
(a)
The centripetal acceleration of the ball.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1SP
The centripetal acceleration of the ball is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The radius of the circle is
Write the equation for the centripetal acceleration.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus the centripetal acceleration of the ball is
(b)
The magnitude of the horizontal component of the tension in the string required to produce the centripetal acceleration.
(b)
Answer to Problem 1SP
The magnitude of the horizontal component of the tension in the string required to produce the centripetal acceleration is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The mass of the ball is
The horizontal component of tension in the string provides the
Write the equation for centripetal force.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus the magnitude of the horizontal component of the tension in the string required to produce the centripetal acceleration is
(c)
The magnitude of the vertical component of the tension required to support the weight of the ball.
(c)
Answer to Problem 1SP
The magnitude of the vertical component of the tension required to support the weight of the ball is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The mass of the ball is
In the vertical direction there is no any motion. This means that the vertical component of tension supports the weight of the ball so that vertical component of tension in the string is equal to the weight of the ball. Thus, total force in the vertical direction is zero.
Write the equation for the weight of the ball.
Here,
The value of
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus the magnitude of the vertical component of the tension required to support the weight of the ball is
(d)
The vector diagram showing the two components of tension in the string and to estimate the magnitude of the total tension from the diagram.
(d)
Answer to Problem 1SP
The vector diagram showing the two components of tension in the string is given in figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
The following figure gives the component of tension in the string.
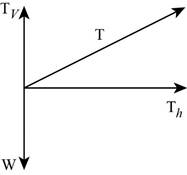
Figure 1
Here,
The magnitude of tension
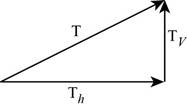
Figure 2
If base of a triangle gives the horizontal component of tension and height of the triangle gives the vertical component of tension, then the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle will give the magnitude of the total tension in the string.
Write the equation for the tension in the string.
Here,
The horizontal component of the tension is equal to centripetal force and vertical component of tension in the string is equal to weight of the body.
Therefore, Substitute
Conclusion:
The vector diagram showing the two components of tension in the string is plotted in figure 1 and the total tension in the string is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS OF EVERYDAY PHENOMENA
- = = R4 R5 = 12.5 Q. A - In the circuit shown, R₁ = R₂ = R 3 voltmeter measures the potential difference across the battery. When the switch is in position 1, the voltmeter measures V₁ = 13.8 V. When the switch is in position 2, the voltmeter measures V2 = 13.4 V. What is the emf ☐ of the battery? 14.93 = What is the battery's internal resistance r? r = V CH Ω R₁₂ V S R₁ 02 2 R₁ 4 R3 R 5arrow_forwardConsider the arrangement of charges shown in the figure. Four charges of equal magnitude Q but varying sign are placed at the corners of a square as indicated. A positive charge q is placed in the center. What is the direction of the net force, if any, on the center charge? Indicate your answer by placing the appropriate label in the first box. Then, suppose that the charge q were to be displaced slightly from the center position. On the figure, label each box with the arrow that best indicates the direction of the net force that would act on q if it were moved to that location. Net Force Answer Bank no force ↑ +2 0 -Q -Q +Qarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- When an electromagnetic wave is reflected at normal incidence on a perfectly conducting surface, the electric fieldvector of the reflected wave at the reflecting surface is the negative of that of the incident wave.a) Explain why this should be so.b) Show that the superposition of the incident and reflected waves results in a standing wave.c) What is the relationship between the magnetic field vector of the incident and reflected waves at the reflectingsurface?arrow_forwardSuppose there are two transformers between your house and the high-voltage transmission line that distributes the power. In addition, assume your house is the only one using electric power. At a substation the primary of a step-down transformer (turns ratio = 1:23) receives the voltage from the high-voltage transmission line. Because of your usage, a current of 51.1 mA exists in the primary of the transformer. The secondary is connected to the primary of another step- down transformer (turns ratio = 1:36) somewhere near your house, perhaps up on a telephone pole. The secondary of this transformer delivers a 240-V emf to your house. How much power is your house using? Remember that the current and voltage given in this problem are rms values.arrow_forwardIn some places, insect "zappers," with their blue lights, are a familiar sight on a summer's night. These devices use a high voltage to electrocute insects. One such device uses an ac voltage of 3970 V, which is obtained from a standard 120-V outlet by means of a transformer. If the primary coil has 27 turns, how many turns are in the secondary coil? hel lp?arrow_forward
- Hi, Does Quantum physics theory means all branches for example quantum relativity, Quantum mechanics, Quantum field theory, and string theory? Can you explain each one of them? Bestarrow_forwardDear Scientist in physics , How are doing, my name is Yahya from Saudi Arabia and currently in my first semester to pursue Master's degree in physics. I have been watching all interviews of some scientists in physics on YouTube Channel and somthing has got my mind. I studied my bachelor 's degree in biology and I have been contacting Professor's Bruce Lipton many times and he explained epigenatic well. He was talking about physics many times. He said if you want to understand who we are and how we think, you need to understand Physics well. So I have decided to study physics. I have some questions : Why is the community of physics are divided? What is the difference between Quantum physics, quantum field theory, Quantim theory, and classical physics? What is quantum consciousness theory as well. What do they mean by wave function collapse? Why professor Roger's always has another opinions in quantum consciousness theory?? Best Regards, Yahyaarrow_forwardGiven water's mass of 18g/mole and the value of the fundamental charge (charge magnitude of the electron and proton), use the largest charge density from the article to determine what fraction of water molecules became ionized (charged) due to triboelectric effects when it flows through the material that causes the largest charge transfer. Give your answer in e/molecule, or electrons transferred per molecule of water. For instance, a value of 0.2 means only one in five molecules of water loses an electron, or that 0.2=20% of water molecules become chargedarrow_forward
- no AI, pleasearrow_forwardSketch the resulting complex wave form, and then say whether it is a periodic or aperiodic wave.arrow_forwardDuring a concentric loading of the quadriceps muscle in the upper leg, an athlete extends his lower leg from a vertical position (see figure (a)) to a fully extended horizontal position (see figure (b)) at a constant angular speed of 45.0° per second. Two of the four quadriceps muscles, the vastis intermedius and the rectus femoris, terminate at the patellar tendon which is attached to the top of the tibia in the lower leg. The distance from the point of attachment of the patellar tendon to the rotation axis of the tibia relative to the femur is 4.10 cm in this athlete. a b (a) The two quadriceps muscles can exert a maximum force of 225 N through the patellar tendon. This force is applied at an angle of 25.0° to the section of the tibia between the attachment point and the rotation axis. What is the torque (in N⚫ m) exerted by the muscle on the lower leg during this motion? (Enter the magnitude.) N⚫ m (b) What is the power (in W) generated by the athlete during the motion? W (c)…arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





