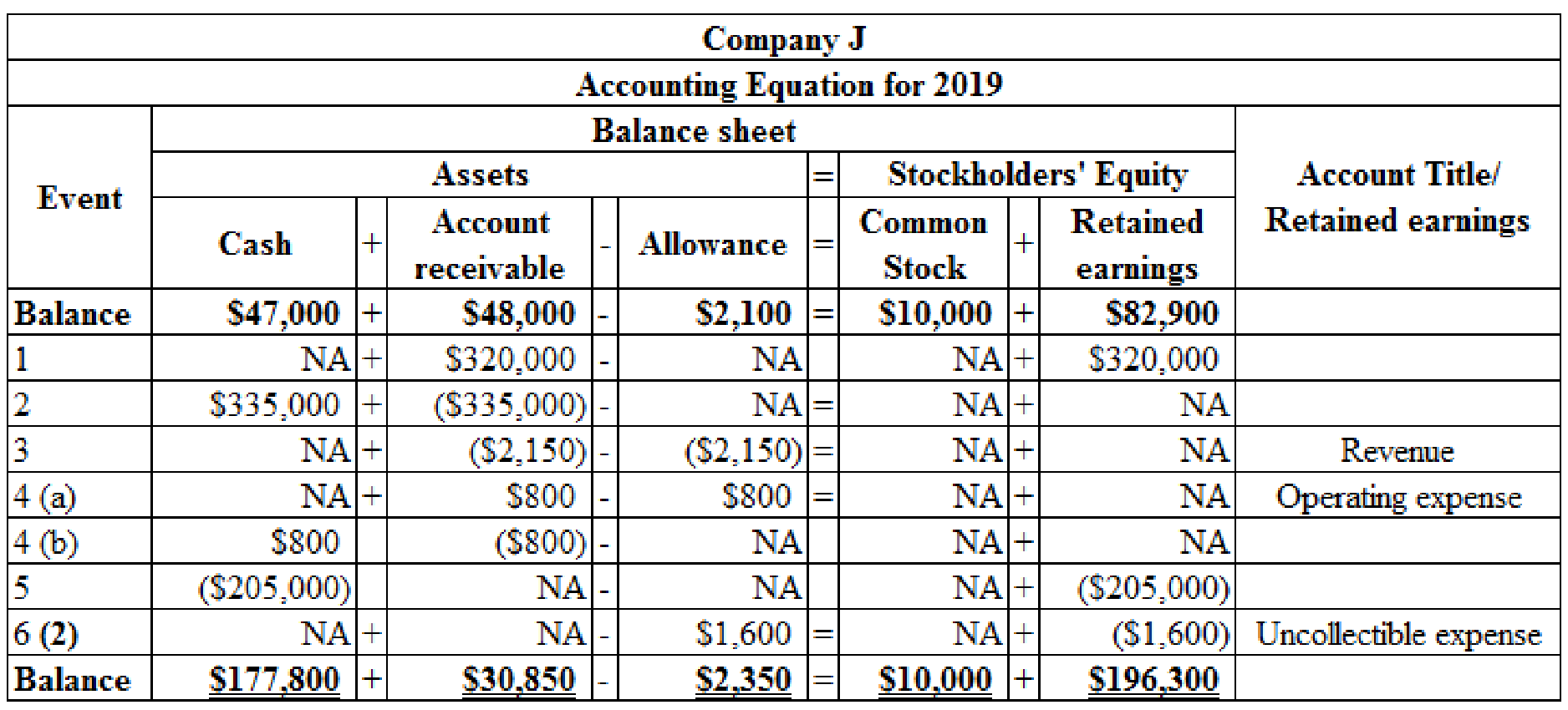
Table (6)
Working note 1:
Determine the uncollectible account expense for 2018:
Given: The services provided on account are $210,000 and the estimated percentage of uncollectible is 1%.
Working note 2:
Determine the uncollectible account expense for 2019:
Given: The services provided on account are $210,000 and the estimated percentage of uncollectible is 0.5%.
d)
Prepare the income statement, statement of changes in stockholders’ equity, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows for 2018 and 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare an income statement for the year 2018:
| Company J | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Revenue | ||
| Service revenue | $210,000 | |
| Total revenues | $210,000 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Operating expense | $125,000 | |
| Uncollectible accounts expense | $2,100 | |
| Total expenses | $127,100 | |
| Net income | $82,900 | |
Table (7)
Statement of changes in the stockholders’ equity: This statement reflects whether the components of stockholders’ equity have increased or decreased during the period.
Prepare the statement of changes in stockholders’ equity for the year 2018:
| Company J | ||
| Statement of changes in stockholders’ equity | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Beginning common stock | $10,000 | |
| Add: Common stocks issued | $0 | |
| Ending common stock | $10,000 | |
| Beginning retained earnings | $0 | |
| Add: Net income | $82,900 | |
| Less: Dividends | $0 | |
| Ending retained earnings | $82,900 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | $92,900 | |
Table (8)
Balance sheet: Balance Sheet is one of the financial statements that summarize the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Prepare the balance sheet for the year 2018:
| Company J | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| As of 31st December, 2018 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $47,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | $48,000 | |
| Less: Allowance for doubtful accounts | ($2,100) | $45,900 |
| Total assets | $92,900 | |
| Liabilities | $0 | |
| Stockholders’ equity | ||
| Common stock | $10,000 | |
| Retained earnings | $82,900 | |
| Total stockholders' equity | $92,900 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $92,900 | |
Table (9)
Statement of Cash flows: Statement of cash flows is a statement reports the source and application of cash between two balance sheet dates. It shows how the cash is sourced and used for the company’s operating, investing, and financing activities.
Prepare the statement of cash flows for the year 2018:
| Company J | ||
| Statement of cash flow | ||
| For the year ended 31st December, 2018 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Cash flow from operating activities: | ||
| Inflow from customers | $162,000 | |
| Outflow from customers | ($125,000) | |
| Net cash flow from operating activities | $37,000 | |
| Cash flow from investing activities | $0 | |
| Cash flow from financing activities | ||
| Inflow from issue of common stock | $10,000 | |
| Net cash flow from financing activities | $10,000 | |
| Net change in cash | $47,000 | |
| Add: Beginning cash balance | $0 | |
| Ending cash balance | $47,000 | |
Table (10)
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare the income statement for 2019:
| Company J | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Revenue | ||
| Service revenue | $320,000 | |
| Total revenues | $320,000 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Operating expense | $205,000 | |
| Uncollectible accounts expense | $1,600 | |
| Total expenses | ($206,600) | |
| Net income | $113,400 | |
Table (11)
Statement of changes in the stockholders’ equity: This statement reflects whether the components of stockholders’ equity have increased or decreased during the period.
Prepare the statement of changes in stockholders’ equity for 2019:
| Company J | ||
| Statement of changes in stockholders’ equity | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Beginning common stock | $10,000 | |
| Add: Common stocks issued | $0 | |
| Ending common stock | $10,000 | |
| Beginning retained earnings | $82,9000 | |
| Add: Net income | $113,400 | |
| Less: Dividends | ($0) | |
| Ending retained earnings | $196,300 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | $206,300 | |
Table (12)
Balance sheet: Balance Sheet is one of the financial statements that summarize the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Prepare the balance sheet for 2019:
| Company J | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| As of 31st December, 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $177,800 | |
| Accounts receivable | $30,850 | |
| Less: Allowance for doubtful accounts | ($2,350) | 28,500 |
| Total assets | $206,300 | |
| Liabilities | $0 | |
| Stockholders’ equity | ||
| Common stock | $10,000 | |
| Retained earnings | $196,300 | |
| Total stockholders' equity | $206,300 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $206,300 | |
Table (13)
Statement of Cash flows: Statement of cash flows is a statement reports the source and application of cash between two balance sheet dates. It shows how the cash is sourced and used for the company’s operating, investing, and financing activities.
Prepare the statement of cash flows for 2019:
| Company J | ||
| Statement of cash flow | ||
| For the year ended 31st December, 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Cash flow from operating activities: | ||
| Inflow from customers | $335,800 | |
| Outflow from customers | ($205,000) | |
| Net cash flow from operating activities | $130,800 | |
| Cash flow from investing activities | $0 | |
| Cash flow from financing activities | $0 | |
| Net change in cash | $130,800 | |
| Add: Beginning cash balance | $47,000 | |
| Ending cash balance | $177,800 | |
Table (14)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- Please provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forwardCan you demonstrate the accurate method for solving this General accounting question?arrow_forward
- Can you explain this general accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardI am searching for the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





