
Essentials Of Business Analytics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781285187273
Author: Camm, Jeff.
Publisher: Cengage Learning,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 26P
South Shore Construction builds permanent docks and seawalls along the southern shore of Long Island, New York. Although the firm has been in business only five years, revenue has increased from $308,000 in the first year of operation to $1,084,000 in the most recent year. The following data show the quarterly sales revenue in thousands of dollars:
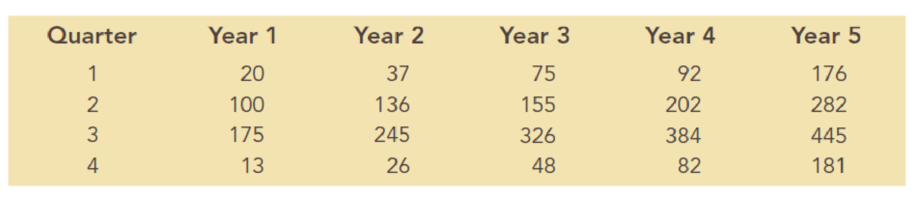
- a. Construct a time series plot. What type of pattern exists in the data?
- b. Use a multiple regression model with dummy variables as follows to develop an equation to account for seasonal effects in the data: Qtr1 = 1 if quarter I, 0 otherwise; Qtr2 = 1 if quarter 2, 0 otherwise; Qtr3 = 1 if quarter 3, 0 otherwise.
- c. Based on the model you developed in part (b), compute estimates of quarterly sales for year 6.
- d. Let Period = 1 refer to the observation in quarter 1 of year 1; Period = 2 refer to the observation in quarter 2 of year 1; … and Period = 20 refer to the observation in quarter 4 of year 5. Using the dummy variables defined in part (b) and the variable Period, develop an equation to account for seasonal effects and any linear trend in the time series.
- e. Based on the seasonal effects in the data and linear trend estimated in part (c), compute estimates of quarterly sales for year 6.
- f. Is the model you developed in part (b) or the model you developed in part (d) more effective? Justify your answer.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A retail store manager claims that the average daily sales of the store are $1,500.
You aim to test whether the actual average daily sales differ significantly from this claimed value.
You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include:
Null hypothesis,
Alternative hypothesis,
Show answer (output table/summary table), and
Conclusion based on the P value.
Showing the calculation is a must. If calculation is missing,so please provide a step by step on the answers
Numerical answers in the yellow cells
Show all work
Show all work
Chapter 5 Solutions
Essentials Of Business Analytics
Ch. 5 - Consider the following time series data:
Using...Ch. 5 - Refer to the time series data in Problem 1. Using...Ch. 5 - Problems 1 and 2 used different forecasting...Ch. 5 - Consider the following time series data:
Compute...Ch. 5 - Consider the following time series...Ch. 5 - Consider the following time series...Ch. 5 - Prob. 8PCh. 5 - Prob. 9PCh. 5 - Prob. 10PCh. 5 - For the Hawkins Company, the monthly percentages...
Ch. 5 - Corporate triple A bond interest rates for 12...Ch. 5 - The values of Alabama building contracts (in...Ch. 5 - The following time series shows the sales of a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 15PCh. 5 - The following table reports the percentage of...Ch. 5 - Consider the following time series: a. Construct a...Ch. 5 - Consider the following time series:
Construct a...Ch. 5 - The Seneca Children’s Fund (SCF) is a local...Ch. 5 - The president of a small manufacturing firm is...Ch. 5 - Consider the following time series: a. Construct a...Ch. 5 - Consider the following time series...Ch. 5 - The quarterly sales data (number of copies sold)...Ch. 5 - Prob. 25PCh. 5 - South Shore Construction builds permanent docks...Ch. 5 - Hogs & Dawgs is an ice cream parlor on the border...Ch. 5 - Donna Nickles manages a gasoline station on the...Ch. 5 - The Vintage Restaurant, on Captiva Island near...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please find the answers for the yellows boxes using the information and the picture belowarrow_forwardA marketing agency wants to determine whether different advertising platforms generate significantly different levels of customer engagement. The agency measures the average number of daily clicks on ads for three platforms: Social Media, Search Engines, and Email Campaigns. The agency collects data on daily clicks for each platform over a 10-day period and wants to test whether there is a statistically significant difference in the mean number of daily clicks among these platforms. Conduct ANOVA test. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: also please provide a step by on getting the answers in excel Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value.arrow_forwardA company found that the daily sales revenue of its flagship product follows a normal distribution with a mean of $4500 and a standard deviation of $450. The company defines a "high-sales day" that is, any day with sales exceeding $4800. please provide a step by step on how to get the answers Q: What percentage of days can the company expect to have "high-sales days" or sales greater than $4800? Q: What is the sales revenue threshold for the bottom 10% of days? (please note that 10% refers to the probability/area under bell curve towards the lower tail of bell curve) Provide answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forward
- Business Discussarrow_forwardThe following data represent total ventilation measured in liters of air per minute per square meter of body area for two independent (and randomly chosen) samples. Analyze these data using the appropriate non-parametric hypothesis testarrow_forwardeach column represents before & after measurements on the same individual. Analyze with the appropriate non-parametric hypothesis test for a paired design.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
 College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...
Algebra
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...
Algebra
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:McGraw Hill

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...
Algebra
ISBN:9781680331141
Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt


College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305071742
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Correlation Vs Regression: Difference Between them with definition & Comparison Chart; Author: Key Differences;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ou2QGSJVd0U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Correlation and Regression: Concepts with Illustrative examples; Author: LEARN & APPLY : Lean and Six Sigma;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xTpHD5WLuoA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY